Everything you need to know about industrial valve types & applications from this article. (High recommended to Favorites )
There are lots of industrial valves in general industry, power plant, chemical plant, refining, oil and gas, water and wastewater treatment, with a variety of valve types, functions, size, materials, pressure rating, operation method, etc., It’s confusing for purchaser or Newbies who have just entered the valve industry.
So before introducing much terminology and technical knowledge, I shall picture a simple diagram to get a more intuitive understanding of all valves for you.
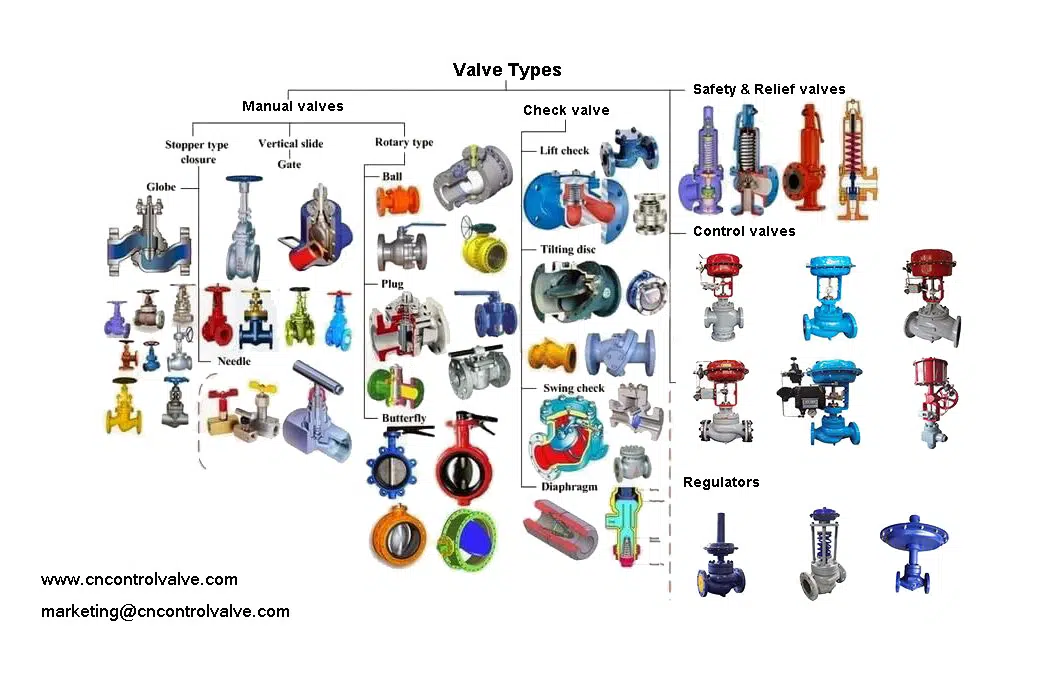
9 Different Type of Valves Used In Plants
Basic Guideline of Selection For 9 Typical Industrial Valves
1. Ball Valves
The ball valve is a type of isolation valve which is the most common valve used in industry, because of its excellent operating characteristics. The ball valve can be contacted by welding, threaded and flanged, and available in a wide range of sizes, materials, temperature, pressure, and tight shutoff.
According to the valve body assembly, the ball valve is classified into three types.
● One-Piece Ball Valve
● Side Entry: Two-Pieces Ball Valve
● Side Entry: Three-Pieces Ball Valve
● Top Entry Ball Valve
According to different stems for the ball that classified into two types.
● Floating Ball Valve
● Trunnion Ball Valve
On the basics of bore profile, ball valves are classified into three types.
● Full Bore Ball Valve
● Reduced Bore Ball Valve
● Segmented Ball Valve
● Multi-Port Ball Valve
On the basics of connection type, the ball valve is classified into three types.
● Flanged Ball Valve
● Welding Ball Valve
● Threaded Ball Valve
For different body materials, ball valves are classified:
❏ Brass Ball Valve
❏ Carbon Steel Ball Valve
❏ Stainless Steel Ball Valve
❏ PVC(Polyvinyl Chloride) Ball Valve
❏ PP (Polypropylene)Ball Valve
❏ GFPP(Glass Fiber-Reinforced Polypropylene) Ball Valve
❏ PVDF(Polyvinylidene Difluoride) Ball Valve
❏ PE(Polyethylene) Ball Valve
The different operation methods also classified three types of ball valves.
● Manual Ball Valve
● Pneumatic Ball Valve
● Electric Ball Valve

Get a Quote
Our headquarters STONE Valve in Taiwan has over 30 years of experience in manufacturing ball valves. Your project of the ball valve will take a professional quote and technical support.
2. Gate Valves
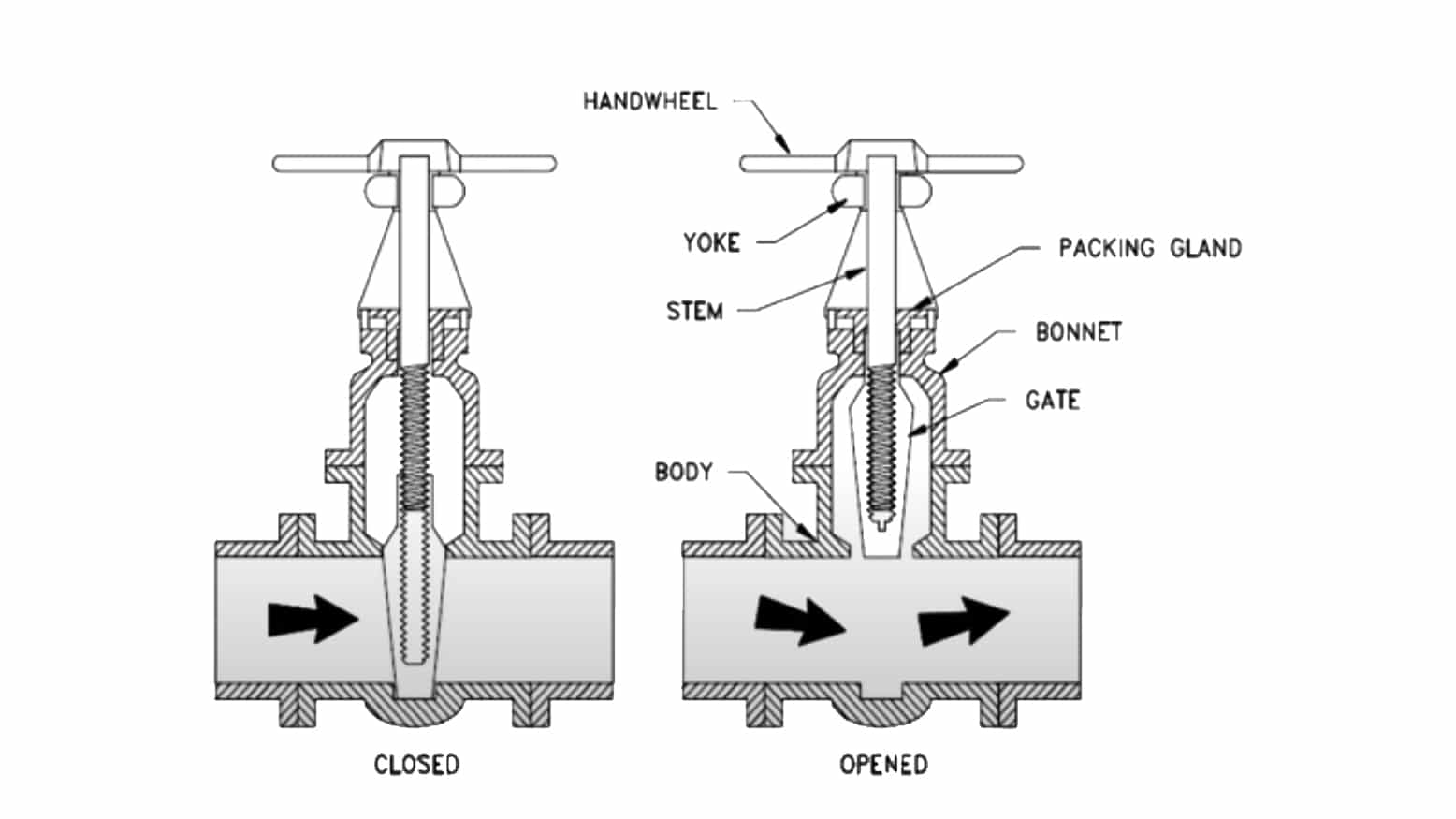
Gate valve is the most common isolation valve in industry, with a linear motion to open and close the flow. As its disc is like a gate, so named a gate valve. There are various types of gate valves, knife gate valves, wedge gate valves, parallel slide gate valves, pipeline slab gate valves, and so on.
