What is a Blowdown Valve (BDV)
The blowdown valve is used to keep the boiler water level rise within the desired limits during a rapid start-up of a high-pressure system. Increased pressure causes an increase in flow speed, which can lead to metal surface straining and cavitation. The valve must also withstand the corrosive environment created by boiler pickling, as well as potential wear problems caused by precipitated solids. Therefore the internal design structure of the drain valve must be effective in preventing related problems.
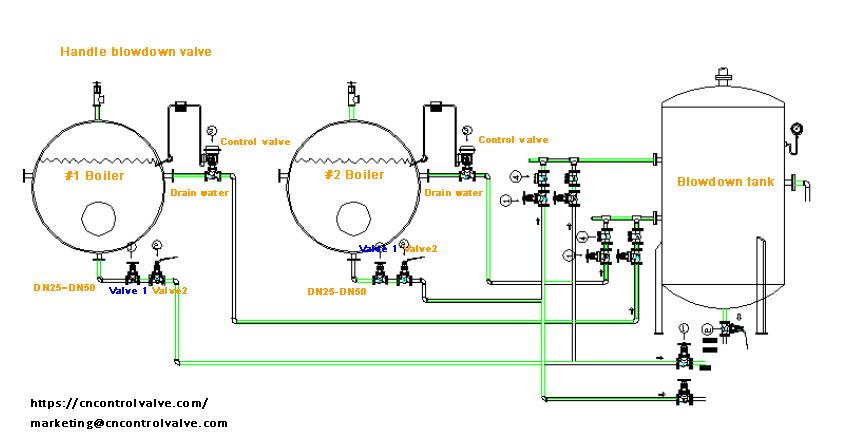
Manual/Handle Blowdown Valves




Automatic Blowdown Valves
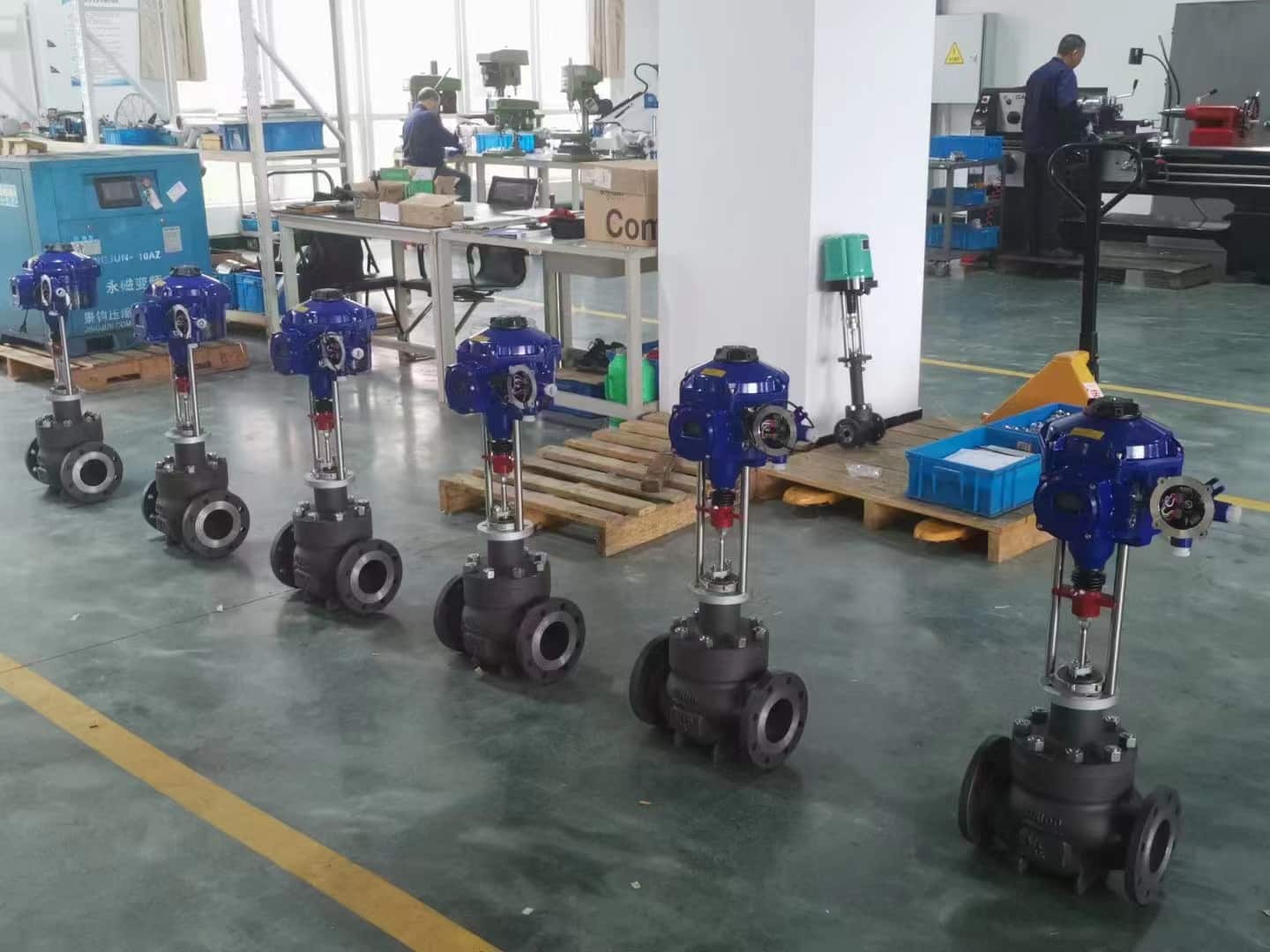
