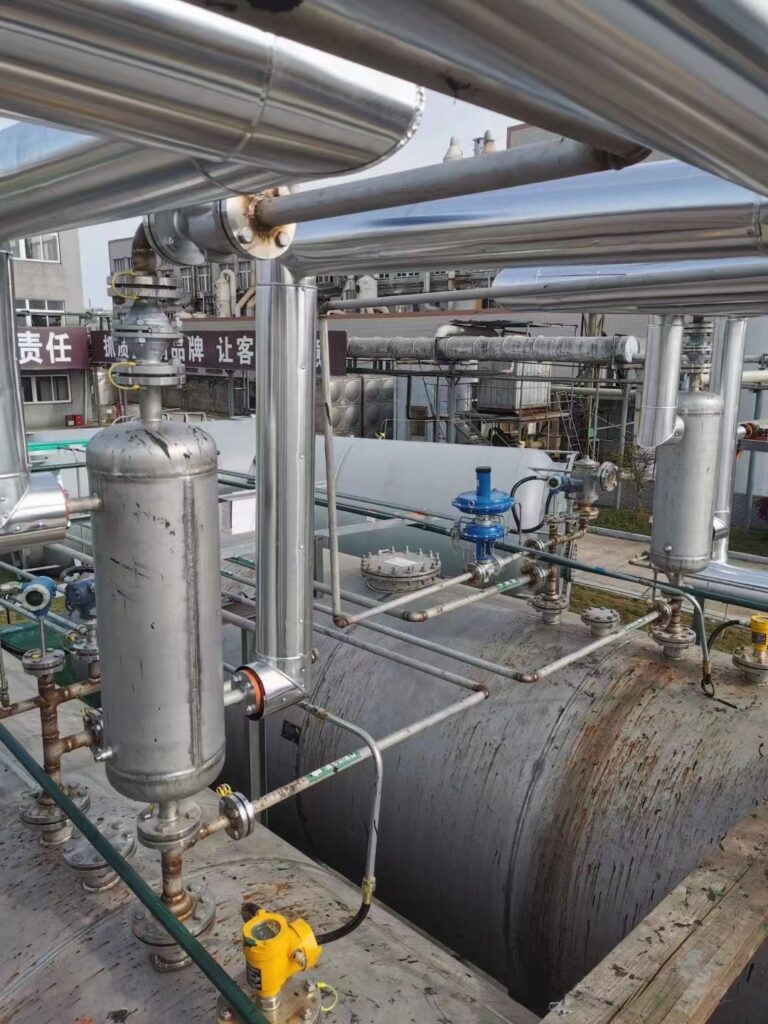
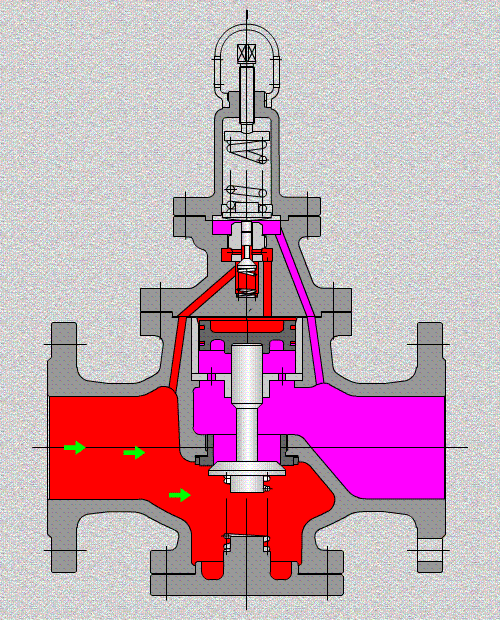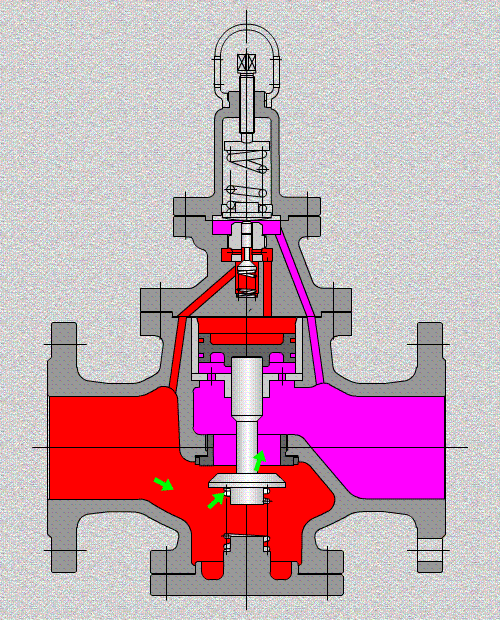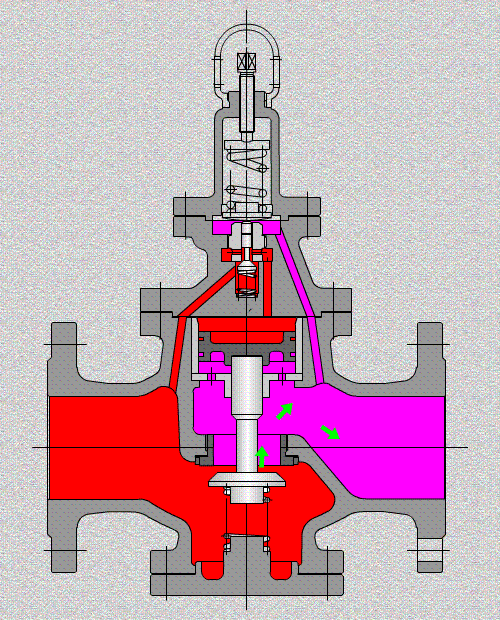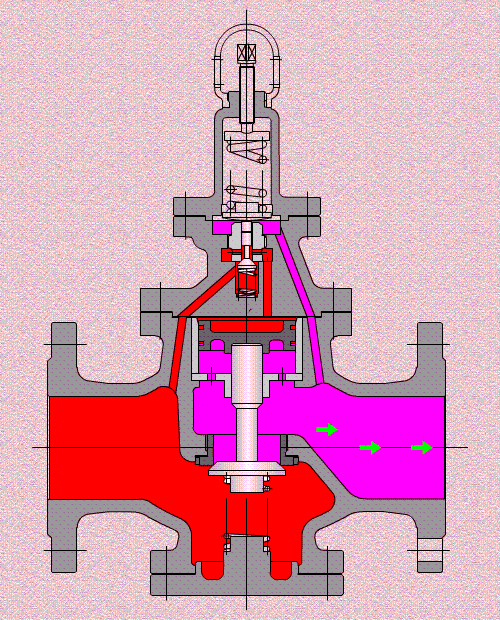
A valve is a mechanism that is used to open, modulate, and shut off the pipelines by controlling the opening of the passageways of the valve for industrial processing. And it can serve for water, steam, air, oil, or other media, fluids could be liquids, gases, or both two-phase, with handle, handwheel/gear operated, electric actuated, solenoid actuated, pneumatic actuated, or hydraulic actuated.