Gate valve only works for fully close and fully open, it can not be used for proportion controlling conditions. But as the passageway of a gate valve is unobstructed, which results in minimum pressure loss.
Due to the unobstructed design of valve passages, it is very common to work for pig during pipe cleaning procedures.
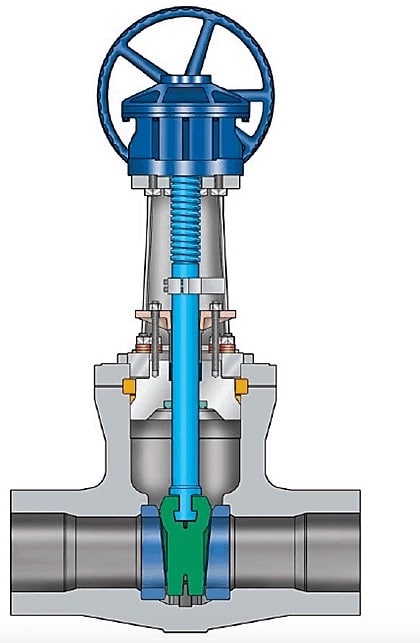
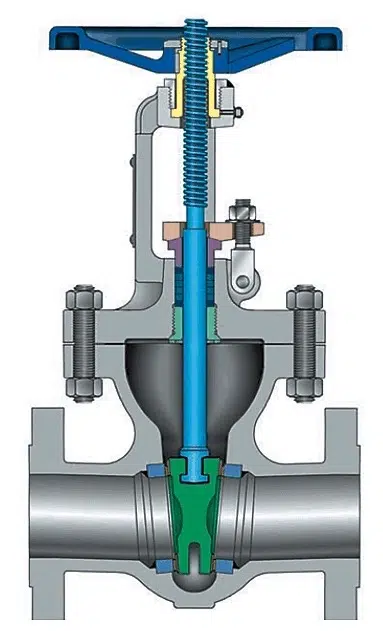
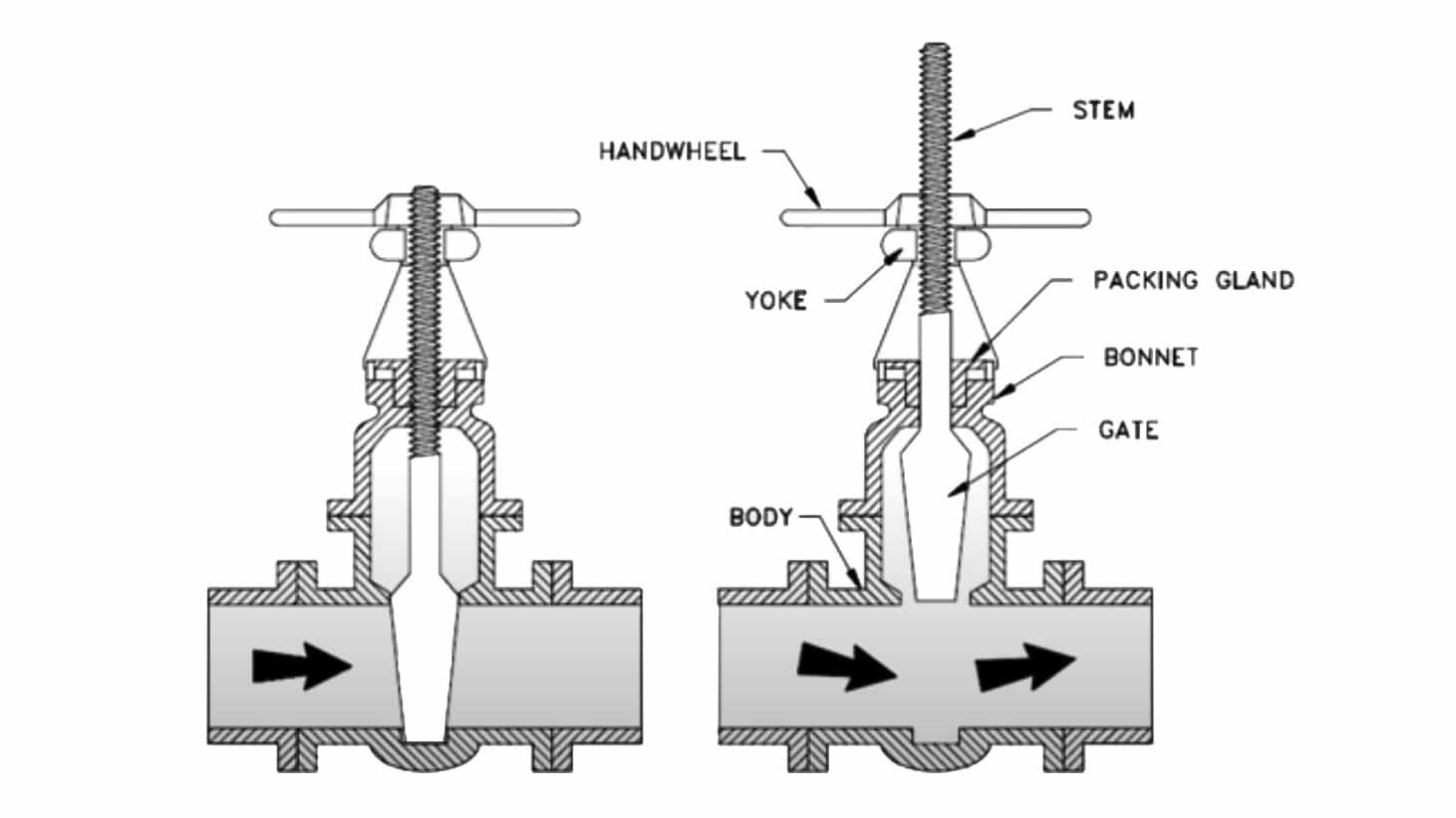
How Many Kinds Of Materials Are Made For Gate Valves?
