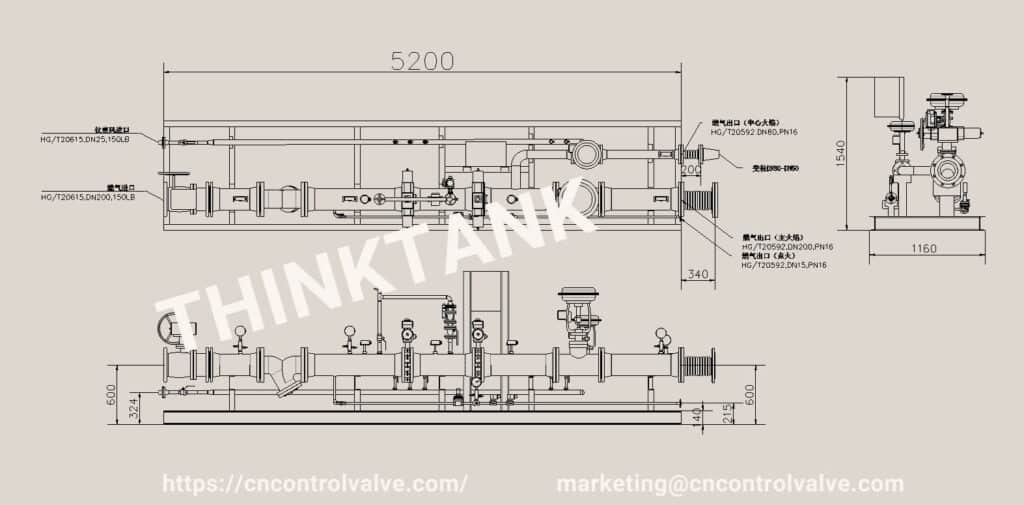
If you are an engineer or sales in the industrial field, then you definitely know the steam boiler on site. But you may not deeply understand what boilers exactly do, how boilers work, and how to select the right, safe and efficient steam boiler for the application.
Don’t worry, steam boilers aren’t complicated to understand, you will learn everything in detail in this guide.
What Are Steam Boilers?
One of the most common types of boilers, a steam boiler converts thermal energy from the fuel it uses to heat the water inside the boiler into steam, which may then be utilized for a variety of industrial and domestic purposes. So we can simply say a steam boiler is a pressurized container that uses heat transfer to turn water into steam for a variety of purposes. There are many types of fuel for heating, including gas, coal, biomass and fuel oil, etc. Gas steam boilers are the most popular due to the policy of protecting the environment.
What Are The Types Of Steam Boilers?
A steam boiler is a heating system that generates steam. It generates energy by boiling water to produce steam. It is a heat exchanger with a combustion chamber and a water container that produces steam for external use. Steam boilers are available in a variety of sizes, from extremely small to huge for more demanding applications.
To heat water, a steam boiler burns fuel. Steam is created when heat and water combine. To make steam, three types of heat are used: radiation, convection, and conduction.
Types of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers are characterized by their structure, adaptability, tube type, type of fuel, and pressure output. When boilers were first developed, they were as efficient as current boilers but hazardous due to a lack of control systems. A boiler’s size, fuel, and dimensions fluctuate depending on the work it is meant to do and the industries in which it is utilized. The fuel power types include natural gas, fossil fuels, coal, electricity, and wood materials. The fuels differ in terms of cost, environmental friendliness, and efficiency. As the need for electricity and power generation has grown, alternative fuels such as biomass and garbage or trash have been created.
Electric Boilers
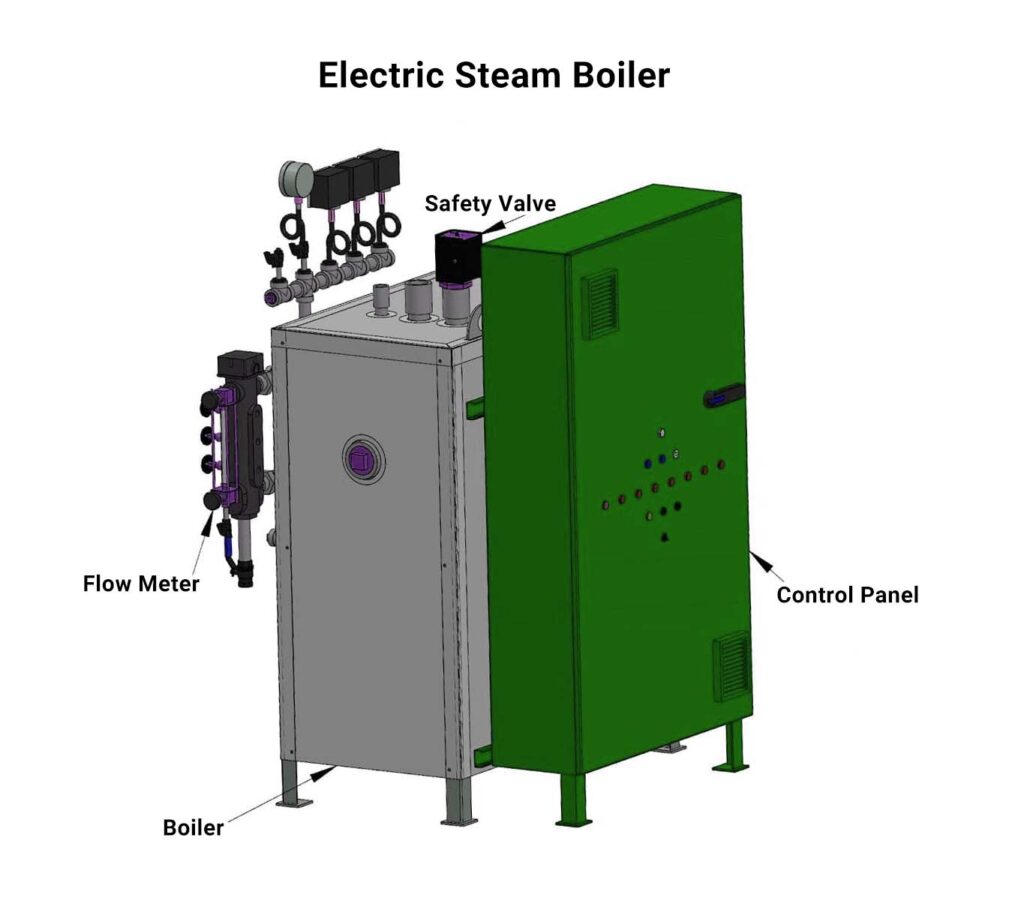

Electric boilers utilize electric components to create heat, it is a more efficient and fast technique of heating. It is an environmentally, cleaner solution since it does not require fuel combustion. Electric boilers are more durable, require less cleanup, and do not require regular maintenance. The only issue that must be managed with electric boilers is the accumulation of scale in the water storage tank.