Valves are commonly used in power stations, chemical plants, sugar plants, thermal power plants, refineries, textile plants, water treatment plants, paper mills, pharmaceutical industry, nuclear power plants, and other industrial fields, it can be said that where there are pipelines will exist valves.
Valves by function can be divided into:
Isolation valves
What is the purpose of an isolation valve?
Isolation valves are a key component in industrial fluid process systems, and they are typically used to stop the flow of fluid into a specific area of the system. It can enable pneumatic control, manual control, or electric control of fluid flow.
Which valves are isolation valves?
- Parallel gate valve
- Wedge gate valve
- Knife gate valve
- Pipeline gate valve
- Straight-through globe valve
- Angle type globe valve
- Slant type globe valve
- Double-seated globe valve
- Three-way globe valve
- Water blow relief valve
- Weir-type diaphragm valve
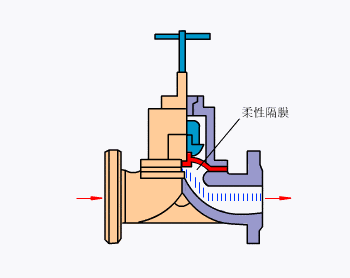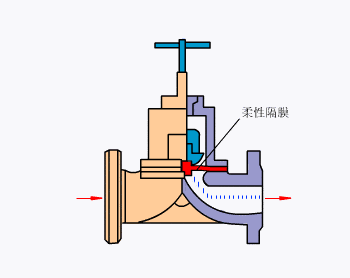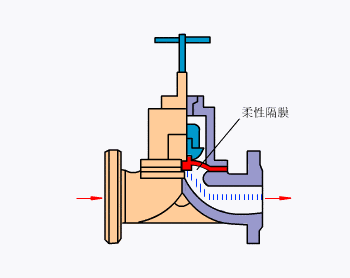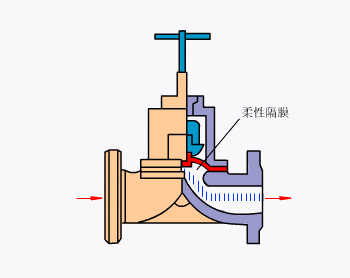
- Full diameter diaphragm valve
- Clamping valve
- Straight-through needle valve
- Angle needle valve
- Solenoid valve (the above valves belong to the sliding stem valve)
- One-piece ball valve
- Two-body ball valve
- Three-body ball valve
- Trunnion ball valve
- Multi-port ball valve
- Butterfly valve
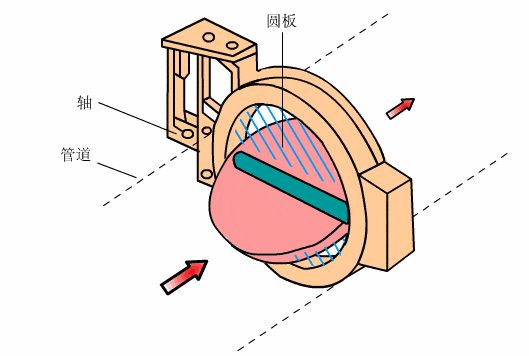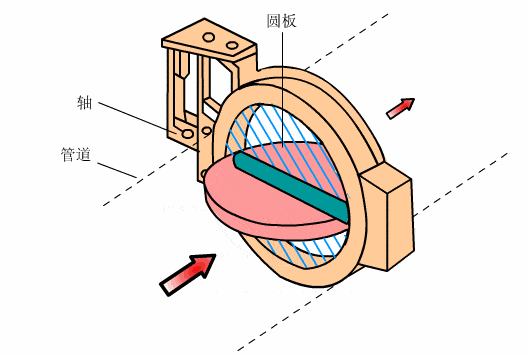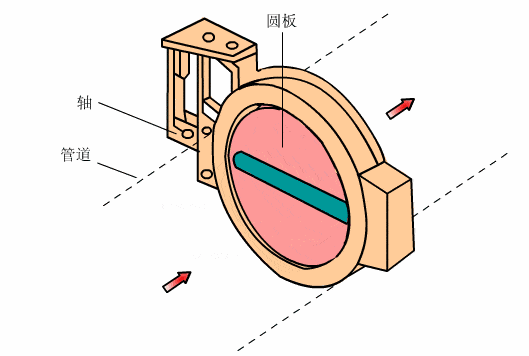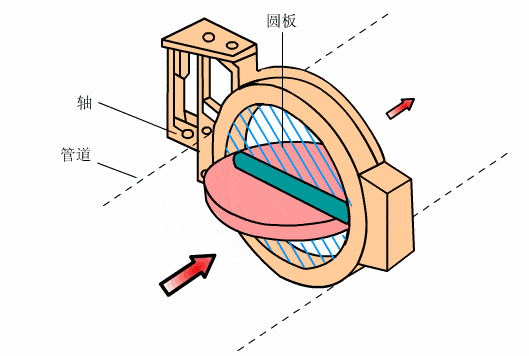
- Parallel plug valve
- Conical plug valve
- Oil seal plug valve
- Eccentric plug valve
- Multi-pass plug valve (the above valves belong to the rotary valve)
- Blind valve
- Fire valve
- Sample valves
- Flush valve
- Float valves
- Exhaust valve
- Combined shut-off and relief valves
- Combined double shut-off and drain valves
- Combined shut-off check valves valve sets
- Dry solids valves
- Clean sending table valves
- Dry solids isolation valves
- Radial parallel slide valve
- Double flap valve
- Rotary valve
- Non-metallic valves
- Sanitary valves(the above valves belong to the special valve)
Which valve is best for isolation?
