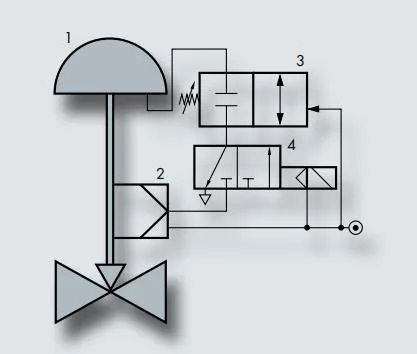
Valve accessories are key components that enhance valve function and performance in a variety of industrial, commercial and residential applications. Selecting the appropriate valve accessories is critical to ensuring the efficient operation, safety and longevity of your valve system. As a control valve manufacturing company, THINKTANK has rich practical experience in the selection of valve accessories. Through this article, we will share these professional selection skills, that is, common valve accessories and factors to consider when selecting them.
top valve accessories selection tips
When selecting valve accessories, it’s crucial to consider a range of factors that can influence the efficiency, safety, and functionality of your valve assembly. Here are some top tips to guide you through the selection process:
1. Understand the Valve’s Function: Before choosing accessories, it’s important to fully understand the primary function of the valve – whether it’s for isolating, regulating, or non-return purposes. This will impact the type of accessories required.
2. Know Your Process Conditions: The nature of the media (liquid, gas, corrosive, etc.), pressure, temperature, and flow rate are all vital considerations that can affect the compatibility and durability of the valve accessories.
3. Determine the Operation Mode: Decide if the valve will be operated manually or if it requires automatic operation. For automatic operations, you’ll need to select the appropriate actuators, solenoids, or positioners.
4. Select the Right Actuator: If the operation is automatic, choose between electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators based on the available power source and the required torque.
5. Consider the Control Type: For modulating valves, you may need smart positioners that can accurately control the valve position based on the input from the control system.
6. Look for Interoperability: Ensure the accessories are compatible with the valve’s make and model. They should also be easily integrable with your existing control systems.
7. Assess Environmental Conditions: The working environment of the valve can have a significant impact. Accessories must be able to withstand the ambient conditions, such as temperature extremes or corrosive atmospheres.
8. Safety Compliance: Valve accessories should meet all relevant safety and industry standards to ensure the safety of the operation and the longevity of the valve assembly.
9. Ease of Maintenance: Choose accessories that facilitate easy maintenance. This can reduce downtime and maintenance costs over the valve’s service life.
10. Consider Future Needs: Think about the potential for process changes in the future and select accessories that can accommodate such changes or upgrades.
11. Consult with Experts: When in doubt, it’s always best to consult with valve and accessory experts. Of course we, THINKTANK experts can offer free insights and recommendations based on our extensive experience.
12. Evaluate Total Cost of Ownership: While initial cost is important, also consider the long-term costs associated with energy use, maintenance, and the potential for expensive downtime if the valve fails.
13. Prioritize Quality: Investing in high-quality accessories from reputable manufacturers can save money in the long run due to their reliability and durability.
14. Look for Value-Added Features: Some accessories come with additional features like diagnostics or predictive maintenance capabilities, which can offer more value for your investment.
15. Keep Spare Parts on Hand: It’s wise to keep a stock of essential accessories and spare parts for critical valve assemblies to minimize potential downtime.