Hot Water Boilers
Tanks that transmit heat to water that is circulated for heating purposes constitute hot water boilers. They are composed of stainless steel, cast iron, aluminum, and steel and are resistant to high temperatures and pressure.
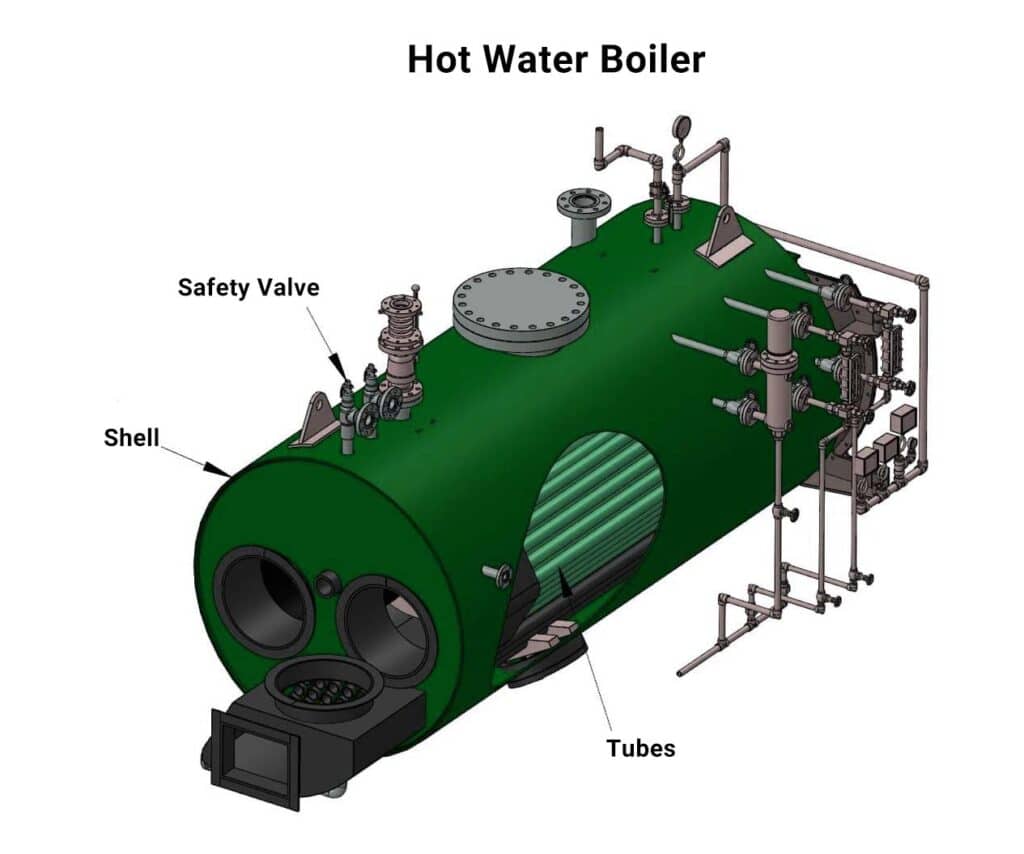
The varieties of hot water boilers are distinguished by their fire- or water-based tube systems. Fire tube hot water boilers consist of tubes filled with water; heat travels through the tubes and warms the water surrounding them. Water flows through the tubes of water tube boilers while the tubes are heated.
Gas Boilers
Natural gas or propane fuels gas steam boilers, which are more efficient than ordinary boilers. The fuel for a gas boiler is supplied from an external source that is directly linked to the boiler. The design of a gas steam boiler determines how heat is distributed. Gas steam boilers are applicable for industry and low-pressure applications.
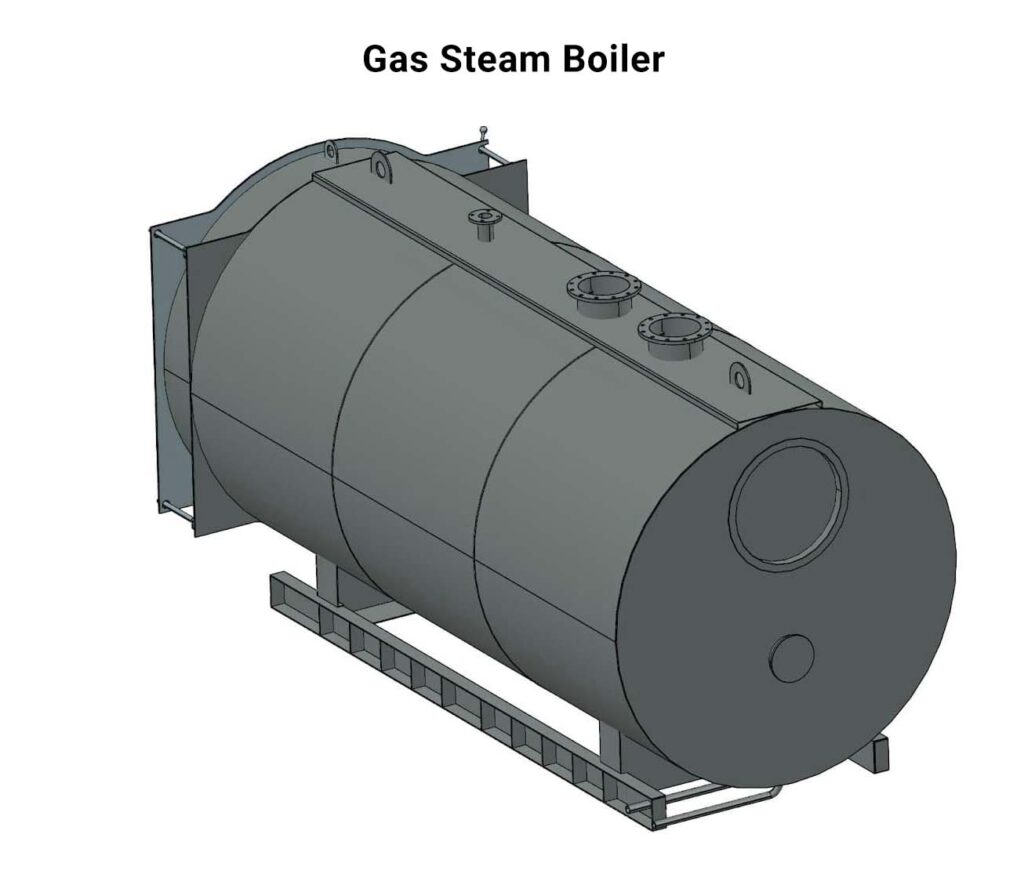

Oil Boilers
Oil steam boilers work similarly to gas boilers, only oil is fired in the combustion chamber rather than gas. The exchanger that warms the water is heated by the burning oil. Oil-fired steam boilers may achieve an efficiency of above 90 percent. Even though they are more expensive than gas steam boilers, they often last twice as long.