We can’t simply say which type of isolation valve is the best, because depending on the application conditions and different budgets, we need to choose different types of isolation valves.
There are two common types of isolation valves used in industrial service: gate valves and ball valves. Choosing between these two types of valves usually requires a good understanding of your process, and on a large diameter pipeline with a limited budget, a gate valve may be the better choice. However, for conditions where sealing performance and fast shutoff are required, a ball valve is a better choice than a gate valve.
Both ball and gate valves provide isolation function with some flow regulation. Ball valves utilize a steel ball to control the flow of fluid or gas. When the bore is in line with the fluid flow, the valve full opens on the pipeline, allowing the maximum fluid capacity to pass. A ball valve uses a handle/actuator to turn the ball a quarter-turn horizontally to adjust the bore size that allows fluid flow.
A gate valve, on the other hand, uses a plate, disc, or wedge to stop or allow the flow of water. In most cases, gate valves utilize a handwheel for multi-turn operation, which moves the wedge up and down. Because it requires 360° of rotation to open or close the valve, this means that gate valves take longer to open and close the valve.
While both ball and gate valves are effective in isolation of the fluid flow, there are several differences between them, with ball valves generally being better suited for critical and severe service applications.
Ball Valve vs Gate Valve
| Ball Valve | Gate Valve | |
| Shutoff | Shutoff fast | Shutoff slowly |
| Service Life | Long-lasting and less prone to damage | Prone to corrosion at the valve stem |
| Budget | More expensive than gate valves for the same size | Usually less expensive for the same size |
| Ports | Multi-Ports can be over 2 ports | Limited to 2 ports |
| Leakage | Tight shutoff, 0 leakages for soft-seat ball valve, leakage class IV for metal to metal ball valve | More prone to leaks compared to ball valves |
| InstallationSpace | Less space for height installation. | More space for sliding stem action. |
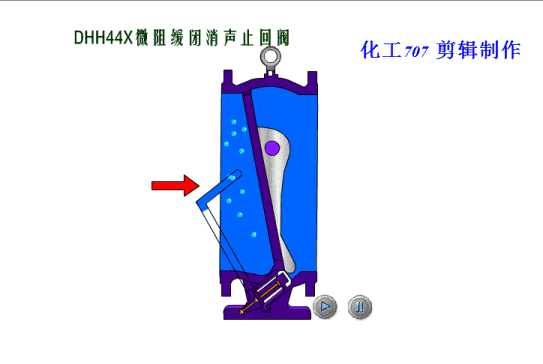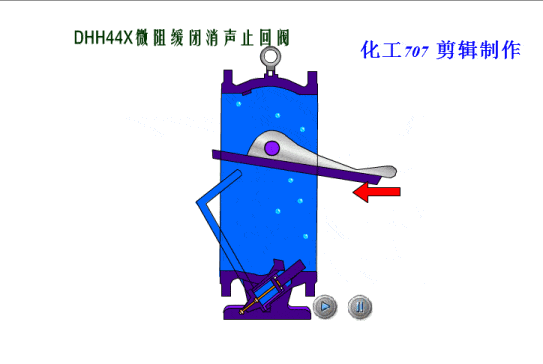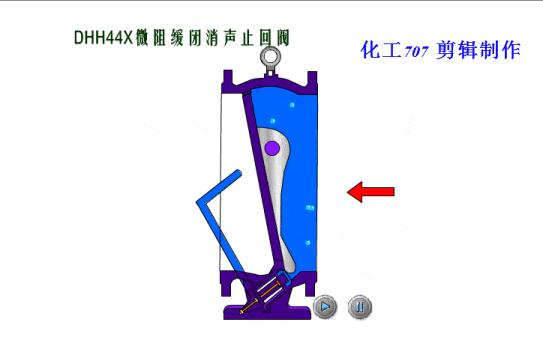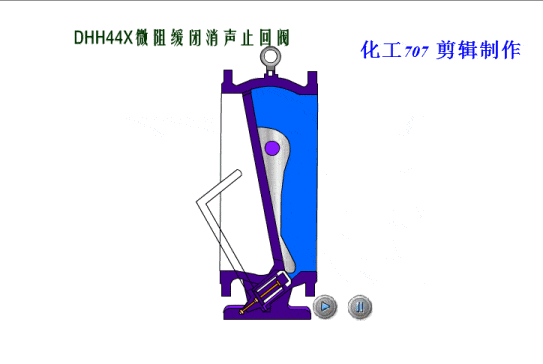
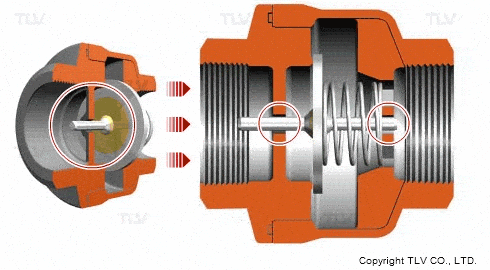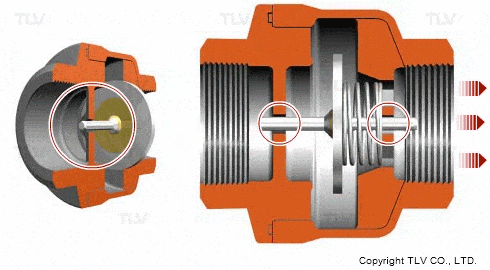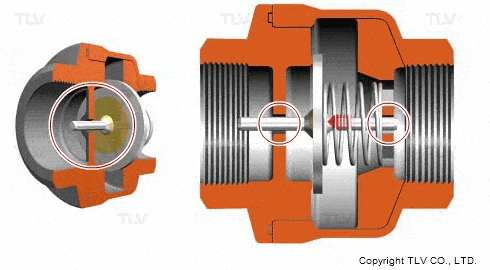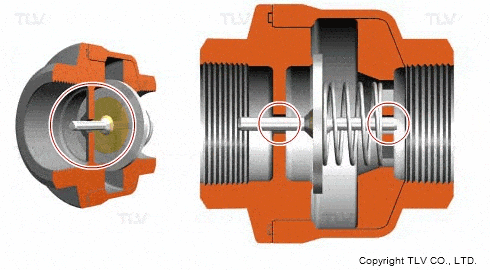
Check valves/non-return valves
The simplest valve is the check valve, also called the non-return valve, as the name implies this valve allows fluid to flow in only one direction and can automatically close under backflow pressure to stop the flow in the original direction. This type of valve operates automatically by the physical principle of the fluid itself, without the need for an additional actuating mechanism.