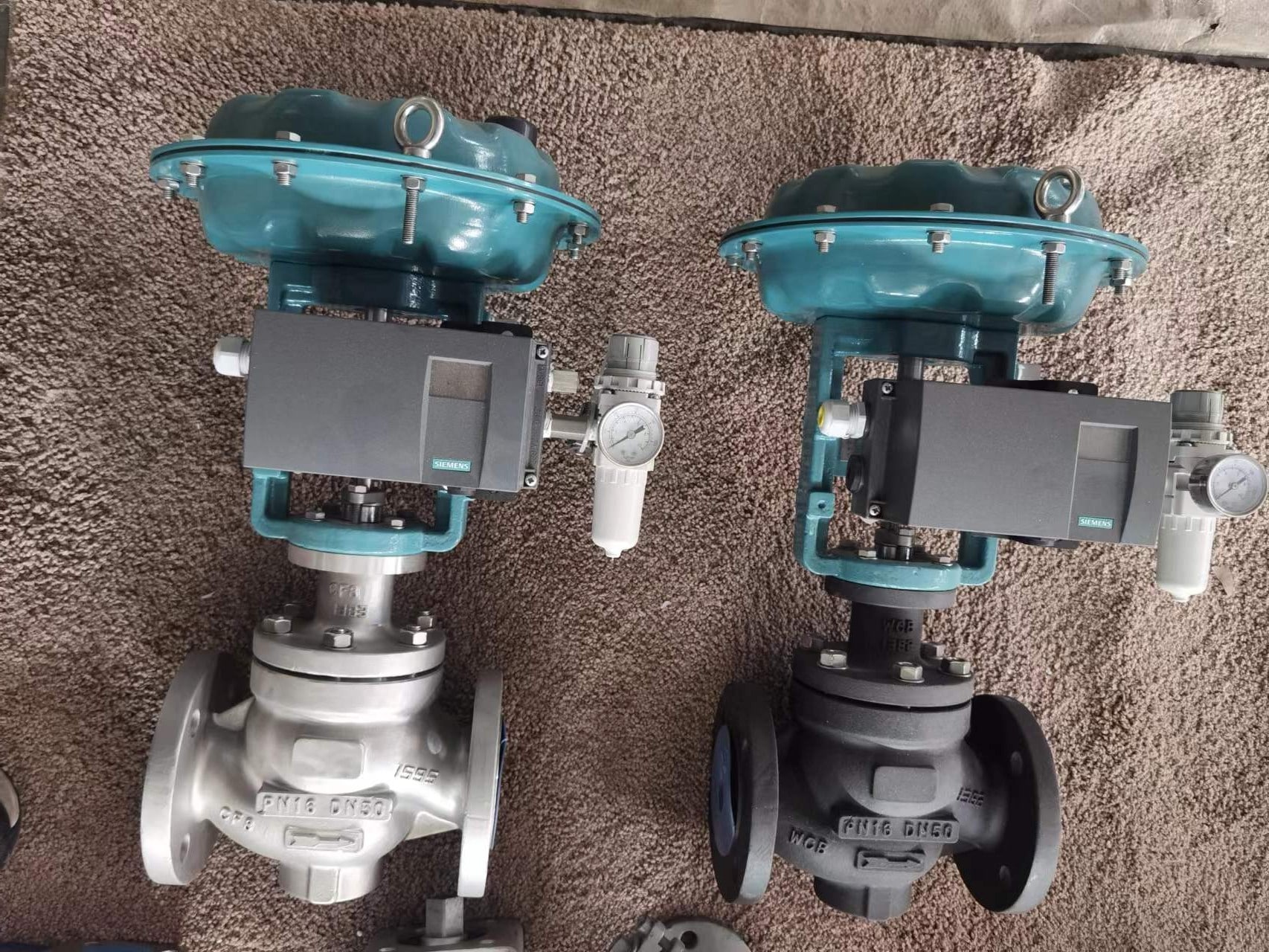
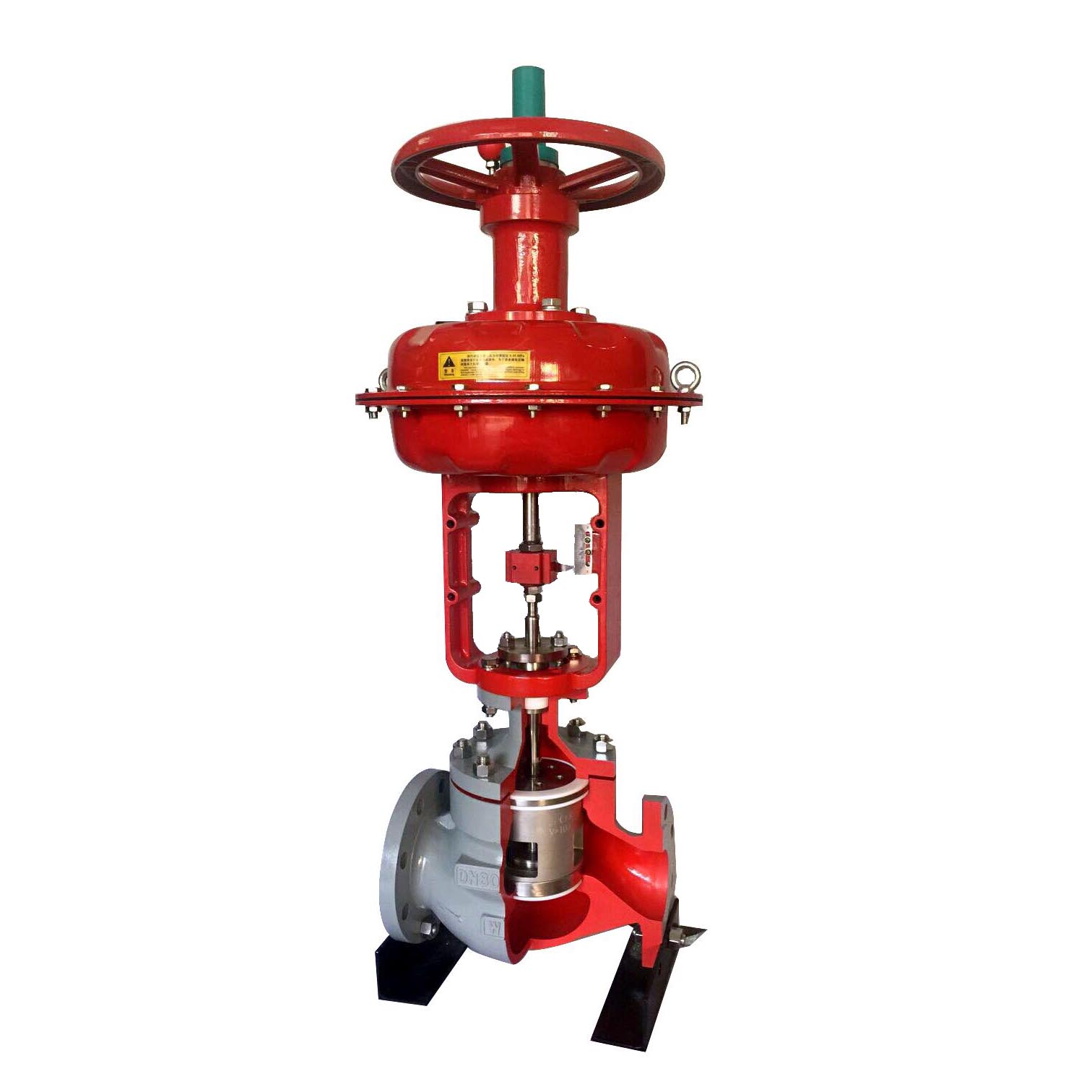




What is the Purpose of a Blowdown Valve
The primary purpose of a blowdown valve is to regulate a constant flow of steam/fluid at an elevated differential pressure and also to remove dirt, sediment, and limescale.
What are the Types of Blowdown Valves
Blowdown valves are used either continuously or intermittently depending on the service requirements and play an important role in fossil fuel boilers to remove dissolved solids from the boiler water. Generally, only one blowdown valve is used in a boiler. If more than one blowdown valve is used in a