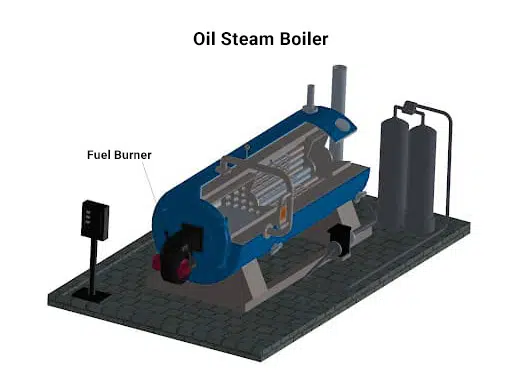
Concerning oil boilers, the necessity for an oil tank that must be supplied often to maintain a consistent fuel supply is a challenge.
Low Pressure Boilers
Low pressure steam boilers transmit heat at pressures between 10 and 15 psi and 149 degrees Celsius (300 degrees Fahrenheit). This type of boiler is utilized when sudden temperature changes are not necessary and a constant temperature is desired. Low pressure steam boilers are quite popular because they can supply steam considerably more quickly than high pressure steam boilers.

High Pressure Boilers
High pressure steam boilers generate extreme pressure to drive machinery and equipment. The strength and power of a high pressure steam boiler are generated by a pump that delivers high-pressure steam into the circulation system. To be considered a high pressure steam boiler, a boiler must be capable of producing pressures between 15 psi and 800 psi at temperatures above 121°C (250°F).

The pressure and temperature of high-pressure steam boilers are routinely checked to ensure their safety and efficiency. The high pressure loads of high pressure steam boilers are categorized as batch or continuous, with batch loads serving short-term needs and continuous loads serving long-term needs.
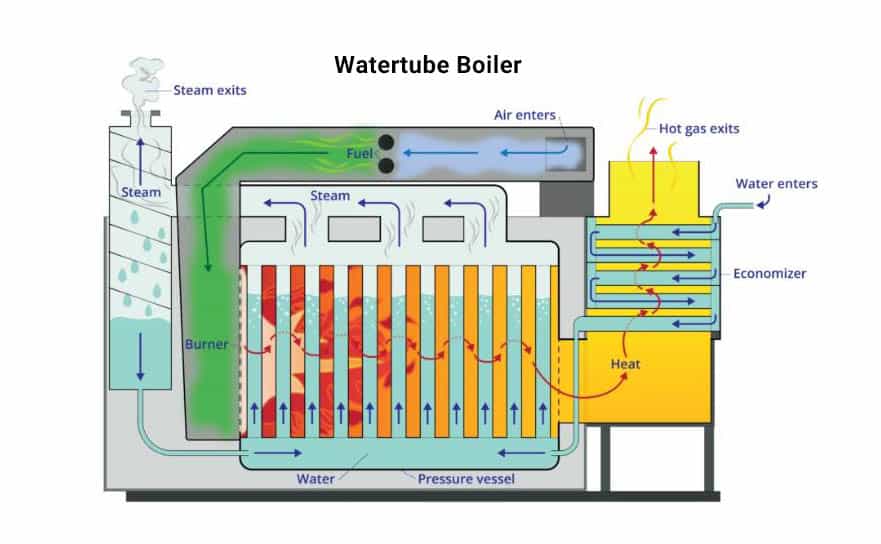
Watertube Boilers
Water tube boilers circulate water via the boiler’s tubes. The combustion chamber generates a fire that encircles the tubes and warms them, so heating the water. This boiler design generates high-pressure steam by the tangential pressure in the tubes, also known as hoop stress, this pressure is applied to the circumference of the tubes, similar to the pressure exerted on the bands of a wood barrel as it is filled.
Various varieties of water tube boilers have been in use since the invention of the first boiler, although their design has evolved progressively through the years.