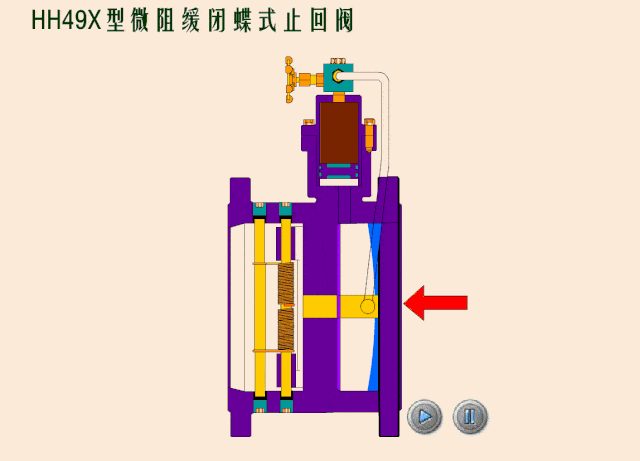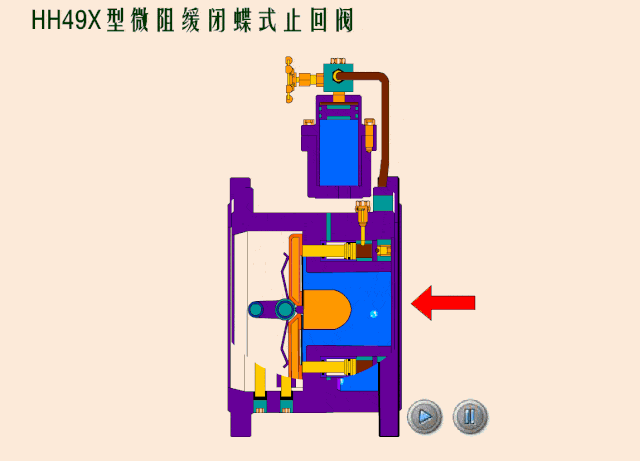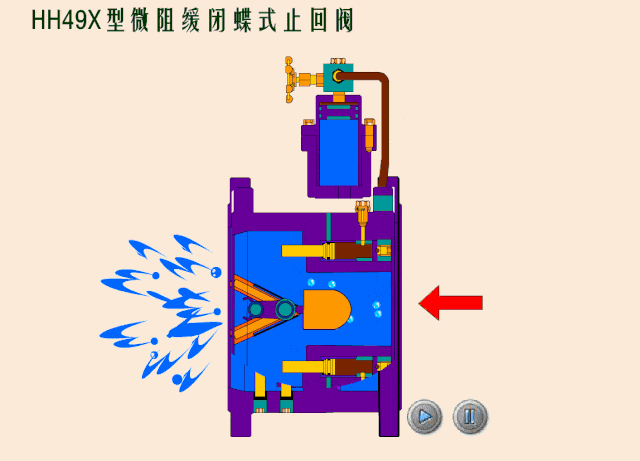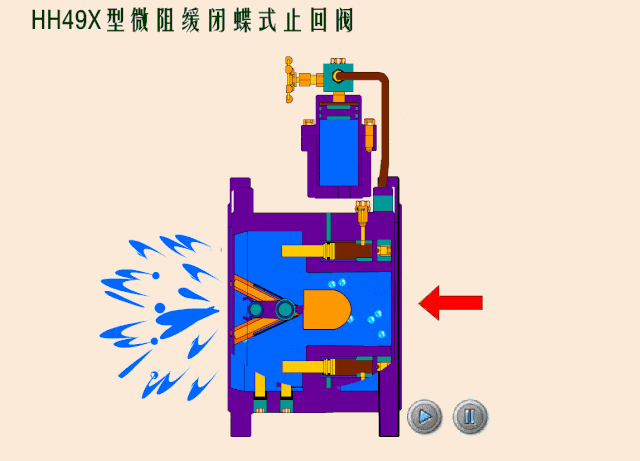
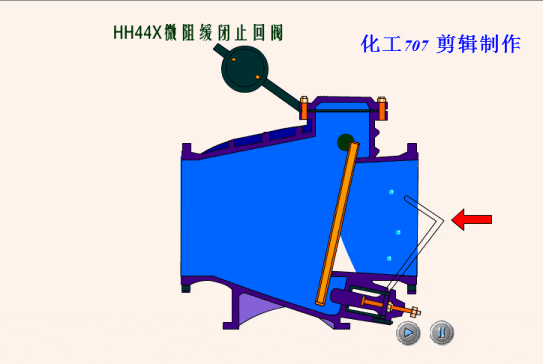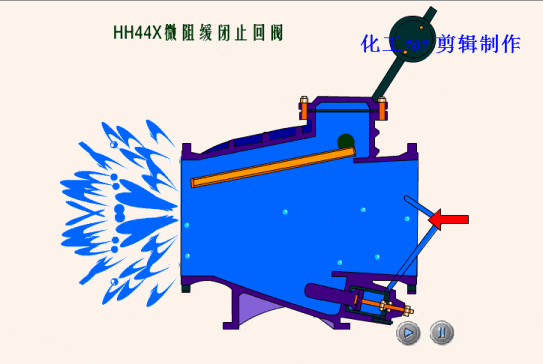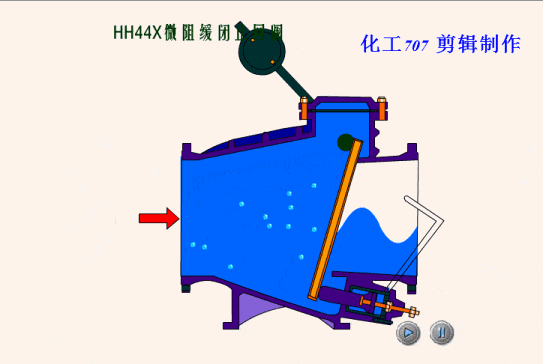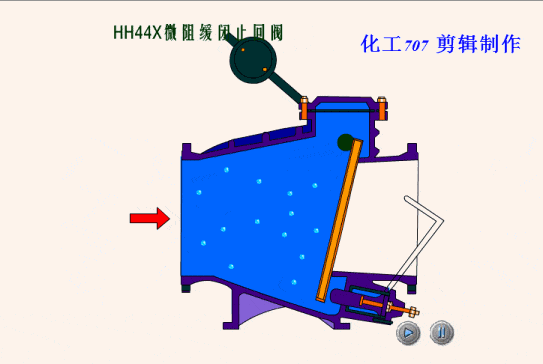
Based on the different types of designs for check valves, we can classify check valves as
- Swing check valve
- Swing check valve with external load
- Double flap check valve
- Piston check valve
- Spherical check valve
- Diaphragm check valve
- Check bottom valve
- Control switch check valve
Regulators
Self-acting pressure regulators are used to keep the adjustable set-point pressure within a certain range in tanks or processes. It doesn’t request any auxiliary energy to operate valves but by the medium energy itself.