According to different materials, gate valves classify below types.
- Alloy steel gate valve
- Stainless steel gate valve
- Bronze gate valve
- Cast steel gate valve
- Cast iron gate valve
How Many Bonnet Types For The Gate Valves?
There are three types of gate valve bonnet, union type, bolted, and screwed-in type.
Different Seat: Resilient seated gate valve, Metal seated gate valve.
How Many Stem Types For The Gate Valves?
- The rising stem gate valve is also called the outside screw and yoke(OS&Y) gate valve.
- Non-rising stem gate valve, which uses inside screw stem.

Gate Valve VS Ball Valve
● Cost: Gate valve is more cost-effective than a ball valve In the engineering of shut-off conditions.
● Action time: Compare with the ball valve, the gate valve needs more time to open to close the valve. So it is usually used for application which doesn’t need frequent opening and closing, just simply to isolate the pipeline.
● Sealing: Ball valve has more excellent sealing performance than the gate valve. In the fully closed position and with flow pressure, the gate valve has a positive seal, but under very low pressure like 3psig, it maybe has a little leakage out of the gate valve seat.
How Many Types Of Wedge Designs Are For The Gate Valves?
There are many types of the disc or wedges designed for gate valves, but mostly we are talking about four types.
- Solid wedge
- Double disc-parallel faced
- Split wedge
- Flexible wedge
Above 4 type disc of gate valve, only no. 2 double parallel disc with parallel seat, others with inclined seats.
What Are The Advantages Of The API Wedge Gate Valves?
- Large Flow Capacity
- Small Fluid Resistance
- Simple Construction with Easy Operation
- Replaceable Seat Kit
- Face-to-face is short than the ball valve, and globe valve.
3. Globe Valves
Globe valve, here I talk about the conventional globe valve, not globe type control valve. I put a globe type control valve to the control valve part, which here means a stop valve.
A globe valve is often used for isolation service, the flow path through the globe valve follows a constantly changing process, which increased flow resistance, that’s why the globe valve has a higher pressure drop than the gate valve, plug valve, and ball valve(those valves are straight-through path)
For more details on globe valve, you can refer to this article.
According to the different body designs, the globe valve is classified as a Tee pattern globe valve, Z type globe valve, Y pattern globe valve, and angle pattern globe valve.
What Is The Function Of The Globe Valves?
A Globe valve is an industrial valve that uses a spherical body, a moveable plug, and a stationary seat ring.
The main function of the globe valve is to proportion modulating flow capacity or process pressure and shutoff flow.
Globe valve available to assembly handwheel, gear operator, pneumatic actuator, electric actuator, and hydraulic actuator.
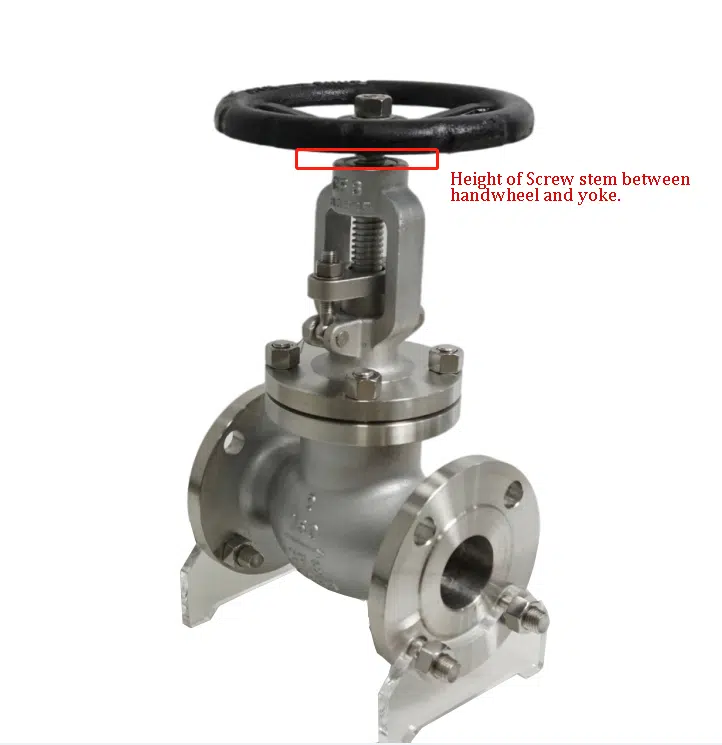
How Do I Know If The Globe Valve Is Open or Close?
As a general rule, you can check the height of the screw stem between the handwheel and yoke, if only 1 – 3 thread displacement that means the globe valve is in a close position. When the valve is at an open position, it will show more height of the thread.

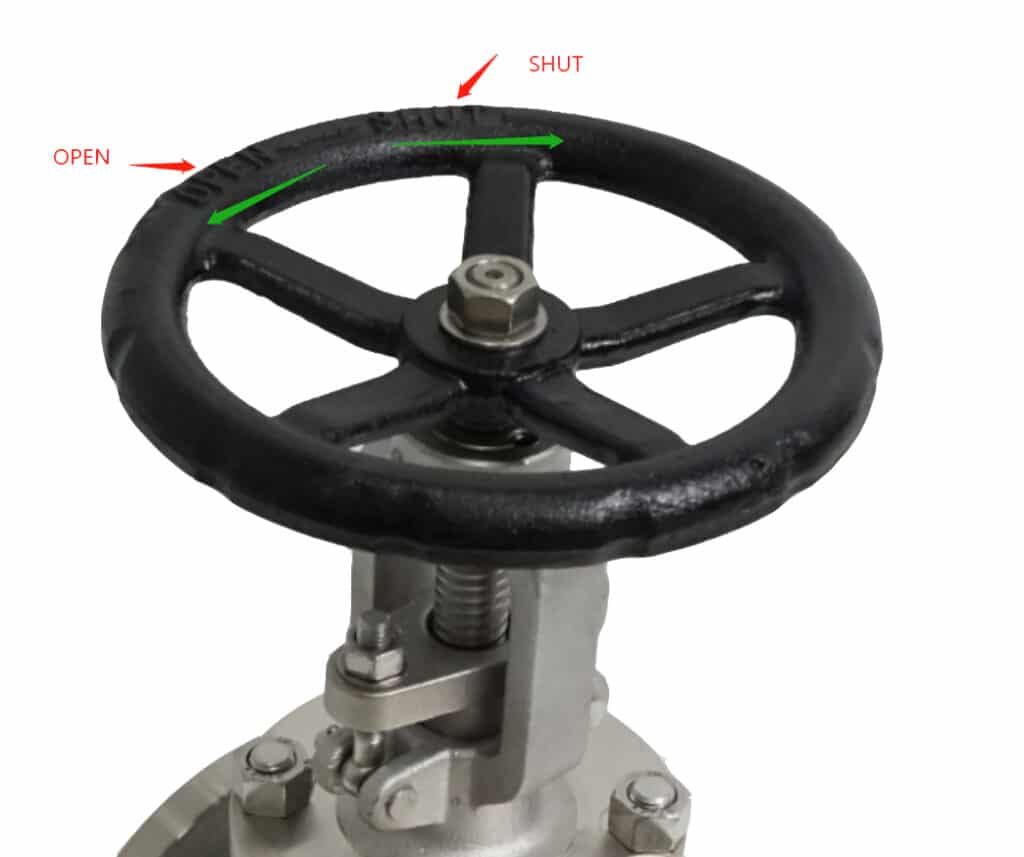
How To Shut Off The Globe Valves?