Benson Boilers, Loeffler Boilers, and La Mont Boilers
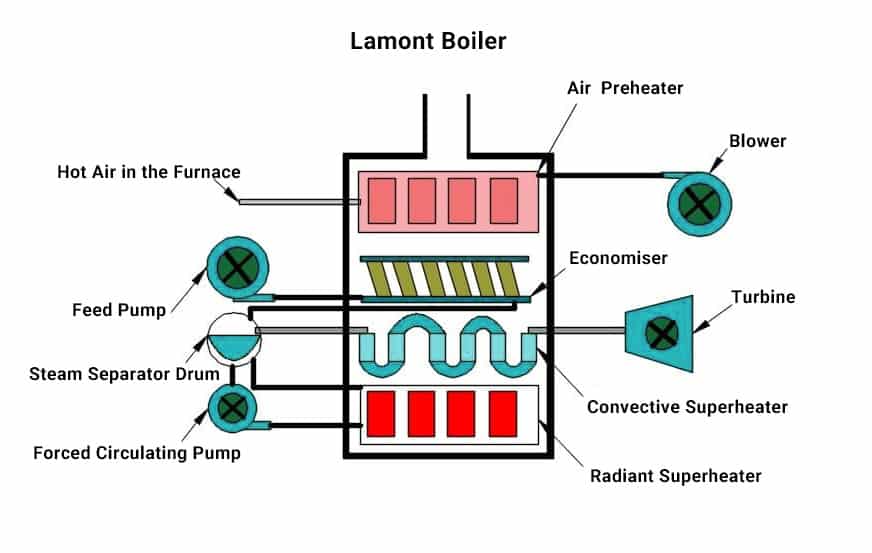
Steam boilers made by La Mont, Benson, and Loeffler create enormous amounts of steam with excellent efficiency by using forced circulation and draught fans. Water is pushed through small-diameter, closely-spaced tubes by a centrifugal pump. The economizer, which uses the flue or exhaust gases from the combustion chamber to warm the water, is what gives a La Mont, Benson, and Loeffler their efficiency.
Firetube Boilers
In a fire tube steam boiler, water flows through the boiler’s heated tubes. Inside the tubes, coal or oil-heated gases generate heat, which is transmitted to the water by thermal conduction to make steam. Low-pressure steam is produced by fire tube steam boilers. Cochran, locomotive, and Lancashire are the three primary kinds of fire tube steam boilers.
An economizer can be added to a fire tube steam boiler to improve its efficiency and heat recovery system.
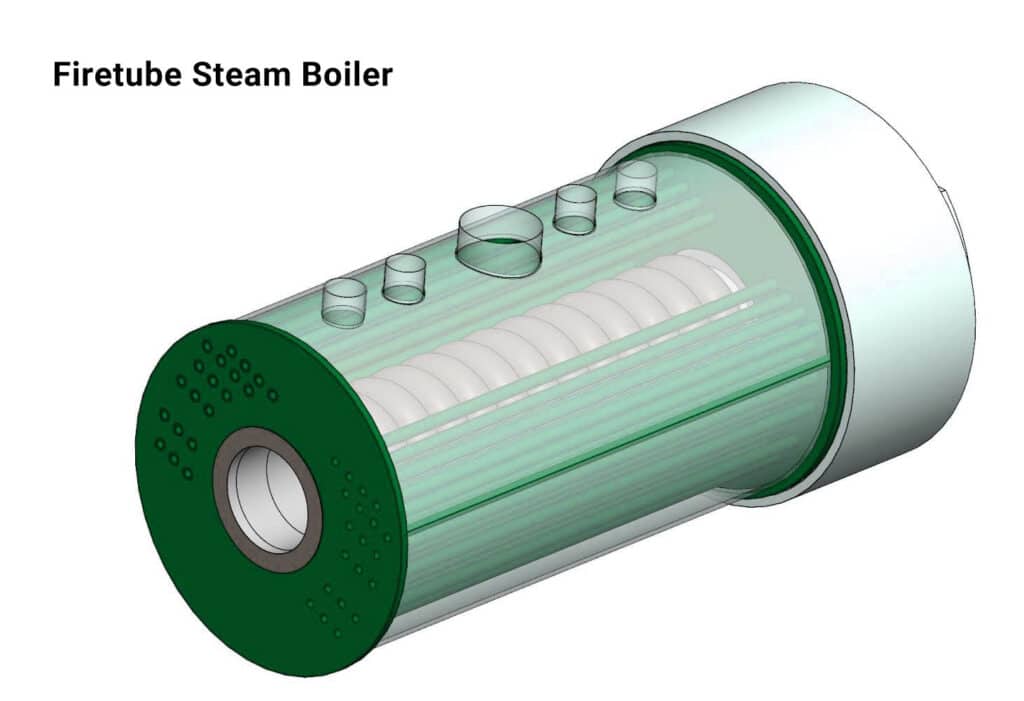

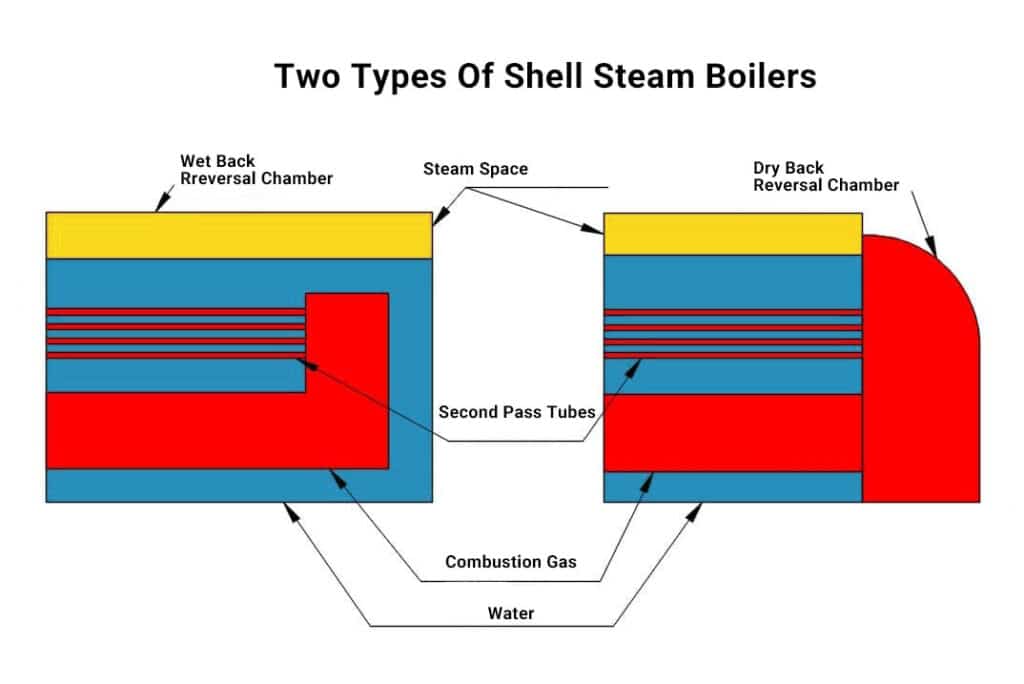
Shell Boilers
Shell boilers have a shell, which is often composed of steel, around their heat transmission surfaces. The number of passes heat makes before being expelled depends on the mix of tube layouts utilized. Flue boilers commonly referred to as shell boilers, contain lengthy water tanks with fire tubes. These fire tubes transfer heat from the furnace or combustion chamber to the water.