Top 15 Selection Tips For Pneumatic Actuator
| NO. | Parameter Classification | Option | Description |
| 1 | Description of the pneumatic actuator by the client | 1) Diaphragm type 2) Cylinder type 3) Special type | Generally, clients will provide a clear description. If there is no clear description, choose based on experience or commonly used products. |
| 2 | What action type of pneumatic actuator is used for | 1) Single-acting cylinder; 2) Double-acting cylinder; 3) Special type cylinder. | The action type of the pneumatic actuator must be clearly described for accurate selection in the next step. |
| 3 | Brand requirement (Here for quarter-turn actuators) | 1) Manufacturer’s choice (preferably their own product); 2) Bettis / BIFFI; 3) Rotork; 4) Limitorque; 5) Other specified brands, such as Pro-control, Neles, etc. | This should be chosen based on actual request. |
| 4 | Selection of air supply pressure | 1) 2bar 2) 3 bar 3) 4 bar 4) 5 bar 5) 6 bar | For diaphragms type pnuematic actuator, the air supply pressure used for selection is generally not too high, usually from 1.4~4.0bar; for cylinders, it may be between 3~6 bar, see the inquiry document for specific requirements. |
| 5 | Torque or thrust value | 1) For linear valves, the thrust value needs to be provided, please provide detailed thrust parameters; 2) For quarter-turn valves, the torque value needs to be provided, generally including at least 5~6 torque values, such as BTO, BTC, RUN, ETO, ETC, MAST, etc., for the accuracy and cost-effectiveness of selection, please provide detailed torque values. | Torque and thrust are one of the most important parameters for calculating the actuator, please provide them accurately. |
| 6 | Valve stroke | 1) For linear valves, provide the accurate valve stroke; 2) For quarter-turn valves, confirm if the valve turn is 0~90 ° or 0~180 °? | Please noted that this is mainly for linear valves. |
| 7 | Safety factor needed for selection | 1) 1.0, which means the value provided already includes a safety factor, no need to add extra; 2) 1.25 times 3) 1.3 times 4) 1.5 times 5) 2.0 times 6) Customer’s special required safety factor, etc. | Safety factor is an important parameter in selection, please make sure the customer provides it and let the actuator manufacturer select according to the requirement. |
| 8 | Actuator housing material requirement | 1) Cast aluminum 2) Cast iron 3) Carbon steel 4) Stainless steel 5) Other special materials | Actuator material, sometimes customers have material requirements, but in most cases, the manufacturer selects based on their product, just pay attention to the requirements. |
| 9 | Actuator seal material requirement | 1) Natural rubber 2) Nitrile rubber 3) Viton rubber 4) Other special materials | This material part, mainly because there are low temperature, high temperature, and other special circumstances requirements, so please pay attention to the specific requirements. |
| 10 | Requirements for ambient temperature | 1) No low temperature needed, normal ambient temperature; 2) Low temperature needed, not lower than -20°C; 3) Low temperature needed, not lower than -40°C; 4) Low temperature needed, not lower than -60°C; 5) High temperature needed, please list the high temperatures; 6) Other special ambient temperatures, please mention. | Temperature issues must be paid attention to because for different manufacturers, different temperatures will lead to completely different actuator models and series selection, and the price difference is also significant, so theoretically, when selecting, the first thing to determine is the actuator’s requirements for ambient temperature. |
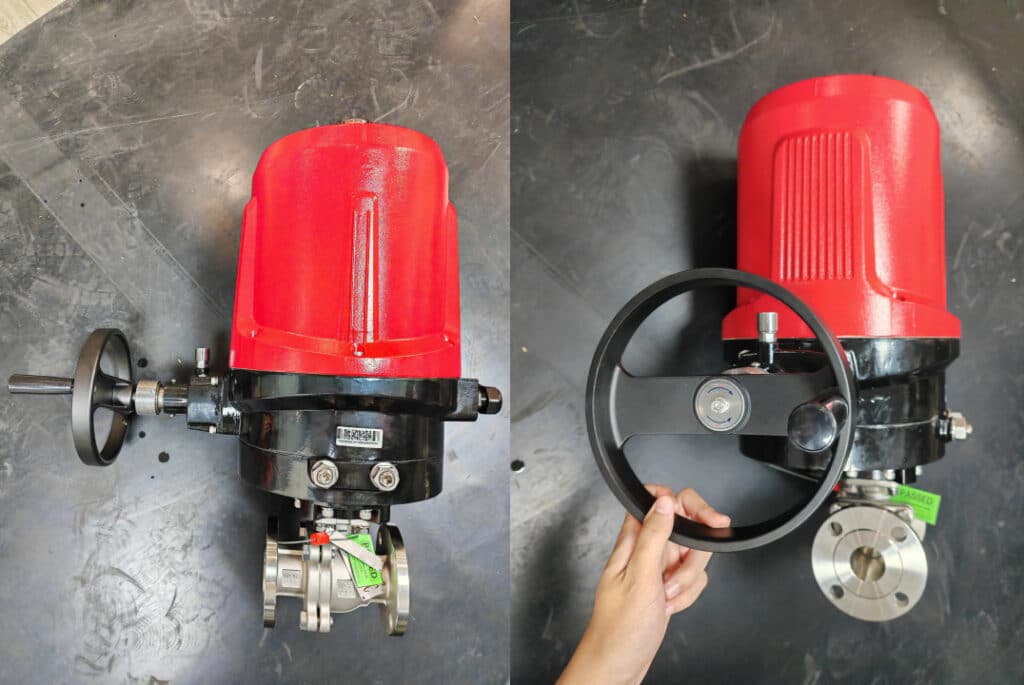
| 11 | Is a handwheel mechanism included? | 1) No handwheel mechanism; 2) With handwheel mechanism, and the handwheel is top-mounted; 3) With handwheel mechanism, and the handwheel is side-mounted; 4) With handwheel mechanism, and there are special requirements. | The handwheel mechanism must be paid attention to because it affects the price significantly, and whether it is included or not, for the actuator manufacturer, the model and even the series are different. |
| 12 | Does it come with stroke adjustment or travel limit? | Do actuators at the 0° and 90° positions need 5° or 10° of adjustability? Can this be met, or does the owner have specific requirements for travel limits? | Stroke adjustability is necessary for certain valves, such as triple offset butterfly valves and trunnion mounted ball valves. Therefore, when selecting actuators for these types of valves, it’s important to ensure that the actuators can be adjusted at both the 0° and 90° positions. Special circumstances also require special attention. |