As a general rule, turn the handwheel clockwise to close the globe valve, and turn counterclockwise to open the valve. There will be a switch mark and arrow on the handwheel.

4. Check Valves

What Is Check Valve Means?
The check valve is also called a non-return valve, which means when the direct flow valve is open, and the reverse flow then the valve closes.
What Are Check Valve Types?
There are two types of check valves used on site.
1. Swing Type Check Valve
The swing check valve is a swing type disk away from the seat to allow flow indirect way, reverse flow as the valve closes, to prevent backflow.
The main components of the check valve include the body, bonnet, disc, and hinge.
2. Lifting Type Check Valve
The lifting check valve usually includes a piston check valve and ball check valve, it is particularly suitable for high-pressure conditions and special installation positions. The lifting check valve can be installed vertical pipeline or horizontal position.
For more check valve types you can read this article.
What Is A Check Valve Used For?
The check valve also called the non-return valve which only allows water, air, steam, or other medium flow one-way direction. The main function of the check valve includes 4 points.
- To protect the pump or expensive equipment from reverse flow damage.
- For the pipelines of the sewage system or desalination system, a check valve makes wastewater or osmosis sewage backflow into the system.
- To maintain the pressure of the water system when the pumps shut off.
- To prevent the discharge of the medium in the container.
When Should Check Valves Be Used?
In a general rule, for the steam system here are 2 typical ways to use a check valve.
- If the outlet of the trap is recycled into the same condensate collection line, it needs to install a check valve, in case to prevent condensate water discharged from equipment in operation may flow back to other equipment that is not running.
- There are many reasons to cause a water hammer in steam pipe systems. One of the main causes of water hammer in the condensate recovery line is because of the backflow of condensate from the lifting pipeline. The installation of check valves in these places is of great help in preventing water hammers caused by backflow.
Where Should A Check Valve Be Installed?
As a general rule, the high pressure at the outlet of the pump can be directly sent to the boiler, the pipeline connected with the high-pressure main pipe, or to the high-level water tank. During operation, when the pump suddenly stops running for some reason, the pressure in the pump disappears, and the high-pressure water connected to the outlet of the pump will flow back to the pump in the reverse direction. So here need to install a check valve(outlet of the pump), it will be closed immediately when happened this situation, to prevent high-pressure water from flowing back to the pump. If the outlet of the pump is not equipped with a check valve, the high-pressure water will flow back to the pump in the reverse direction, and the impeller of the pump will reverse under the impact of the high-pressure water. The impeller or the other parts will be damaged because of the impact load of high-pressure water on it, also the main pipe pressure decrease, and the boiler water level will drop, which will affect the safe operation.

How Does a Check Valve Fail? Top 4 Reason to Cause Check Valve Fail
Check valve plays a very important role in the industry system, it may not the most expensive valve but is like a guard to prevent expensive device effects due to backflow damage.
So we need to know the reason the cause of check valve failure, and we should be able to prevent them happen.
Here are the top 4 reasons that may cause check valve failure.
- Incorrect selection and installation
There are many types of check valves, and selecting the right type, and size for the system is crucial. So make sure the check valve is meet your application, especially for flow capacity data. Then please note the flow direction of the check valve and the position and direction of the check valve during installation. - Insufficient maintenance
Routine maintenance work is very necessary for industrial processes. Check carefully during the maintenance procedure, for the ball valve, gate valve, and globe valve, check valve those general valves, lookout for signs of the bonnet, body, and actuator(if assembly), and also check the pipeline if there has metal impurity, which will cause damage of valve seat or internal components, even cause valve stuck and can’t work well. If you find out any signs of wear, replace damaged components or complete valves as soon as possible. - Swing pin or spring broken/weak
Except for the wrong selection of check valves, most check valves fail because of a swing pin or spring broken. It will cause the check valve absolutely fail to work or can’t shut off tightness or fast response.
When reverse flow at the pump discharge, it will cause spin of the pump to backward and damage pump with extremely costly. - High-temperature condition
If the check valve work at high-temperature application, you should observe these valves often, in case to prevent the valve fails early due to high temperature. If you see any sign of wear on the check valve, replace them immediately to avoid more loss.
Does A Check Valve Reduce Water Pressure?
A check valve is used in allows the process medium to flow in one direction way, and to prevent backflow by automatically close.
So check valve can’t reduce water pressure, more important is it can’t discharge fluids from low pressure into a higher pressure line, because the back pressure is higher than the upstream pressure/inlet pressure of the check valve, and the swing or disc can’t open.
What Is A Silent Check Valve?
The silent check valve is a priority design of silent operation with positively closing, and prevents water hammer, surges and vibration. The silent check valve combine of body, seat, disc, spring, sleeve, o-ring and retaining screws, etc.,
- Body 2. Retaining 3. Disc 4. Spring 5. Sleeve 6. O-ring
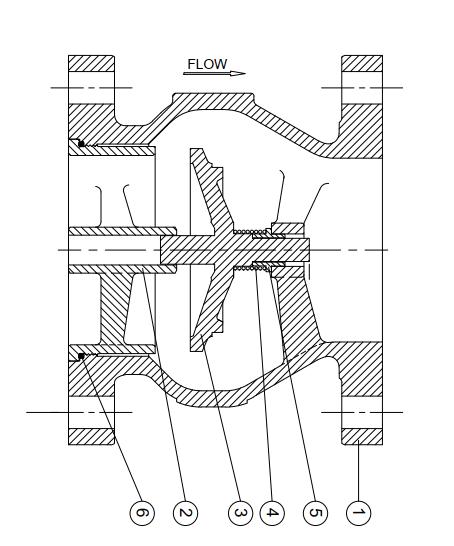
Will A Check Valve Stop The Water Hammer?
A regular check valve can’t stop a water hammer, but because of a slam shut off, or a sudden valve closure, only a non-slam check valve, nozzle check valve or silent check valve can prevent a water hammer.
What Is A Spring-Loaded Check Valve?
A spring-loaded check valve is one common kind of non-return valve, which allows flow in one direction, in case prevent fluids backflow. Usually, a spring-loaded check valve is suitable for reducing water hammer, and benefit can be installed in any position, no matter horizontal, vertical, or otherwise.
Which Is Better Swing Or Spring Check Valve?
The swing check valve and spring-loaded check valve are both used to prevent reverse flow. Many people ask which is better, a swing check valve or a spring-loaded check valve?
A responsible engineer will not simply answer which is better, but explain how to select the right type of check valve for your application. Here we just list some cases.
- A swing check valve only installation of horizontal flows or vertical upward flows. But the spring-loaded check valve can be installed in any position.