The Cornish boiler was the oldest example of this sort of boiler. It was a long cylinder with a single, sizable flue or pipe that held the heat or fire. The Lancashire steam boiler, which had two fire flues, took its place.
The simplest type of boiler that produces steam effectively and affordably is a shell steam boiler, sometimes referred to as a shell and tube boiler.
Techniques for Heating a Boiler
The heat emitted by burning is absorbed by a steam boiler. Either radiation, convection, or conduction is used to move heat. The kind of steam, fuel, and transfer surface all affect how much heat is transmitted.
Radiation
The energy that all substances and elements emit is radiation. It is the ongoing transfer of energy utilizing electromagnetic waves between surfaces. When a steam boiler is used, the flame created in the combustion chamber radiates heat into the boiler’s tubes. The rate at which electromagnetic waves are absorbed determines the amount of heat produced by radiation heating.
Convection
When a liquid or gas is heated, convection occurs, which is the transport of heat inside the heated liquid or gas. As the heated liquid or gas combines with the colder liquid or gas, it warms it as well. When a steam boiler’s fluid is heated, it loses density and becomes lighter, which triggers the convection process. As the lighter hot fluid or gas goes out, heavier, colder fluids or air move in. The process starts afresh when hot fluids are swapped out for cold ones.
Conduction
Heat is transported from one surface to another by physical contact known as conduction. When a metal is heated, the heated object it touches is also heated. In a steam boiler, conduction occurs when heat is transferred from the heated outside portion of the tubing to the warm interior and the cool water within.
The Operation of Steam Boilers
Steam boilers use combustible fuel to boil water, which produces pressurized steam power.
Depending on whether the boiler is a firetube or watertube, the water is heated differently. Their names reveal the main difference between the two.
- Watertube Boiler
In a watertube boiler, water is contained within a number of tubes, and steam is produced by transferring heat from the combustible fuel source to the tubes’ outer surfaces.
- Firetube Boiler
In a firetube boiler, the combustible fuel source is contained inside a tube that is surrounded by a water-filled vessel. As the water around the tube gradually heats up, steam is eventually produced.
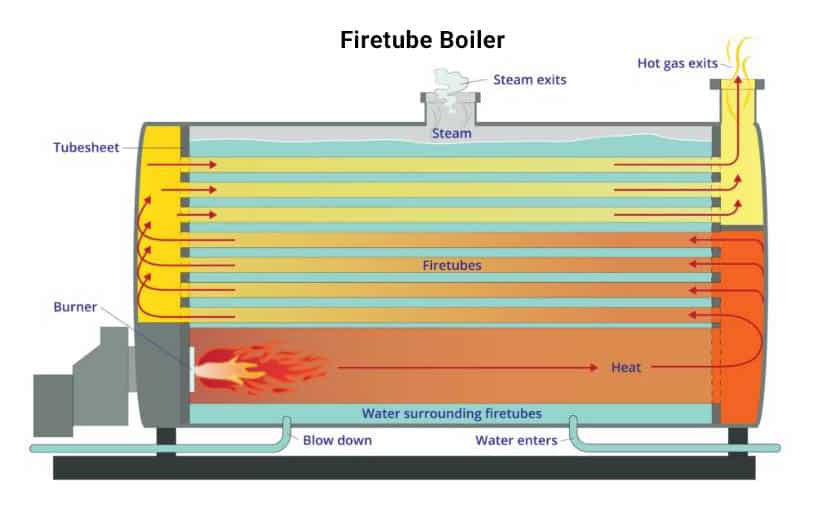
The Structure of the Boiler System
- Pressure vessel: A pressure vessel is a container for gases or liquids that are kept at a high temperature and pressure. The pressure vessel of a boiler is made of a very durable material, frequently steel.
- Burner: The burner burns fuel and oxygen to provide heat for the boiler. Natural gas, low-pressure propane, No2 oil, coal, and other fuels are examples of fuel sources.
- Tube: Water is heated outside and is contained inside metal tubes found inside watertube boilers. Firetube boilers use hot gas to heat the water around the tubes as it goes through one or more of them.
- Economizer: A heat exchange device known as an economizer transfers thermal energy that would otherwise be wasted in exhaust gasses and uses it to warm the water entering the boiler. As a result, the boiler is more efficient since less extra energy is needed to heat the incoming water.
- Deaerator Tank: Deaerators are heated, pressured feedwater tanks that remove dissolved gases, including carbon dioxide, from the water that is supplied into the boiler. Otherwise, the boiler might experience significant damage from dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Heat Exchanger: Without the two materials physically interacting, a heat exchanger transmits heat from one to the other. In a boiler, a heat exchanger transfers heat from the hot gas to the water.
- Operators may adjust boiler parameters including pressure and temperature using the control panel. Control panels for commercial and industrial boilers come with in-depth analytics.
- Feedwater Tank: The boiler uses the water in the feedwater tank to produce steam. It is a collection tank. The cleaned water is gathered in the feedwater tank before being piped into the boiler. The feedwater tank is used to inject and mix boiler chemicals that eliminate oxygen and safeguard the metals inside the boiler. Condensate water from steam that condenses below the boiler point can be collected in facilities with condensate return lines and fed back into the system to recover the treated water.
- Burning Process: In order to generate heat, the combustion system first mixes the fuel and air. An essential part of the boiler combustion system is ensuring the proper air to fuel ratio.
- System for reverse osmosis:
- Reverse osmosis works by applying increased pressure to the raw water side of the RO and forcing the water past the semi-permeable RO membrane, leaving nearly all (about 95% to 99%) of the dissolved contaminants in the reject stream.