| 13 | Failure position in case of air loss? | 1) Fail Close (FC) 2) Fail Open (FO) 3) Fail Last (FL-1) 4) Fail Lock (FL-2) 5) Other requirements, please specify in detail. | 1) Often, the failure position listed in the data sheets refers to the position in case of air loss. Do not assume that the air loss failure position is the same as the power failure position; they are mostly consistent, but there can be inconsistencies. 2) Please note, if the owner’s specification for air loss is FL, it does not necessarily mean Fail Lock, it could also mean Fail Last. The purpose and process of the air circuit for locking and maintaining are different, this must be carefully noted. |
| 14 | Failure position in case of power loss? | 1) Fail Close (FC) 2) Fail Open (FO) 3) Fail Last (FL-1) 4) Fail Lock (FL-2) 5) Other requirements, please specify in detail. | If the failure position in case of power loss is not specified in the data sheet, it is assumed to be the same as the air loss failure position. If the data sheet specifies that the air loss and power loss failure positions are different, attention must be paid during the configuration of the air circuit. For single-acting pneumatic actuators, if the air loss and power loss failure positions are inconsistent, an air reservoir may need to be added to achieve the desired failure position during power loss. This is sometimes the reason why single-acting cylinders are fitted with an air reservoir. |
| 15 | Are there any other requirements? |
Top 16 Selection Tips For Solenoid Valve
| No. | Parameter Category | Options | Explanation |
| 1 | What type of cylinder is used for? | 1) Single-acting cylinder; 2) Double-acting cylinder; 3) Special type cylinder. | The type of cylinder must be clearly described. |
| 2 | Brand requirement | 1) Manufacturer’s choice; 2) ASCO; 3) Norgren (Herion); 4) Bifold; 5) Other specified brands, such as KANEKO, SMC, and Parker, etc. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 3 | Connection method between solenoid valve and cylinder | 1) NAMUR standard surface mounting (flange); 2) Pipe connection (pipe type); 3) Other connection methods. | Pipe connection (pipe type) is a universal connection method, but it is more costly; NAMUR surface mounting (flange) is limited to small cylinders and it’s a restricted connection but cost-saving. |
| 4 | Type of solenoid valve – 1 | 1) Two-position three-way (3/2 Way); 2) Two-position five-way (5/2 Way); 3) Three-position five-way (5/3 Way); 4) Special types. | A single-acting cylinder must use a two-position three-way solenoid valve; however, a double-acting cylinder does not necessarily require a two-position five-way solenoid valve; it can also be controlled by a two-position three-way solenoid valve operating a two-position five-way pneumatic valve, so the specific situation should be analyzed in detail. |
| 5 | Type of solenoid valve – 2 | 1) NC (Normal Close); 2) NO (Normal Open); 3) U (Universal); 4) Special types. | This should be provided by the manufacturer based on actual requirements, but ensure the correctness of the selection result. |
| 6 | Solenoid drive action | 1) Direct action (direct type); 2) Pilot type. | Generally, the manufacturer will choose based on the situation; sometimes the owner will also have requirements for direct or pilot type, so pay attention to this option. |
| 7 | Operating voltage of solenoid valve | 1) 24V DC; 2) 110V AC @ 50HZ; 3) 220V AC @ 60HZ; 4) Other special voltages, etc. | Choose the correct operating voltage according to customer requirements; generally, the options of 24VDC and 220VAC are more common. |
| 8 | Coil housing material? | 1) Cast aluminum; 2) Stainless steel; 3) Other materials. | Any standard solenoid valve from any manufacturer is composed of two parts: the coil part (including the wiring part, called Coil in English) and the valve body part (called Body in English). Therefore, it is more accurate to describe these two parts separately. |
| 9 | Valve body material? | 1) Cast aluminum; 2) Brass; 3) Stainless steel; 4) Other materials. | The coil and valve body materials need to be defined separately before the final confirmation of the entire solenoid valve’s material can be made, so please pay special attention to this point. |
| 10 | Valve port size? | 1) 1/4″ NPT; 2) 1/2″ NPT. | There are just two options, generally, it is 1/4″ NPT, and 1/2″ NPT is rarely used. |
| 11 | Electrical interface material? | 1) 1/2″ NPT; 2) 3/4″ NPT; 3) M20*1.5; 4) Special interface size. | Generally, choose from the first three options listed, which is to say, pick one from the three. |