- If you have a limited budget but for large flow capacity conditions, a swing check valve definitely is your first choice.
- As spring-loaded check valve has sprung to relieve pressure from the system slowly, which creat a safer environment for industrial processes.
What Is The Difference Between A Check Valve And A Backflow Preventer?
Check Valve V.S Backflow Preventer
Technically check valve and backflow preventer is a similar function for industrial processes that prevent fluids backflow.
A check valve is just a simple non-return valve, but a backflow preventer is a module assembly of check valves. It is used in high-hazard environments and needs to completely protect the flow safe while even one part failed.
You can easier to find the backflow preventer installed where potable water connects to non-potable water.
● HVAC system
● Irrigation system
● General indsutral system
● Fire suppression system
5. Butterfly Valves
A butterfly valve is a 90° turn rotational motion valve that is used to on/off or control the flowing medium in a process. And particularly for large capacity conditions.
What is the different type of butterfly valves?
● Centric Butterfly Valve
● Lined Butterfly Valve
● Double Eccentric Butterfly Valve
● Triple Offset Butterfly Valve






Do Butterfly Valves Have A Flow Direction?
As a general rule, a butterfly valve is a bi-direction industrial valve, but it does have a preferred flow direction in case to protect the valve and extends service life, also with lower operating torque.
What Is The Difference Between A Ball Valve And A Butterfly Valve?
Ball Valve V.S Butterfly Valve
The ball valve and butterfly valve both can isolate fluids in the processing system. So what is the exact difference between the ball valve and butterfly valve? We are going to describe the difference from 6 points.
- Flow capacity.
A butterfly valve can provide a larger flow capacity than a ball valve, it is easy to available in a large pipeline. - Application
Butterfly valves are easy to clean, so they are commonly used in sewage, beer, and soda production, etc. Butterfly valves are very popular in waste treatment plants, and chemical, agricultural, and food industries.
Ball valves can be used at high temperatures or both liquid and gas with some solid particles. They are common in power plants, oil and gas, refining, and so on. - Zero leakage
If conditions require zero leakages when shut off the medium, a ball valve with a high tight seal than a butterfly and make perfect sealing. - Operating condition
The ball valve can be used for higher temperature and pressure than the butterfly valve. Usually, below 5.0Mpa and temperature below 250 degrees C can use a butterfly valve, higher than data we can use a ball valve. - Flow ports
A butterfly valve only has two ports, while a ball valve could have more than two ports, it can be three ports(T or L type), or four ports. - Function
Ball valve and butterfly valve both can isolation process medium, but also can proportional flow control. But for small sizes, like below DN100, V port or segmented ball valve has better regulating performance than butterfly valve. For large sizes, we can use high performance or triple offset butterfly valves to control the flow capacity. - Costs
For the same size, definitely butterfly valve is more cost-effective than the ball valve(O type).
| Item | Butterfly valve | Ball valve |
| Weight | Lighter weight even at larger pipe diameters | Very heavy at larger pipe diameter and may require support |
| Installation space | Requires smaller installation space | Requires larger space than a butterfly valve |
| Size | Suitable for larger pipe diameter (above DN 150), particular due to lightweight | Better suited for smaller pipe diameter (below DN 50) |
| Leakage | Prone to leakages at a high-pressure difference | Provides tight seal even at a high-pressure difference |
| Cost | Cheaper than a ball valve, particularly for larger sizes | More expensive compared to a butterfly valve |
| Flow control | Suitable for ON/OFF control but can be used for proportional control. | Functions well for both ON/OFF and modulating control |
| Flow restriction | Valve disc restricts flow creating a pressure drop. | Full port ball valves have no pressure drop. |
| Connection style | It has a flange style with a lug or wafer design | A wide array of connection types with threads or flanges |
6. Plug Valves
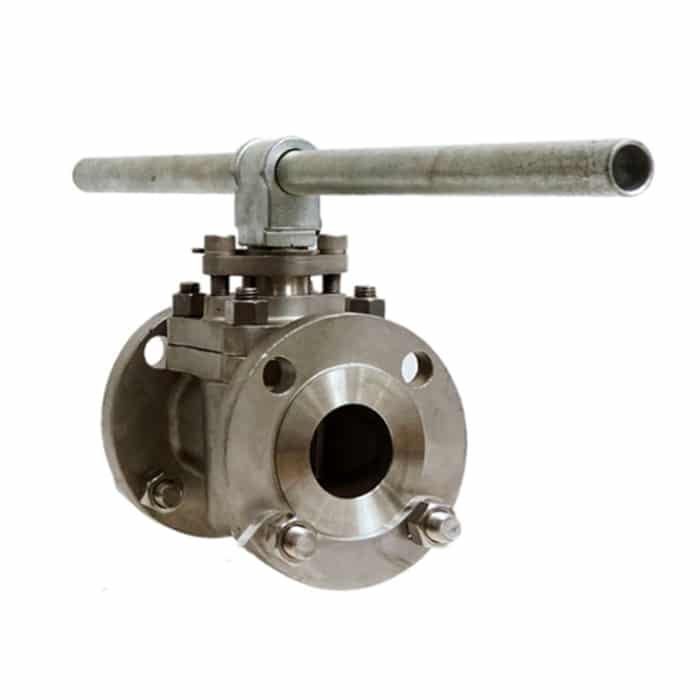
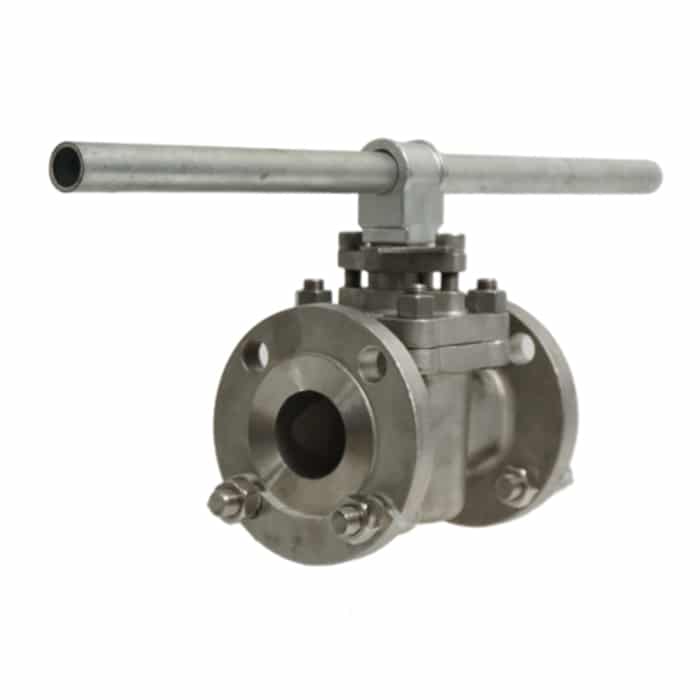


How Many Different Types Of Plug Valves Are In The Industry?
A plug valve is an isolation valve that is a quarter-turn shutoff valve. The plug can be designed in tapered or cylindrical form. Plug valves are available in different port types.
As a general rule, there are 4 types of plug valves with different designs.
Non-Lubricated Plug Valves
Non-lubricated plug valves are mainly used in the petrochemical, refining industry, and RO plants.