- Chemical Monitoring Systems: Carefully regulated chemical addition can improve a boiler’s performance. Chemical monitoring systems enable accurate level monitoring and continuous analysis.
- Types of Fuel The heat produced by the boiler is ultimately obtained from burning fuel. Coal, gas, and oil are frequently used fuels. To increase efficiency, coal is frequently heated and pulverized before use. Biomass, such as wood chips or other natural resources, may be utilized less often.
- Water Treatment: To increase the lifespan of the boilers, the water that they utilize must be treated before entering the boiler. By eliminating dissolved particles like calcium and magnesium, water softeners and reverse osmosis systems assist in water preparation by lowering the likelihood of scale buildup inside the boiler. Feedwater tanks are also involved in the water treatment process since they employ heat to lessen the amount of dissolved gases that might cause the boiler to oxidize and corrode.
Firetube Boilers vs. Watertube Boilers
Firetube boilers and watertube boilers are the two primary types of boilers you will find on the market today, as was previously discussed. Let’s examine each type’s operation in more detail.
Firetube Boilers
In firetube boilers, a flame travels through a closed tube. The ambient gas is warmed by the flame. The water within the vessel is heated to the degree to which steam is created as a result of the heat being passed through the tube walls.
The history of firetube boilers is extensive. They did after all power some of the first steam locomotives in history. More industrial operations are switching to watertube boilers for increased safety and efficiency due to the enormous stored pressure and inherent inefficiencies.
Watertube Boilers
A furnace warms the gas that passes through tubes carrying water in watertube boilers. The heat is passed via the tube walls, heating the water within the tubes to generate steam. Typically, watertube boilers can generate far more pressure than firetube boilers.
As watertube boilers do not encapsulate huge quantities of water, they pose a lower inherent danger than firetube boilers. In addition to being more efficient, watertube boilers are favored for intense industrial processes.
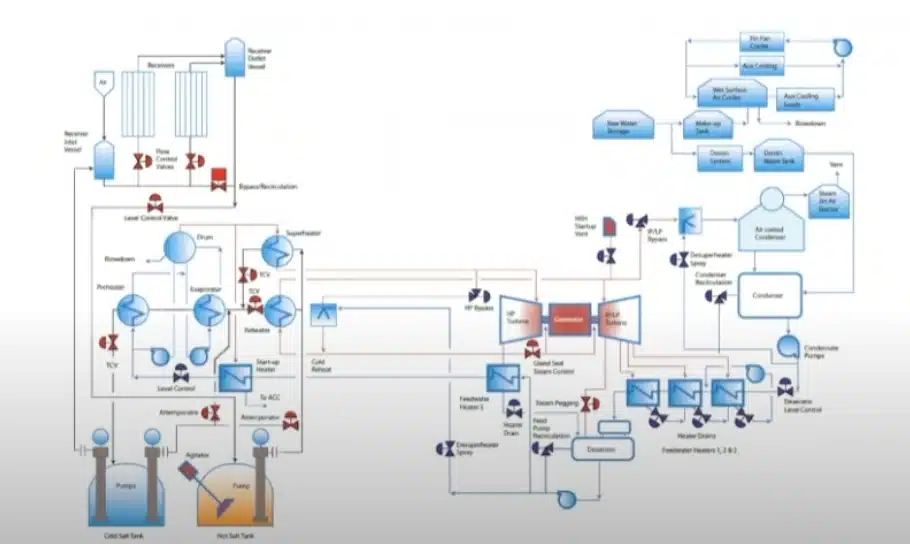
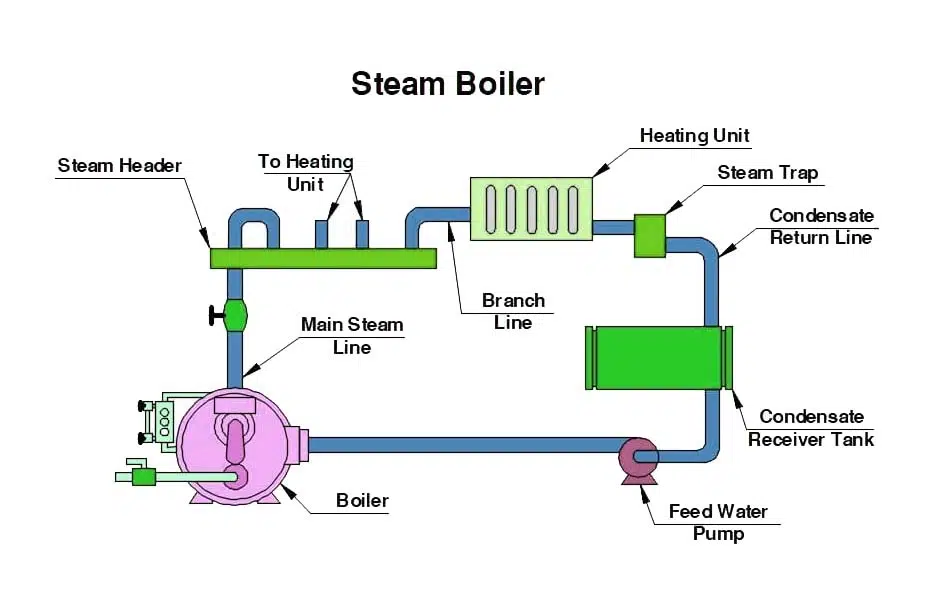
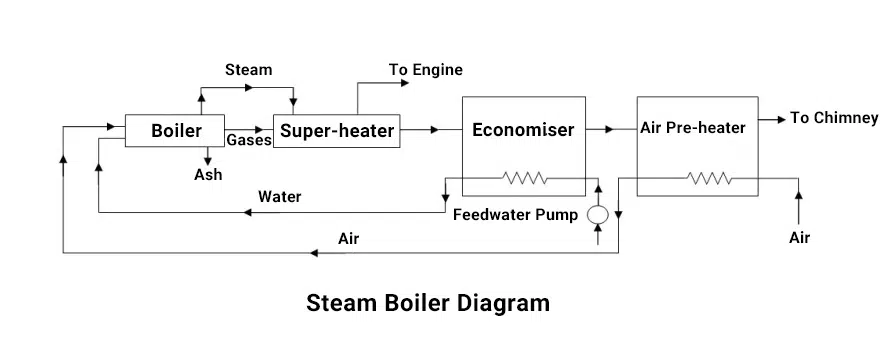
Steam Boiler Diagram
A steam boiler is a closed vessel in which water and fuel are burned to create steam. The steam must be delivered securely and in the desired condition (as regard its pressure, temperature, quality and required rate).