| 12 | Explosion-proof rating? | 1) Only dust and waterproof, no explosion-proof required Only IP65/66; 2) Intrinsic safety explosion-proof Exia IICT4/6 + IP65/66; 3) Flameproof explosion-proof Exd IICT4/6 + IP65/66; 4) Other types of explosion-proof. | Generally, choose from the first three options listed, which is to say, pick one from the thre |
| 13 | Power consumption requirements | 1) Standard power consumption: around 10W; 2) Reduced power consumption: less than or equal to 4.0W; 3) Low power consumption: less than or equal to 2.0W; 4) Other power consumption requirements. | Typically, select from the first three options listed, especially from those less than or equal to 4.0W and less than or equal to 2.0W. |
| 14 | Does it come with manual operation? | 1) Manual operation; 2) Manual reset; 3) Other operations. | This usually needs to be defined according to the requirements of the design institute, but for devices with safety integrity level (SIL) requirements, whether the manual operation options can meet SIL needs to be consulted with the manufacturer. |
| 15 | Requirements for ambient temperature | 1) No low temperature required, normal ambient temperature; 2) Low temperature required, not lower than -20°C; 3) Low temperature required, not lower than -40°C; 4) Low temperature required, not lower than -60°C; 5) High temperature required, please list the high temperatures; 6) Please specify Other special ambient temperatures if needed. | Attention must be paid to temperature as different manufacturers may choose different models and series of solenoid valves based on temperature, and the price difference can be significant. Therefore, theoretically, when selecting, one should first determine the solenoid valve’s requirements for ambient temperature. |
| 16 | Are there any other requirements? |
Top 11 Selection Tips For Limit Switch
| NO. | Parameter Classification | Option | Description |
| 1 | What type of cylinder is it used for? | 1) Quarter-turn cylinder; 2) Linear cylinder; 3) Special type cylinder. | The type of cylinder must be clearly described. |
| 2 | Brand requirement | 1) Manufacturer’s choice; 2) Topworx; 3) Westlock; 4) Honeywell; 5) Stonel; 6) Other specified brands. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 3 | Type of limit switch-1 | 1) SPDT (Single Pole Double Throw); 2) DPDT (Double Pole Double Throw); 3) Other types; | Typically, choose between SPDT and DPDT. |
| 4 | Type of limit switch-2 | 1) Mechanical; 2) Proximity; 3) NAMUR inductive (intrinsic safety type); 4) Other special types, etc. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 5 | Casting shell material of the limit switch | 1) Plastic; 2) Casting aluminum; 3) Stainless steel; 4) Other materials. | For chemical plants, casting aluminum is generally sufficient; Stainless steel is rarely used except in marine conditions, such as offshore LNG, offshore platforms, etc. However, different devices require different analysis. |
| 6 | Contact capacity | 1) 1A @ 24V DC; 2) 2A @ 24V DC; 3) 3A @ 24V DC; 4) 3A @ 220V AC; 5) Many other contact capacities are available; | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 7 | Built-in micro switch | 1) Manufacturer’s standard micro switch; 2) Other specified manufacturer’s micro switch, such as P+F, Honeywell, etc.; 3) Other special requirements. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 8 | Electrical interface material | 1) 1/2″ NPT; 2) 3/4″ NPT; 3) M20*1.5; 4) Special interface sizes. | Generally, choose from the first three options listed, i.e., pick one from the three. |
| 9 | Explosion-proof rating | 1) Only dust and waterproof, no explosion-proof required Only IP65/66; 2) Intrinsic safety explosion-proof Exia IICT4/6 + IP65/66; 3) Flameproof explosion-proof Exd IICT4/6 + IP65/66; 4) Other types of explosion-proof. | Generally, choose from the first three options listed, i.e., pick one from the three. |
| 10 | Requirements for ambient temperature | 1) No low temperature required, normal ambient temperature; 2) Low temperature required, not lower than -20°C; 3) Low temperature required, not lower than -40°C; 4) Low temperature required, not lower than -60°C; 5) High temperature required, please list the high temperatures; 6) Please specify other special ambient temperatures. | Attention must be paid to temperature because different manufacturers may choose different models and series of limit switches based on temperature, and the price difference can be significant. Therefore, theoretically, when selecting, one should first determine the limit switch’s requirements for ambient temperature. |