Since the self-acting pressure control valves do not need air supply or electric power to operate, so it’s kind of the most cost-effective pressure control valves to achieve a simple process of pressure control.
- Constant pressure regulator
- Differential pressure regulator
- Constant flow regulator
- Overflow shut-off valve
- Low pressure shut-off valve
- Switching valve
- Three-way changeover valve
Control valves
As industrial automation processes are upgraded, more and more control valves are being used in process circuits. Almost every plant consists of hundreds of control loops. All loops are in turn networked together and used to keep a number of important process variables within defined limits to ensure the quality of the final product. These parameters include pressure, flow, temperature, level, etc. The sensors and transmitters collect the process variables to the controller, after comparing with the desired setpoints, the controller sends a corrective signal to control valves, in case modulating the valve opening to reach the required value.
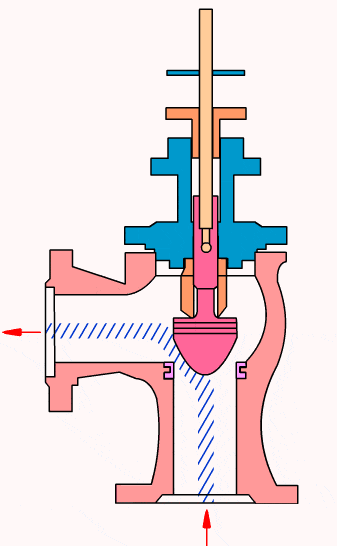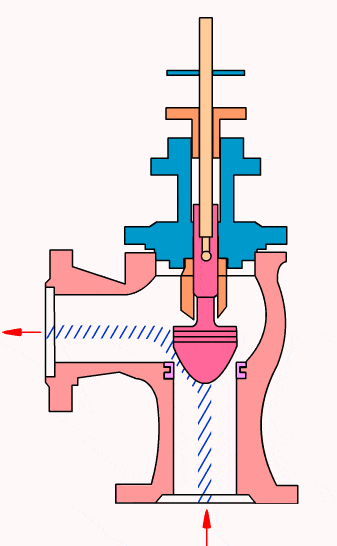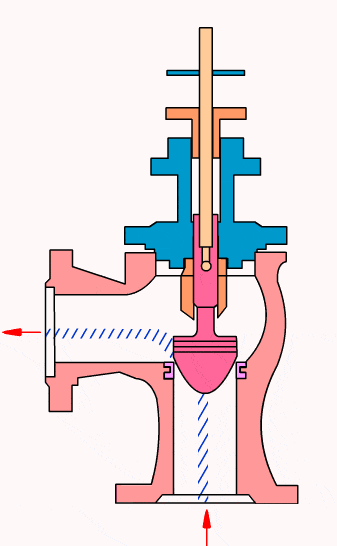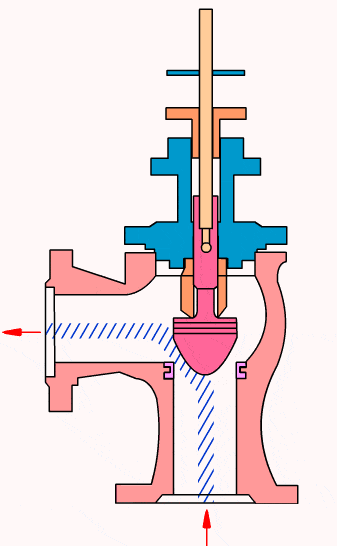
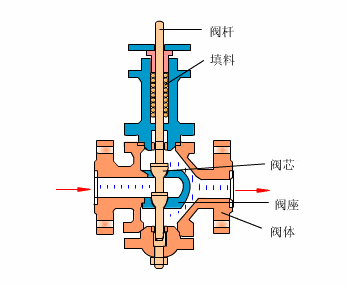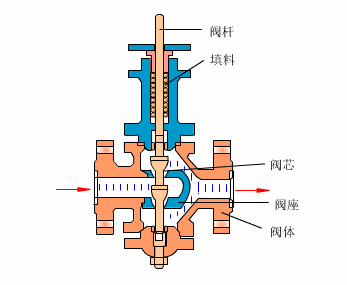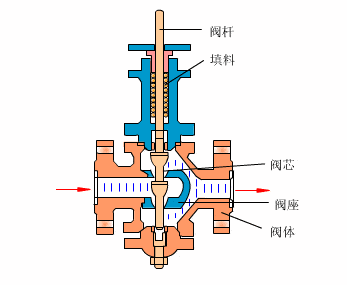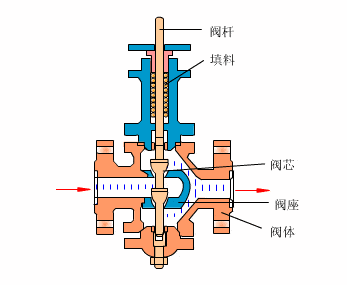