Non-lubricated plug valves use the sleeve to reduce friction between the plug part and body.
It is commonly used in minimum maintenance needs, and where liquids could be trapped or solidify and potentially block the valve.
Applicable standards of Non-Lubricated Plug Valve:
a) Design & Manufacture: API 599, API 6D
b) Face to Face: API 6D, ASME B16.10, EN 558, DIN 3202, BS 2080
c) Connection End: ASME B16.5, ASME B16.25, EN 1092, EN 12627, JIS B2220
d) Test : API 598, API 6D, EN 12266, ISO 5208
Sizes: 2″ – 24″ or DN50 – DN600
Pressure Rating: Class 150 – Class 2900 or PN 16 – PN 160
Valve Materials: WCB, LCB, WC6, WC9, C12, C5, CF8, CF8M, Duplex Stainless Steels, etc.
Operated by: Wrench, Gearbox, Pneumatic, Hydraulic, and Electric actuator
Lubricated Plug Valves
Lubricated plug valves are mainly used in crude oil applications.
The lubricated plug valve has grease fitting which injects lubricant to plug face and body seat, in case to reduce friction and sealing ports. Through a radial hole, the lubrication is constantly into lubricant grooves on the plug surface.
Expanding Plug Valves
Expanding plug valve is a special design in which the plug is made of multiple components allowing it to mechanically expand through a wedging action onto the cylindrical body.
Eccentric Plug Valves
Eccentric plug valves are basically plug valve with a plug cut in half, it has minimal friction from open to close, without a significant operating torque but shutoff performance is improved.
Ask For a Quick Quote
THINKTANK manufactures plug valves for over 10 brands with high quality and reasonable prices. Your project of the ball valve will take a professional quote and technical support.
Other different types of plug valves we can see below.
● Two-Way Flanged Plug Valve
● Three-Way Flanged Plug Valve
● Two-Way Threaded Plug Valve
● Three-Way Threaded Plug Valve
● Three-Way Brass Plug Valve
● Two-Way Jacket Plug Valve
● Three-Way Jacket Plug Valve
● Oil Sealing Plug Valve
● Lining PTFE Plug Valve
● Asphalt Special Plug Valve
● ASTM Plug Valve
What’s The Difference Between A Ball Valve And A Plug Valve?
Difference 1
- The ball valve has is a ball in the valve body, which has a bore drilled through it.
- The plug valve has a tapered or cylindrical form as a plugin for the valve body and is usually secured by a spring-loaded screw on the bottom side of the valve, or a bonnet and packing at the top end.
Difference 2
- Ball valve with PTFE, RPTFE, TEFLON, Metal seat ring, and packing box. When the ball valve closes the ball, the fluids get into the dead spaces, in the open position, aggressive fluids harmes the ball surface.
- Plug valve with PTFE, F46, or other materials sleeve. When the valve closes and opens the plug, there are no fluids can remain in the dead spaces.
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of Plug Valves?
A plug valve is a plug top mounted into the valve body which is equivalent to a top-mounted ball valve. Compared with a two-piece or three-piece ball valve, it is a completely different type and application product.
Let us understand the advantages and disadvantages of the plug valve and the main purpose of the plug valve:
Advantages Of Plug Valves
- The valve body of the plug valve adopts an integrated top installation design, simple structure, convenient in-site maintenance, and tight shutoff with zero leakage.
- Used in chemical medium(corrosive medium). In a chemical environment, the valve body is often corroded by the medium. The plug valve has strong impermeability and it can be inner lining to anti-corrosive very well.
- The opening and closing component plug, plug without abrasion of body, easy to maintenance.
- The entire machined surface of the plug valve is only the bonnet and flange, and all other parts are casting finished.
- The plug valve can be designed and produced with specific functions according to user needs. Three-way, four-way, five-way, six-way, double-valve, or multi-valve groups can be customized, as well as various jacket requirements.
- The plug valve is suitable for harsh media, such as fluid corrosion and deposits containing catalytic particles.
- The coated sleeve has surface sealing performance, which can strictly refer to the “zero leakage” test requirements of the API598 soft seal seat and can meet the requirement of ISO15848 valve stem sealing.
The general characteristics of plug valves are long service life and high reliability. It is suitable for a variety of corrosive, abrasive, toxic, continuous operations and other media and equipment, and has the advantages of application in the chemical industry.
Disadvantages Of Plug Valve
- The surface seal design increases the requirements for driving torque. For pneumatic actuators, the requested torque is larger than ball valves, and it will increase the user’s costs.
For example, in the PP process, the main shut-off valve uses a plug valve instead of a ball valve, and the high-frequency switch valve uses a ball valve, so the pneumatic plug valve is basically used in the main cut-off position. - In some applications, improper selection or design of sleeve materials will cause the PTFE sleeve to expand and the valve torque will increase much.
- The price of plug valves is higher than ball valves. However, as the reliability of the plug valve and the total life cycle cost are gradually accepted by domestic users, more and more users will need a plug valve that continues to use the original process design.
Quick To Learn Advantages & Disadvantages Of Plug valve
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Large Capacity | Large torque(high friction needs a large driver) |
| Excellent anti-corrosion performance | High costs(compare with ball valve) |
| Quick opening and tight shut-off | can’t be used in throttling application |
7. Safety & Relief Valves
What Is A Safety Valve?
The safety valve is a special valve that can protect equipment from damaging or exploding. Commonly safety valve is installed in pressure vessels and automatically opens immediately when the accumulation of pressure in a system or vessel is beyond a preset limit. It simply allows the excess pressure to relieve, to prevent any disaster.
Safety valves are widely applied in chemical plants, power plants, boilers and gas storage tanks, petrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and many more. It controls the pressure and discharges a certain amount of fluid by itself without any additional supply of energy.
What Are The Types Of Safety Valves?
There are three types of safety valves in thinktank’s production line.
- Spring-loaded safety valve
A spring-loaded safety valve adopts the force of spring press on the disc against the inlet pressure. - Pilot operated safety valve
Pilot-operated safety valves are a combination of pilot assembly and main valve, the reliving pressure and reseating pressure of the pilot-operated safety valve is controlled by the pilot assembly, which acts as a spring-loaded safety valve. Pilot operated safety valve used in high pressure or large size variations, it has more precise accuracy and fast response.
What Is The Difference Between A Safety Valve And A Relief Valve?
In general, the safety valve and relief valve are both used to release the overload pressure from a pressure vessel system. So what is the exact difference between them? From technical definitions, the safety valve does differently from the relief valve.
A safety valve refers to a pressure valve that is designed to protect life, equipment, and processes. It means the safety valve is the last resort valve that releases pressure to prevent an accident when all other relief valves have failed to adequately release pressure within a system. Simply say the safety valve is a failsafe.
A relief valve is a pressure relief valve that is designed to help the processing facility avoid system failures, and protect equipment from overpressurized conditions. A relief valve is used to control pressure for the optimal functionality of the system.
Here we list 4 differences between a safety valve and a relief valve
- Function
The safety valve’s only purpose is safety, which is designed to release pressure in the system failure or emergency issue immediately. Instead of controlling the pressure of a system, the safety valve open completely and immediately to prevent a disaster.