| 11 | Are there any other requirements? |
Top 10 Selection Tips For Air Filter Regulator
| NO. | Parameter Classification | Option | Description |
| 1 | Brand requirements for air filter regulator | 1) Manufacturer’s choice; 2) SMC; 3) Norgren; 4) ASCO; 5) Rotork(YTC); 6) Other specified brands. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 2 | Main material | 1) Plastic; 2) Cast aluminum; 3) Stainless steel; 4) Other materials. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. Note: The main material is generally metal; plastic is rare. |
| 3 | Cup material | 1) Plastic; 2) Cast aluminum; 3) Stainless steel; 4) Other materials. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. Note: Many manufacturers offer plastic options for cup material, so be sure to pay attention to the real needs. |
| 4 | Air port size | 1) 1/4″; 2) 1/2″; 3) 3/4″; 4) 1″; 5) Other optional sizes. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements and calculations. |
| 5 | Maximum pressure capacity | 1) Not less than 10 bar; 2) Not less than 7 bar; 3) Other special requirements. | Common air filter regulator typically have a body pressure capacity of more than 10 bar, but some manufacturers only have 7-8 bar, so it’s best to pay attention to this parameter when selecting to avoid issues on site. |
| 5 | Determination of air flow rate (CV value) | There are many options available, each manufacturer, each brand, each size is different. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements and calculations. |
| 6 | Filtration precision | 1) 5 microns; 2) 25 microns; 3) 40/50 microns; 4) Other options. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 7 | Drainage option | 1) Automatic drainage; 2) Manual drainage; 3) Other special requirements. | This should be chosen based on actual requirements. |
| 8 | Does it come with a pressure gauge? | 1) With gauge; 2) Without gauge. | Theoretically, a pressure gauge is essential. However, to reduce the total costs, manufacturers may only quote the price of the air filter regulator body without the price of the pressure gauge. If the purchaser does not check carefully, they might underquote the customer, especially if the customer actually needs a gauge. So be sure to pay attention to this unless the customer explicitly states they do not need a pressure gauge. |
| 9 | Material of the pressure gauge? | 1) Aluminum case; 2) Stainless steel case; 3) Other special cases. | |
| 10 | Requirements for ambient temperature | 1) No low temperature required, normal ambient temperature; 2) Low temperature required, not lower than -20°C; 3) Low temperature required, not lower than -40°C; 4) Low temperature required, not lower than -60°C; 5) High temperature required, please list the high temperatures; 6) Please specify other special ambient temperatures. | Attention must be paid to temperature because the choice of model and series of limit switches from different manufacturers based on temperature varies greatly, as does the price. Therefore, when selecting, one must first determine the limit switch’s requirements for ambient temperature. |
Top 13 Selection Tips For Valve Positioner
| NO. | Parameter Classification | Option | Description |
| 1 | Used for what type of pneumatic actuators? | 1) Quarter-turn rotary type pneumatic actuator(single-acting, or double-acting); 2) Linear type pneumatic actuator(single-acting, or double-acting); 3) Special type pneumatic actuator (single-acting, or double-acting). | The type of pneumatic actuator must be clearly described. Actuator manufacturers have different mounting brackets for single and double-acting cylinders. Special types of pneumatic actuator may require special forms of mounting brackets. |
| 2 | Are there any brand specifications? | 1) Fisher; Flowserve; Masoneilan; Samson 2) Metso; Siemens; ABB; Yamatake; Azbil; Rotork YTC 3) Other or domestic brands 4) No specified brand, choose according to customer requirements? | Before selecting a positioner, be sure to read the tender document and the technical and brand requirements of the owner’s side for the positioner, then decide which brand and series of positioners to choose. |
| 3 | Working stroke range | 1)Quarter-turn rotary type(30~100°); 2)Linear type(10~100mm); 3)Special types (larger working stroke range). | Choose based on the actual working stroke of the pneumatic actuator and installation method. Different manufacturers’ positioners have different stroke ranges, and larger working strokes may involve special customization. |