- Cage type control valve
- Multi-port control valve
- Axial cage type control valve
- Digital valve
- Solenoid valve
- Sliding gate valve
- Clamping valve
- Ball valve
- Characterized ball valves(V notch ball valve, eccentric ball valve)
- Multi-pass valves
- Butterfly valves
- Fishtail valve
- Three-way valve
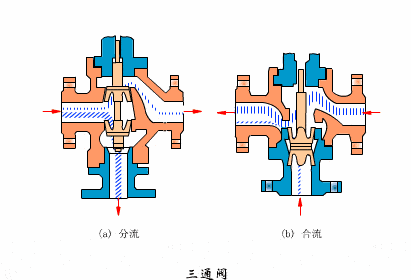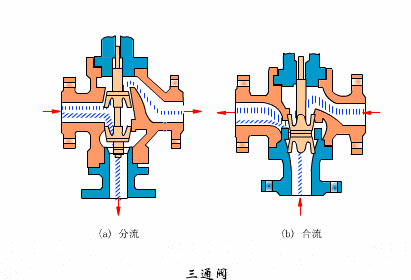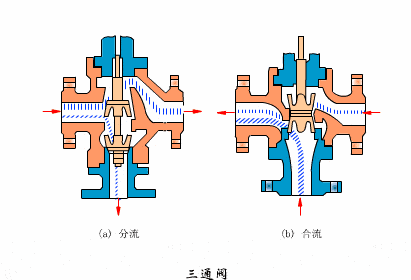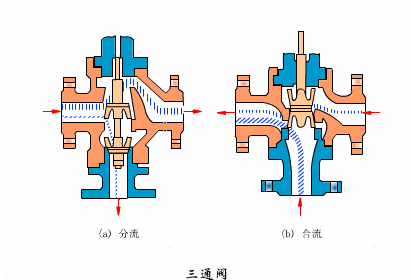
- Eccentric rotary valves
- Automatic pump recirculation valve
- Thermostatic control valves
- Pressure/Temperature Valves
- Control valves for dry solids
- Non-metallic control valves
- Sanitary control valves
Safety relief valves
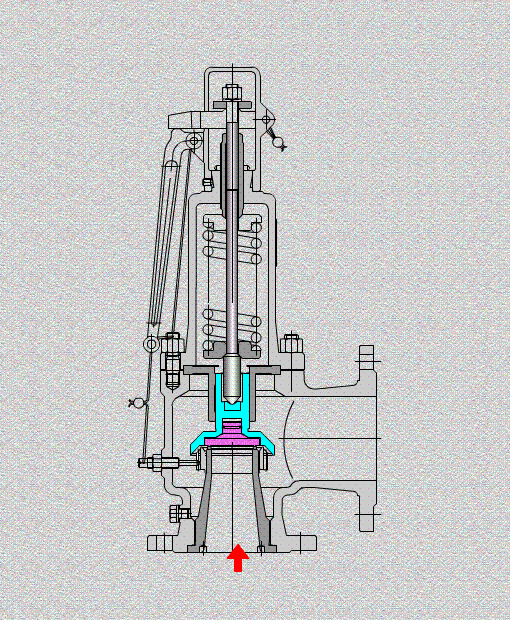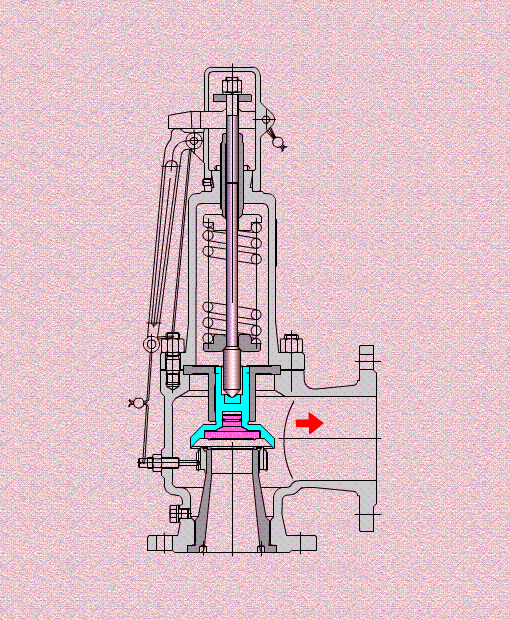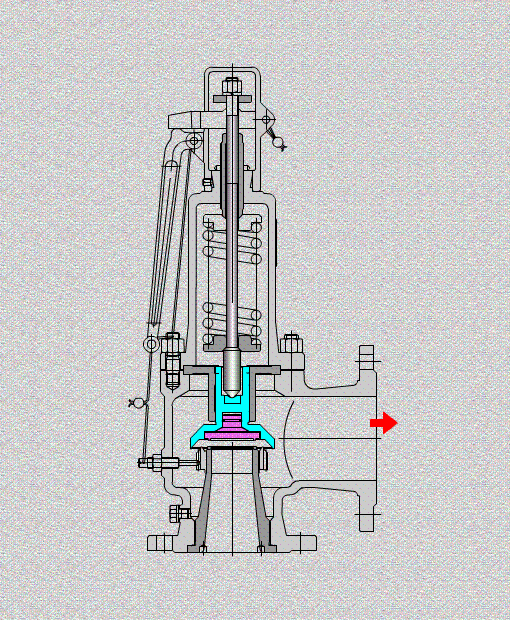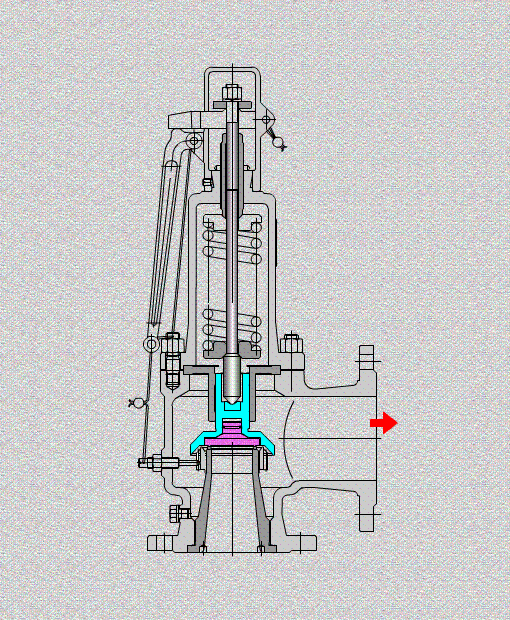
The safety valve is an automatic pressure release device for pressure equipment, containers or pipelines. When the pressure in the protected system rises above the allowable value, the valve automatically opens and discharges part of the excess medium to prevent the system pressure from continuing to rise. When the system pressure drops to a certain value, the valve can automatically close again to ensure The system is operating normally.