A relief valve is a pressure relief valve(PRV), which is designed to control pressure in a system, commonly used for compressed air, water, and steam system. The opening of the relief valve is proportional to the increase in system pressure. The relief valve gradually opens, returning the system to a preset pressure level. When this pressure level is reached, the valve will close again. - Operation
For a safety valve, the opening is immediately when the system pressure reaches the set pressure, to prevent system failure, in order to protect people, property, processes, and environments. It is a safe-fail device which capable of operating at all times. The safety valve is the last resort to prevent a disaster from overpressure conditions.
For a relief valve, the opening is proportional to the increase in the vessel pressure. It means the opening of the relief valve is gradual, not immediately, it allows open only at a preset pressure and releasing fluids until the pressure drops to the desired set pressure. - Setpoint
A setpoint is not equal to set pressure. For a pressure relief valve, a setpoint is a certain pressure level at which PRV opened. Let me explain it, a setpoint of relief valve is set below the maximum system pressure allowed before overpressure conditions occur, it is adjusted to the lowest maximum pressure rating.
When the pressure reaches up to above the setpoint, the relief valve begins to open.
The most important thing is the setpoint must NOT exceed the maximum allowable working pressure of the valve(MAWP).
For the safety valve, the setpoint commonly must never be set above 3% of the working pressure (MAWP).
For the relief valve, the setpoint commonly must never be set above 10% of the working pressure (MAWP). - Types
Safety valves have a wide range of types based on applications and performance in different sites.
Relief valves are classified as direct operated, pilot operated, and internal relief valves.
What Is The Function Of A Safety Valve Fitted In A Steam Boiler?
A steam boiler is a pressure vessel and a generator for steam, the purpose of a boiler is to store highly pressurized steam. But due to the state of pressurization due to the expanding steam may cause the boiler explosion, people hurt, property lost all disasters.
So we keep a safety valve fitted in a boiler to release exceed the pressure in case to prevent such accidents. You may ask why not use a relief valve but a safety valve, you can read the above article named What is the difference between a safety valve and a relief valve?
The function of a safety valve in a boiler is when the system pressure reaches the setpoint, it will open sharp and the opening will be full until the pressure drop to around 4~5% below the working pressure.
A simple example may be very easy to understand if the set pressure is 7 bar, then when the system pressure reaches 7 bar, the safety valve will be full opening. But for the relief valve, if set pressure at 10 bar, then at 11 bar, the relief valve will open more to release an extra 1 bar.
What Is The Function Of Safety Valves?
Simply explain parts of the safety valve’s function role, nozzles like pressure entrance, disc as a lid, and spring-like pressure controller.
The nozzle inside of the safety valve starts to receive a high pressure from the inlet port, when the pressure increases higher than the predetermined pressure, the disc starts to lift and discharge the fluid. and when the inlet pressure decreases while the set pressure, the force of spring closes the disc.
8. Control Valves
THINKTANK is a well-known brand in China, focus on manufacturing control valves for over 15 years. We supply an eccentric plug control valve, single-seated control valve, double-seated control valve, three-way control valve, cage type control valve, and so on, which can be custom engineered to perform specific functions for the end-users requirements.
What Are Control Valves?
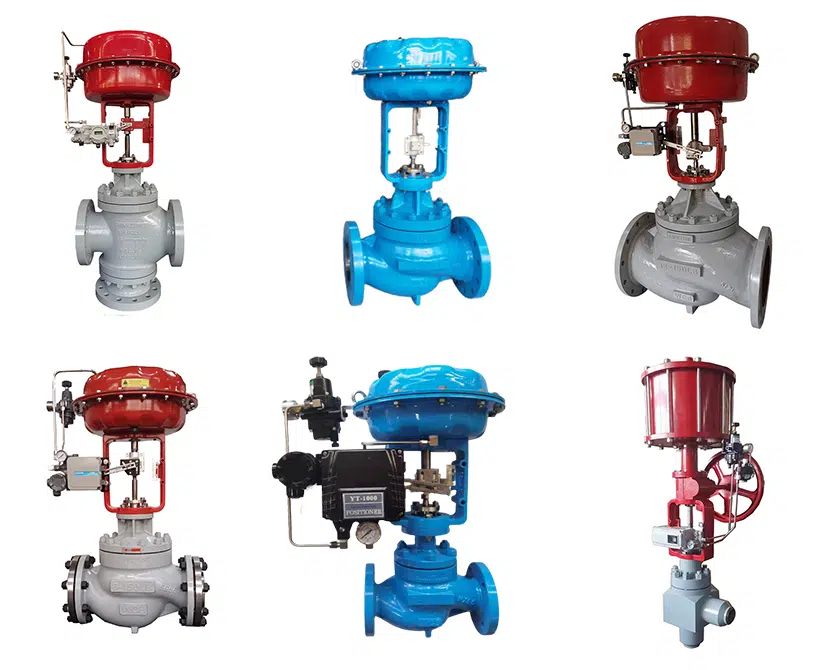

A control valve is one of the most important parts of the control loop. The main function is regulating pressure, temperature, flow rate, or other variables of the process medium in the industry. As a professional globe control valve manufacturer, THINKTANK provides a wide range of control valves for chemicals, oil&gas, power plants, refining plants, pharmaceuticals, etc.
What Are Control Valves Used For?
The control valve is the most common final control device in the process, The control valve regulates the flow of a fluid, such as gas, steam, water, or chemical mixture, to compensate for load disturbances and make the controlled process variable as close as the desired setpoint.
How Do Control Valves Work?
There are three typical types of actuated control valves in the process, pneumatically actuated, electric actuated/motorized actuated, and hydraulic actuated. The working principles of the valve are similar, but a bit different from the actuator part with different ways to operate.
● Pneumatic actuated
Usually, the pneumatic actuator will complete with the positioner along with the assembly of the control valve. Pneumatic actuator receives the air supply from an external source and force to the diaphragm or piston of pneumatic actuator, meanwhile valve positioner receives an input signal 4-20mA or 3-15PSI or others analog signal from PID, and turns the signal response to the actuator, and finally makes actuator proportion drive the valve stem downward/upward strokes control valve.
● Electric/Motorized actuated
An electric actuator is kind of a motor-driven device that uses a power supply to makes motor shaft rotation. Similar to the pneumatic actuator, an electric signal drive the stem downward/upward modulating flow rate, pressure or temperature, etc in the control loop.
● Hydraulic actuated
The hydraulic actuator has more force than the pneumatic and electric actuator, and it uses hydraulic oil to drive the actuator to regulate the control valve. They are mainly used in high-safety systems such as steam turbine exhaust pipes, blast furnace gas residual pressure power generation devices (TRT), and industrial pipe networks with seawater, sewage, flue gas, air, oil, etc. as emergency shut-off valves.
What Do All Control Valves Have? What Are The Main Parts Of The Control Valve?
A control valve is a control device used to regulate the flow of fluids by varying the size of the flow passage.
As a general rule, a control valve consists of 4 main parts, body, bonnet, trim, and actuator.