What Is The Difference Between Hot Water Boiler And Steam Boiler?
A steam boiler warms water similarly to a teapot, but on a bigger and more intricate scale. Despite the fact that no two steam boilers are identical, they all share the following elements: burner, heat exchanger, steam temperature control, combustion chamber, expansion tank, low water cutoff, and safety relief valve.
Hot water heaters are more basic than steam boilers. They just have one job, which is to heat water. Water is frequently heated with heating rods while being kept in a tank. Instead of requiring a storage tank, instant water heaters quickly warm water.
The designs and types of steam boilers vary greatly based on their construction and intended use.
List Parts of Steam Boilers
A Steam Boiler consists of the following vital pieces (Mountings and Accessories) for its correct and secure operation:
- Burner
Air and fuel are injected into the combustion region via the burner. Fuels need to combine with air easily, such as oil, gas, or finely ground coal. The amount of air that enters the burner is controlled via dampers. The air is distributed uniformly around the burner by an impeller. An igniter lights the fuel that is injected into the boiler using pipes known as spuds.
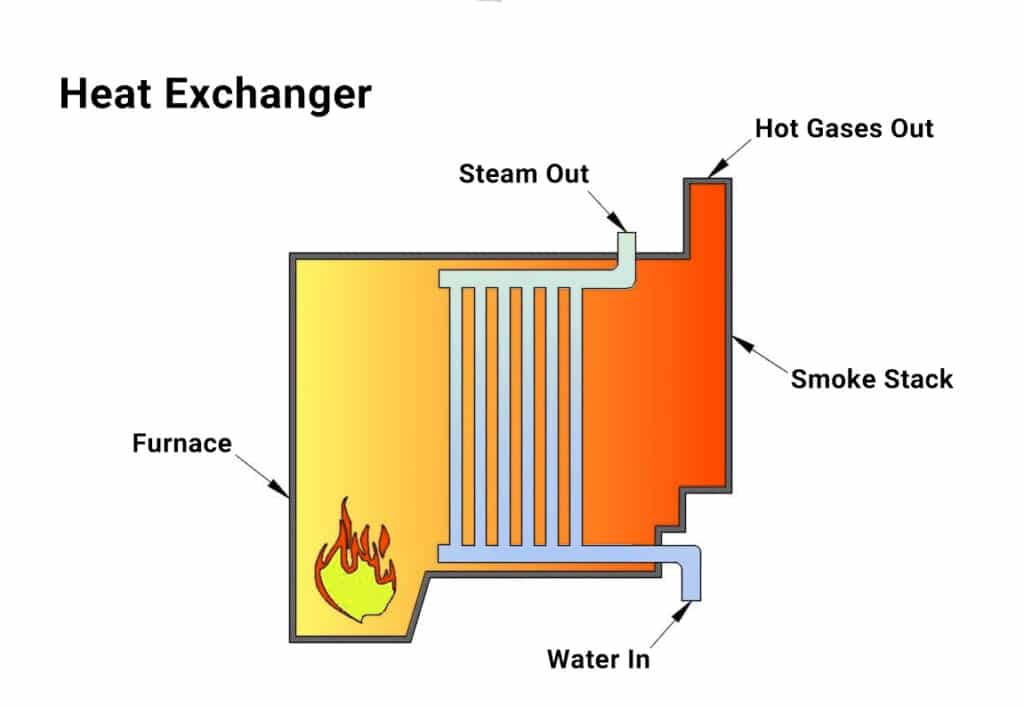
- Heat Exchanger
The heat exchanger prevents the fluids from mixing while allowing for the exchange of heat. In a heat exchanger, the fluid to be heated is submerged in a long, coiled pipe. Through the pipe, gas or a hot liquid warms the water nearby. The ideal material for heat exchangers is stainless steel since it won’t corrode or rust. However, heat exchangers may be formed of a number of materials.
- Steam Temperature Control
Thermal stress may be avoided by carefully controlling the temperature of the steam. In order to reduce fuel expenses, pressure and temperature control are required. Water jets are often used to regulate steam temperature on the first and second-stage superheaters. This is accomplished with the use of an attemperator or desuperheater.
Flue gas bypass, circulation, and the angle at which the burners fire the furnace are other ways to regulate steam temperature. The easiest way to regulate steam temperature is to keep an eye on the steam’s temperature as it leaves the boiler and adjusts the spray water valve.
- Combustion Chamber
The combustion chamber holds the fuel and air interaction and utilizes the heat produced to make steam. The combustion chamber must be suitably insulated to prevent heat loss through radiation in order to increase efficiency. The open box with the burner and controls and the combustion chamber are connected by tubes that carry steam and water. Boiler functioning depends heavily on efficient combustion. The surface of the boiler at the top of the combustion chamber absorbs the heat generated in the combustion chamber.
- Expansion Tank
By providing a space for water to expand, absorb pressure, and control pressure, the expansion tank aids in maintaining the pressure in a boiler. A diaphragm in the tank is separated into two portions, one of which receives water from the boiler and the other of which is controlled by an air valve to release pressure. When the pressure returns to normal, the air valve pushes against the water in the opposite part.
- Low Water Cutoff
When the water level falls below a certain level, a low water cutoff turns off the burner or cuts off fuel to a steam boiler. A dry fired boiler is susceptible to rupture or serious failure. A steam boiler’s low water cutoffs are yet another safety element that helps protect the boiler from danger and damage. They are often used in steam boilers and hydronic devices to shut down the boiler in the event of a water loss and are a standard component of boiler construction.