boiler, the two valves are often used in series to minimize erosion. In this design, one valve acts as the shutoff valve, and the other valve acts as the drain valve. The shutoff valve is usually opened first and closed last. To minimize erosion of the disc and seat, both valves are opened quickly and simultaneously. Most importantly, care should be taken to avoid trapping rust particles in the valve during the drainage process. This is accomplished by opening the valves again so that any remaining rust particles are flushed out with the next passage of steam through the piping. Whenever a boiler is taken out of service for maintenance, the bottom drain valve is usually rebuilt or replaced.
Generally, we classify blowdown valves into two categories, continuous blowdown(CBD) valves, and intermittent blowdown (IBD) valves, since the intermittent blowdown valve works close to the bottom of the boiler, we also call it a bottom blowdown valve.
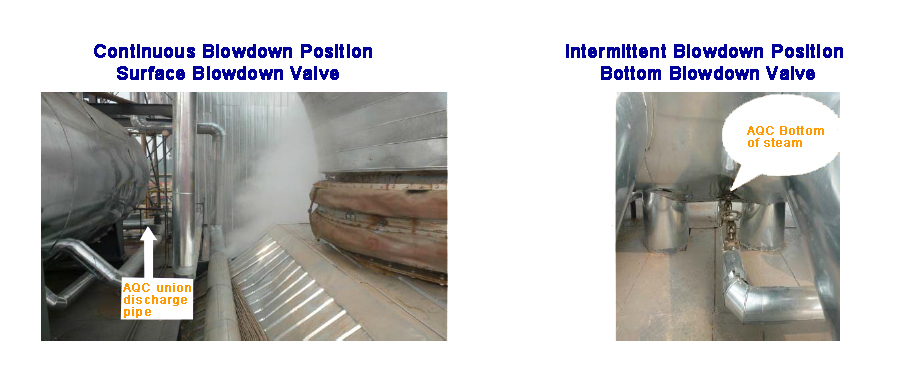
Continuous Blowdown(CBD) Valves | Surface Blowdown Valve
The continuous blowdown valve (CBD) is designed to operate in a constant open position to maintain the TDS level in the boiler ladle by continuously releasing water from the boiler water surface through the blowdown tap. Some engineers also name this valve a surface blowdown valve.