| 4 | Explosion-proof rating | 1) Non-explosive, only waterproof and dustproof IP66; 2) Intrinsic safety (Ex ia IIC T4/T6) +IP66; 3) Flameproof (Ex d IIC T6 Gb) +IP66; 4) Other types of explosion-proof (non-sparking, dust explosion-proof, etc.). | The explosion-proof rating is chosen based on the presence and duration of explosive gases on-site, divided into zones 0, 1, 2 (Zone 0 where hazardous gases are present for more than 1000 hours/year, Zone 1 where they are intermittently present for 10-1000 hours/year, Zone 2 where they are present under accident conditions for 0.1-10 hours/year). Intrinsic safety explosion-proof can be used in Zone 0 and below (must be paired with a safety barrier), flameproof can be used in Zone 1 and below, non-sparking explosion-proof only satisfies Zone 2. The highest surface temperature of the positioner is also divided into groups T1-T6, along with common explosive gases for each temperature group (T1 450°C level lowest, includes hydrogen, acrylonitrile among 46 types of explosive gases, T2 300°C acetylene, ethylene among 47 types, T3 200°C gasoline, butyraldehyde among 36 types, T4 135°C acetaldehyde, tetrafluoroethylene among 6 types, T5 100°C carbon disulfide, T6 85°C level highest ethyl nitrate and ethyl nitrite, etc.). Generally, choose from the first three options listed. Note: Different countries’ explosion-proof standards may vary slightly. |
| 5 | Feedback signal | 1) No feedback signal; 2) 4-20mA feedback signal; 3) 3-15 PSI feedback signa; 3) Other feedback signals. | Choose based on actual requirements; generally, choose one of the first three options listed. |
| 6 | Communication protocol | 1) HART communication; 2) PROFIBUS PA; 3) FOUNDATION Fieldbus; 4) Other communication protocols. | Generally, choose one of the first three options listed. |
| 7 | Air Interface | 1) G1/4 female thread; 2) 1/4-18 NPT; 3) Other interfaces. | Choose based on actual requirements; different manufacturers support different interfaces. |
| 8 | Electrical Interface | 1) M20×1.5; 2) 1/2-14 NPT; 3) Other electrical interfaces. | Choose based on actual requirements; different manufacturers support different interfaces. |
| 9 | Does it come with a pressure gauge assembly? | 1) Single-action pressure gauge; 2) Double-action pressure gauge. | Choose based on actual requirements, used for on-site working gas source diagnostics. |
| 10 | “Safe” position | 1) Three-way reset; 2) Three-way hold. | Choose based on actual operating conditions, used for the safe working position of the actuator in case of control signal, power, and gas source failure, where the positioner can actuate the actuator as required (empty for “reset”; hold for “hold”). |
| 11 | Operating ambient temperature | 1) Non-explosive: -20°C ~ 70°C; 2) Explosive T4 environment: maximum explosive temperature -20°C ~ 60°C; Explosive T6 environment: maximum explosive temperature -20°C ~ 40°C 3) Low temperature version: -40°C ~ 70°C | Choose based on actual operating requirements, clarifying the required explosion-proof grade and environment. T4 and T6 explosion-proof gas group requirements differ. Different manufacturers have different operating temperature ranges. |
| 12 | Enclosure material | 1) Aluminum enclosure; 2) Stainless steel enclosure; 3) Other types of enclosures | Choose based on actual operating conditions to prevent damage to the enclosure in corrosive environments. Generally, an aluminum enclosure is sufficient. |
| 13 | Are there any other requirements? |
Conclusion of Valve Accessories Selection Tips
In conclusion, selecting the right valve accessories is a critical task for industry professionals, one that requires a detailed understanding of the application, a thorough evaluation of the operational conditions, and a careful consideration of safety standards. From actuator types to material compatibility and from control requirements to regulatory compliance, every aspect plays a pivotal role in ensuring the optimal performance and reliability of valve systems. By adhering to the top valve accessories selection tips outlined in this article, professionals can make informed decisions that not only enhance the functionality of their valve assemblies but also contribute to the longevity and safety of their industrial processes. Remember, the key to successful valve accessory selection lies in balancing technical specifications with practical requirements and cost-efficiency, all while never compromising on quality. With these guidelines in hand, industry professionals are well-equipped to navigate the complexities of valve accessory selection with confidence and precision. Meanwhile, if you have any questions about valve accessories selection, please do not hesitate to contact THINKTANK’s experts here. Also you can freely download these tips here.