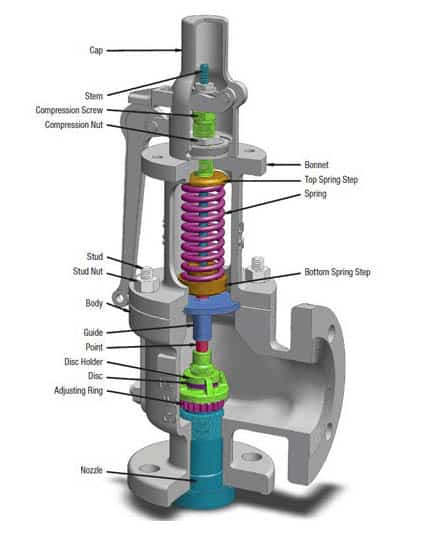
For usage with steam boilers, the pressure release valve is the most crucial safety feature. It guarantees that the pressure that has built up in a steam boiler will be released; this helps prevent a catastrophic accident. Once the pressure has returned to normal, the pressure relief valve closes. It opens when the pressure exceeds a critical level.

Steam Boiler Applications
There are several domestic, commercial, and industrial uses for steam boilers.
The lowest capacity is often found in boilers made for household and commercial usage. They are appropriate for usage in more compact structures and facilities that don’t need a lot of steam power.
Many industrial activities that demand more horsepower may be handled by industrial boilers. Hospitals, university campuses, chemical companies, breweries, food processing facilities, and manufacturing enterprises are just a few places where you might find industrial boilers. Steam is used in car manufacturing facilities to vulcanize rubber for tires and other uses.
Numerous operations in food manufacture and brewing involve steam, including direct food production and equipment and container sterilization. In order to pasteurize food and assure food safety, high-temperature steam is also employed.
Typical Applications
Steam boilers’ typical duty is to provide central heating for homes, offices, enterprises, hospitals, and other buildings. All boilers, regardless of where they are utilized, have the same basic functions and mechanics that act as a confined heat generating combustion process.
A number of fuels are utilized to create heat in a boiler and light the burner. Pumps and heat exchangers transport the generated heat throughout the system. Additional control mechanisms are added to a steam boiler to specialize its function.
- Aquariums
The functioning aquariums are powered by steam boilers. To safeguard the large variety of species on exhibit, the water temperature and water conditions in the aquarium’s various tanks must be properly managed. Gas-powered steam boilers are used in conjunction with heat exchangers to control fresh and saltwater tanks, as well as to generate water currents and surges to simulate ocean conditions.
- Laboratories
Exhaust air is used in college labs for experimentation and testing. Experimenters bring in outside air to replenish the expended air, which might be chilly, necessitating heating. Because laboratories are vast and expansive, they require a huge quantity of heat to heat them. Universities and colleges employ low pressure steam boilers to satisfy the demand.
- Beverages and Food
Products must be heated to certain temperatures during pasteurization in order to kill germs. The flavor of the finished product may suffer if the temperature is not perfectly regulated. Low pressure steam heat is used by brewers and distillers to create reliable batches at a reasonable price. Steam boilers are used by dairy farmers to clean and sanitize their facilities.
- Skyscrapers
It need a powerful energy generation system that can survive continuous use to heat multi-story structures. Skyscrapers are enormous structures that require a number of boilers to efficiently and properly heat them. Skyscraper steam boilers may weigh up to 165 tons and utilize 3000 liters of fuel every hour, which is sufficient to heat 2000 single-family homes.
Since it is simple to transport and always accessible, using water and steam to provide heat for skyscrapers is a very practical and efficient strategy.
- Brewing
Large kettles are used to brew beer, and the kettles are heated and sterilized using steam boilers. The kettles must be thoroughly cleaned and sanitized once the brewing cycle is ended to guarantee that all pollutants are eliminated. The sort of boiler that will be used to maintain the kettles clean and functional is the first factor to be taken into account when designing a brewery.
The leftover grain from the brewing process can be used as steam boiler fuel. It is both an economical and environmentally smart idea.
- Power Generation
A steam boiler’s ability to drive turbines to generate energy is one of its uses. At 900 psi, a large, powerful boiler may produce up to 225,000 pounds of steam per hour. Such a boiler system is capable of producing 20 megawatts of power. Steam boilers may be created using technological advancements and inventions that conserve energy while creating it.
- Lumber Kilns
In the lumber industry, low pressure steam boilers are employed in the kilns that are used to dry specialty lumber products. Kiln drying is necessary for cooking with cedar boards and hard timbers used in furniture construction. To improve the quality of wood goods, companies can dry their products in a safe and efficient manner using a low pressure steam boiler. Low pressure steam heat is perfect for this kind of drying procedure since it is controllable and remarkably constant.
Hot Water Heaters, Boilers, and Furnaces
Furnaces, hot water heaters, and boilers all generate heat, but their structure and operation differ. Let’s explore the variations:
Steam is produced by boiling water in a pressured container. For a variety of commercial and industrial uses, many facilities may set a steam pressure that directly correlates to a steam temperature that can be modified. Domestic central heating systems may effectively heat a home by distributing steam to radiators. The complexity and design of boilers vary according to the use for which they are intended.
Hot water heaters are more basic than boilers. They just have one job, which is to heat water. Water is frequently heated with heating rods while being kept in a tank. Instead of requiring a storage tank, instant water heaters quickly warm water.
Furnaces warm the air that flows through a house or structure, not the water. The air is heated before it is distributed via a series of vents by a heat exchanger that is warmed by the burning of fuel. A thermostat is used to manage the furnace’s temperature.
Conclusion
From this article, we learned that a steam boiler is a heating system that produces steam, which generates energy by heating water to produce steam. A steam boiler heats water by burning fuel. A steam boiler is defined by its construction, portability, type of piping, type of fuel, and pressure generated. Steam boilers absorb the heat released by combustion. The three modes of heat transfer are radiation, convection, and conduction. The design and type of steam boilers vary greatly depending on their construction and use, among other information. THINKTANK is a Taiwan family company specializing in manufacture valves for Top 10 boiler manufacturers in China. If you need industrial valves such as on/off valves, control valves, safety valves, etc., please just feel free to contact us for a free consultation.