Intermittent Blowdown (IBD) Valves | Bottom Blowdown Valve
The purpose of the bottom blowdown valve is to remove boiler sediment to keep the boiler water in compliance with manufacturing standards to improve the efficiency and performance of the boiler.
The function of the intermittent blowdown valve is to release accumulated sludge and sewage through a drain near the bottom of the boiler at regular periods, usually with a predetermined time cycle. There is a special requirement for the bottom blowdown valve to ensure that the valve can be tightly closed after repeated draining actions.
Blowdown Valve for Boiler
In boiler operation, the deposition of impurities is highest at the point where liquid water is converted to steam. The resulting scale forms an insulating layer, impeding the flow of heat through the equipment. As the thickness of the formed scale increases, the rate of steam generation decreases, as does the rate of heat flow. In addition, due to the accumulation of heat, the temperature of the metal surface may increase to the point where the metal surface itself may be damaged. Generally, drain valves are installed on equipment in processes where the working fluid is water. If the water contains solid impurities and some of the water continues to evaporate through some mechanism, such as drafting in a cooling tower or vaporization in a boiler, then the concentration of solid impurities in other water that accumulates in the equipment increases. Drain valves are used to drain a certain amount of liquid from equipment that contains solid impurities that by their nature are insoluble in the working fluid and may be deposited on the surface of the equipment, causing problems with the operation of the equipment.
Why Use Blowdown Valve for Boiler
If the water in the boiler is not well treated in the preparation stage, the density of insoluble substances (TDS) will increase due to steam generation. If the determined limit is exceeded, it can cause damage to the boiler and piping, and eventually lead to equipment failure. Insoluble materials are carried along with steam, and they can increase the conductivity of condensate and cause energy loss. Insoluble materials typically include calcium and magnesium salts, and these insoluble substances are deposited during the steam production process, and we need to remove them through a number of techniques to achieve optimum TDS levels. This operation is known as blowdown, and the valve used for this purpose is known as a blowdown valve.
Advantages of Blowdown Valve
- Productivity is increased by reducing equipment downtime that may periodically occur due to sediment deposits.
- Can be operated automatically or manually. Both automated remote operation and in-situ manual operation are easily possible.
- Simple design, easy maintenance, and low maintenance costs.
Bottom Blowdown Valve Design For Boiler Room
What is the Drainage Process for the Boiler
In order to control the water quality of boiler furnace water to meet the prescribed standards, so that the impurities in the furnace water to maintain within a certain limit, the need to constantly exclude the furnace water containing salt or alkali from the boiler, as well as water slag, sludge, and other sediments, this process is the boiler drainage. The drainage process is an important part of the boiler water quality management, the purpose is to make the boiler system achieve safe operation, reduce consumption and save energy.
Blowdown Methods
Boiler blowdown can be classified as regular blowdown and continuous blowdown.
- Regular blowdown: Also called intermittent blowdown or bottom blowdown, its function is to remove the water slag and soft sediment formed by phosphate treatment accumulated in the lower part of the boiler. Regular blowdown lasts for a short time but has a high ability to discharge the sediment in the boiler. The regular drain is usually set at the lower part of the boiler barrel and the bottom of the union box, and the regular drains should be selected when the boiler is in high water level or low load condition. In small boilers, only periodic discharge is usually installed.