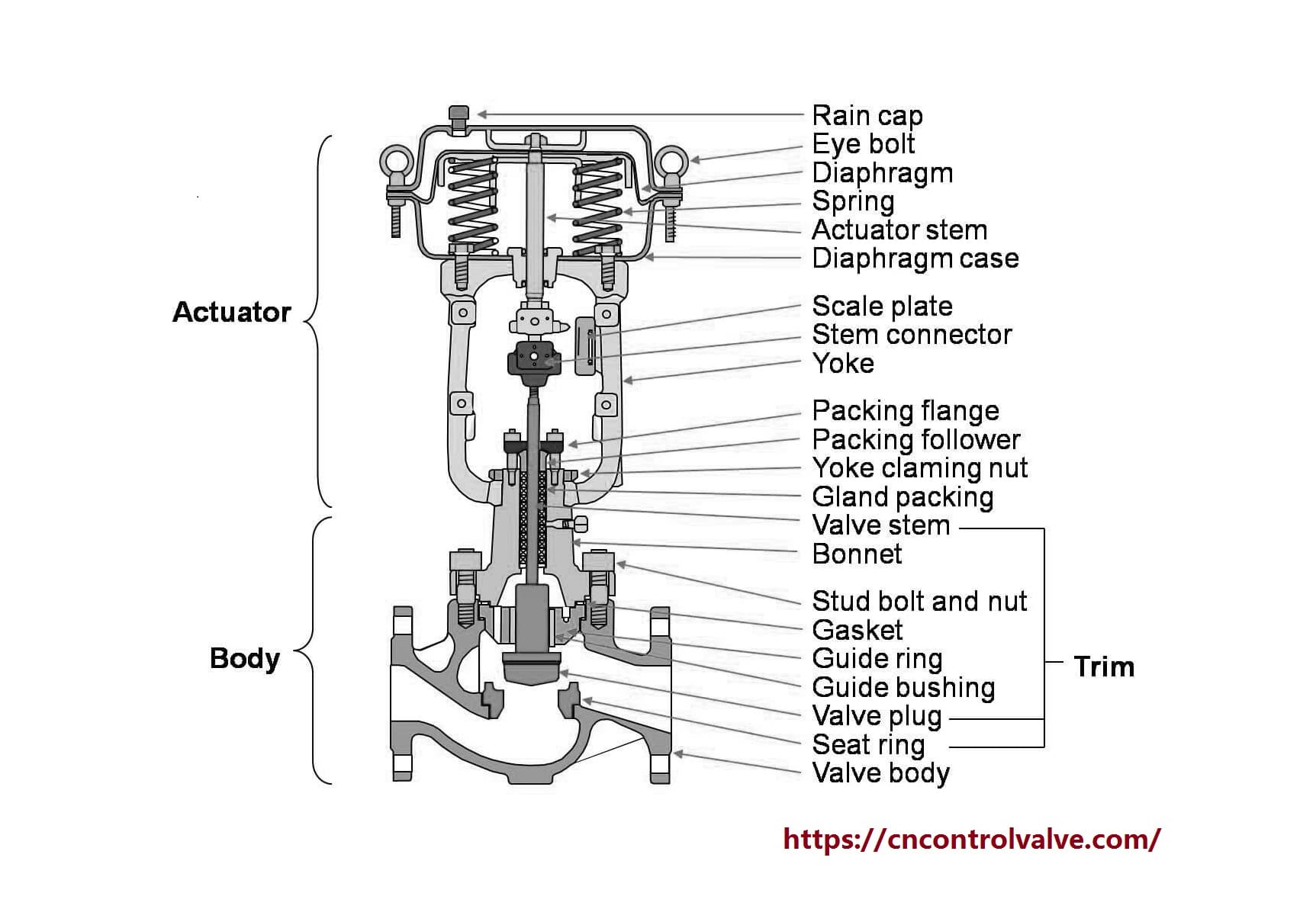
9. Self-Operated Regulators
A self-operated regulator as its functions, we can classify 3 types, self-operated pressure regulator, self-operated temperature regulator, and self-operated differential pressure regulator.




What Is A Self-Operated Valve?
A self-operated valve is not required for auxiliary energy to the active valve but uses the process medium energy itself. It means there is no need for extra pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic power to operate the valve.
How Does A Self-Operated Pressure Reducing Valve Work?
A self-operated pressure-reducing valve is a mechanical device used to control upstream/inlet or downstream/outlet pressure in natural gas plants. Also, it can be used for steam, air, water, and other fluids.
Before we start to learn the principle of self-operated pressure-reducing valves works, first we need to know the main parts of them.
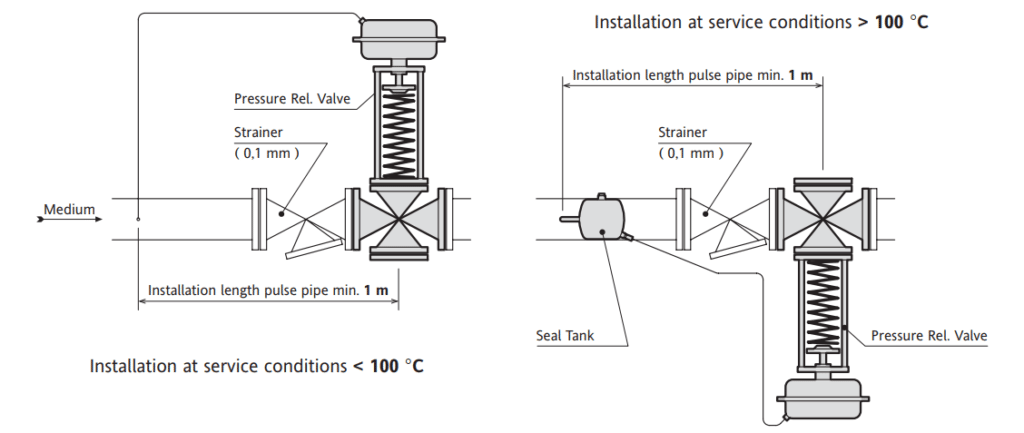
A self-operated pressure-reducing valve consists of three parts, a loading component(spring), a measuring component(diaphragm/piston self-operated actuator), and a restrictive component(valve).
The measuring component is directly connected to the process medium(natural gas) and generates a force against a loading force from the spring, then drive restricting component – valve release pressure.
For example, if a self-operated pressure reducing valve is used to controlling downstream pressure, natural gas medium, the set pressure is 1 bar. So we put the control line at the regulator outlet connected to the downstream pipeline, to measure the process pressure and respond to the diaphragm.
The process medium flows through the valve between the seat and plug by the arrow direction, the downstream pressure P2 is transmitted over the actuator chamber and the control line to the operating diaphragm where it is converted into a positioning force. Then this force act on the valve plug depending on the force of the setpoint springs.
When the downstream pressure P2 increases, the force P2 acts on the diaphragm also increases. At this time, the force on the diaphragm is greater than the force of the set spring, so the valve plug moves toward the closed position, the opening of the valve decreases, and P2 decreases until the force on the diaphragm is balanced with the spring force. So that P2 is reduced to the set value. In the same way, when the pressure P2 after the valve decreases, the action direction is opposite to the above direction
What Is A Self-Contained Pressure Regulator?
A self-contained pressure regulator as the name suggests does not need an external signal or power but the process medium energy to drive itself to open or close the regulator.