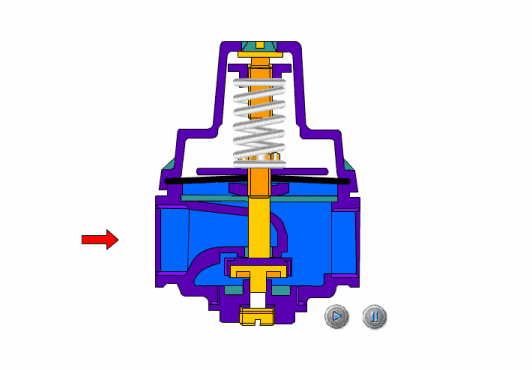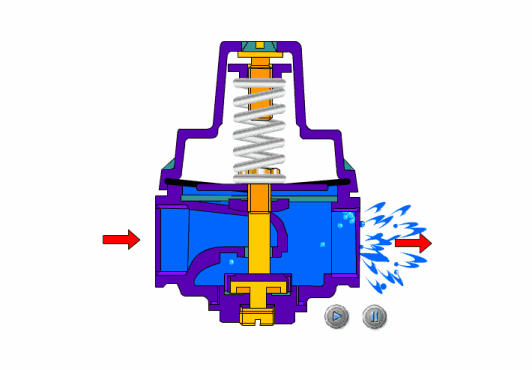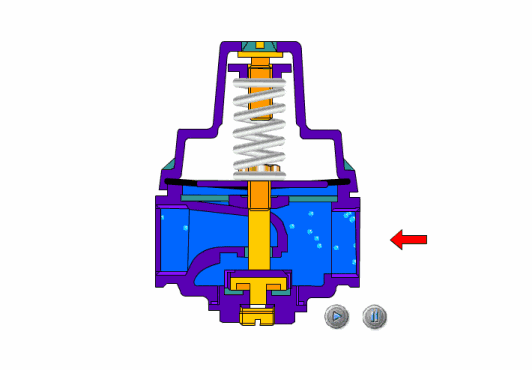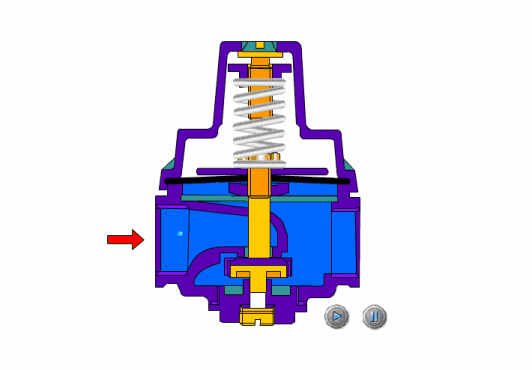
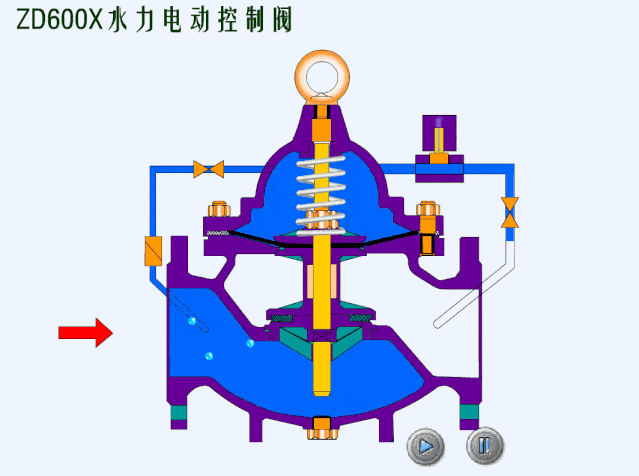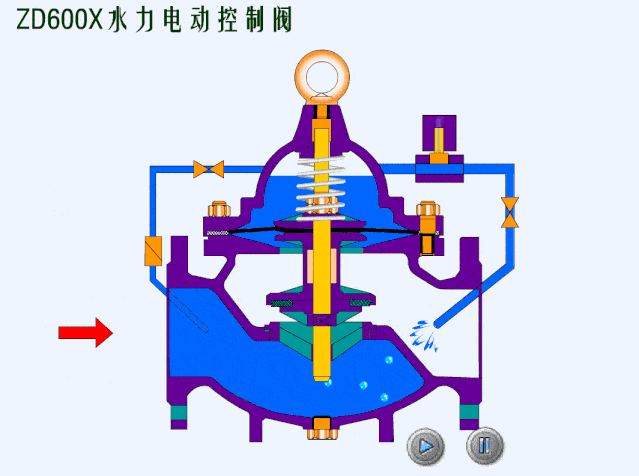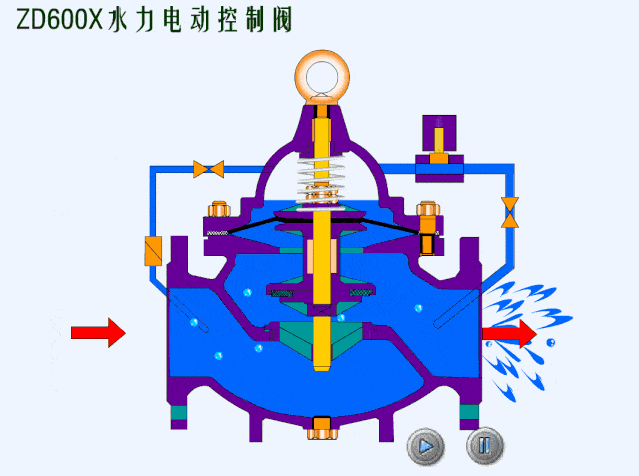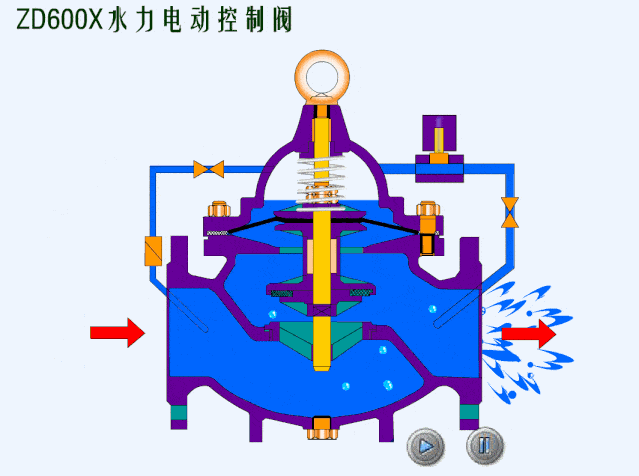
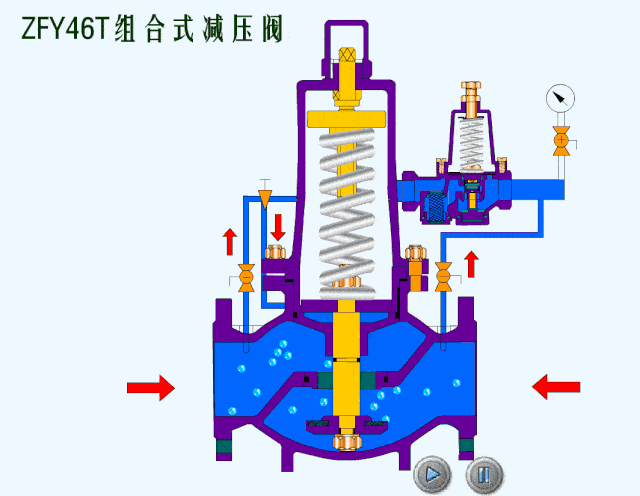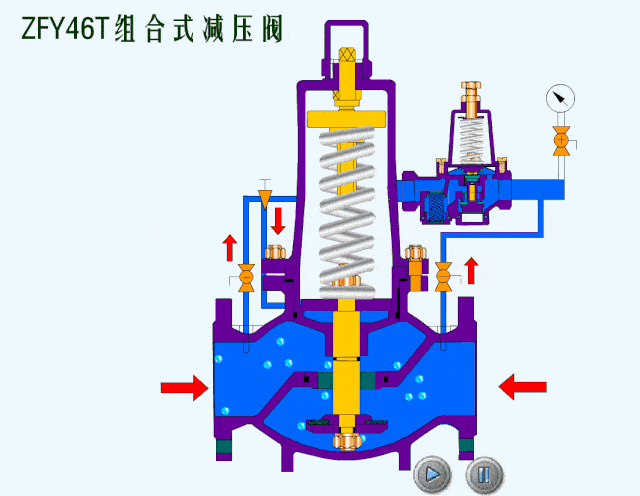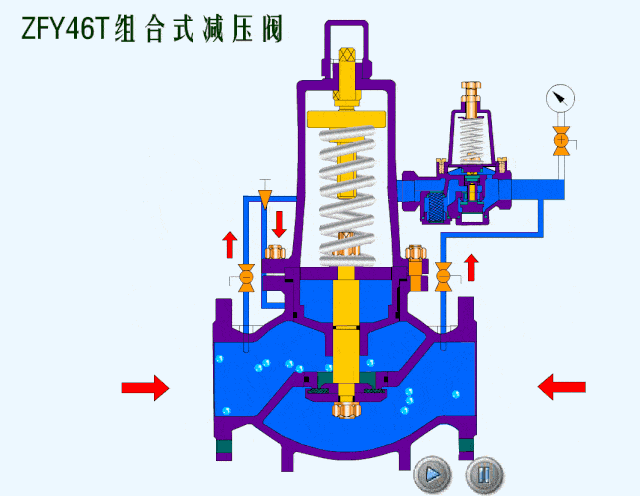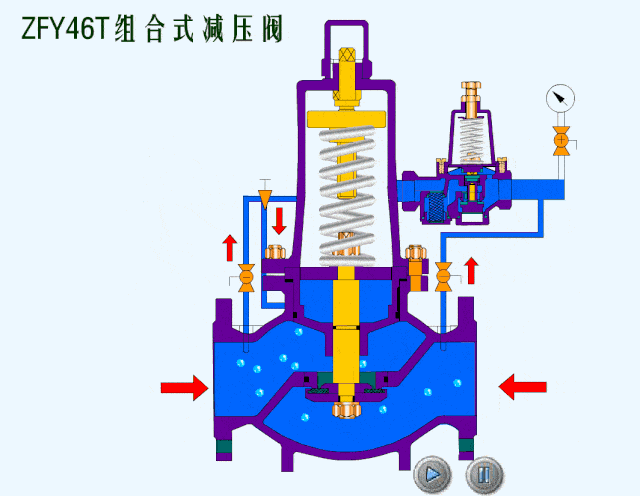
- Spring loaded safety valves
- Pilot operated safety relief valves
- Shear pin safety valves
- Bending pin safety valves
- Thermal safety valves
- Vacuum shut-off valves
- Explosion-proof safety valve
- Non-metallic safety relief valves
- Dual function safety relief valves
Valves are classified based on operator method
- Manually operated valves
- Pneumatic operated valves
- Electric/Motor operated valves
- Hydraulic operated valves
- Solenoid valves