- Continuous blowdown: Also called surface blowdown, it is a continuous process of draining the most concentrated furnace water from the surface layer of the steam ladle furnace water. The purpose is to reduce the salinity and alkalinity of the boiler water to prevent the concentration of the furnace water from being too high and affecting the quality of steam. Continuous drain is generally installed in the steam ladle normal water level (i.e. “0” level) 80-100mm below. Furnace water is continuously evaporated and concentrated so that the highest concentration of salt is near the water surface. Therefore, the continuous drainage orifice should be installed in the area with the highest density of furnace water, in order to continuously discharge high-density furnace water and supplement it with clean feed water, so as to improve the quality of boiler water, and the drainage rate is generally about 1% of the evaporation volume.
Boiler Bottom Drain Device
The boiler drainage device refers to the drainage pipe within the boiler body, blowdown valve, and internal blowdown conduit of the boiler barrel.
The drain valve usually uses a gate valve or globe valve. The nominal diameter of the drain valve is DN25~50, rated evaporation ≥1t/h or working pressure ≥0.7Mpa boiler, the drain pipe should be installed with two drain valves in series.
The traditional design is a combination of 1 slow drain (with gate valve) + 1 fast drain (high-temperature ball valve), but due to the PTFE soft seal inside the ball valve, the valve seat is easily deformed by aging due to the long-term high temperature above 140℃, which eventually leads to valve leakage. And the gate valve sealing groove is easy to accumulate impurities, the gate does not close tightly and leaks. So this design service life is short.
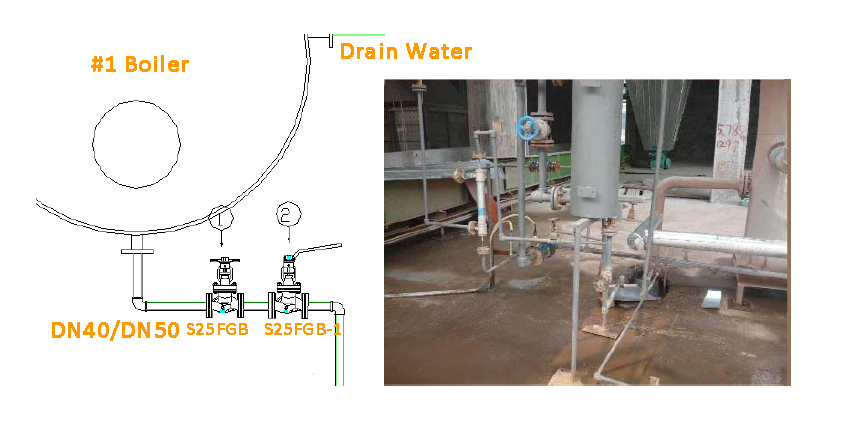
Solution
Use one slow discharge (with bellows shut off globe valve S25FGB) + one fast discharge (quick-opening bellows shut-off valve S25F). The quick opening bellows globe valve S25FGB-1 is a special replacement for the high-temperature ball valve.
Advantages
- The switch is fast and convenient, only needs to make within 180 ℃ rotation, you can achieve from fully open to fully closed or fully closed to fully open, and the sealing performance of the globe valve, as well as the quick switching performance of the ball valve.
- Solve the problem of the traditional quick opening valve stem easily bending then cause to leakage.
Serial Drain Valve Operation Procedure
When discharging, the blowdown valve is subjected to high-temperature liquid flushing and dirt wear and will be cooled to room temperature after it stops draining. In order to improve the drain valve’s frequent poor working conditions such as pressure difference (large differential pressure drop), scale corrosion and wear vibration, and thermal shock, the series drain valve has a certain operation procedure: when discharging, valve 1 (slow opening blowdown valve) is opened first, then valve 2 (quick opening blowdown valve) is opened; when stopping discharging, valve 2 is closed first, then valve 1 is closed.
Valve 1 is a slow-opening blowdown valve, which should have the ability to resist alkaline corrosion of furnace water; valve 2 is a fast-opening blowdown valve, which should meet the action and time requirements of drainage.
In Conclusion
THINKTANK is a reliable blowdown valve supplier, valve manufacturer and factory, with rich experience in replacing international brands for boiler manufacturers and end-users. If you have any related questions about blowdown valves, please feel free to contact us. We are here willing to provide expert service for you.