In the world of compressed air applications, air compressors serve as vital workhorses, delivering pressurized air for an array of tasks. Ensuring the safe and efficient operation of these devices is the responsibility of air compressor safety relief valves, also recognized as pop-off valves or pressure safety valves.
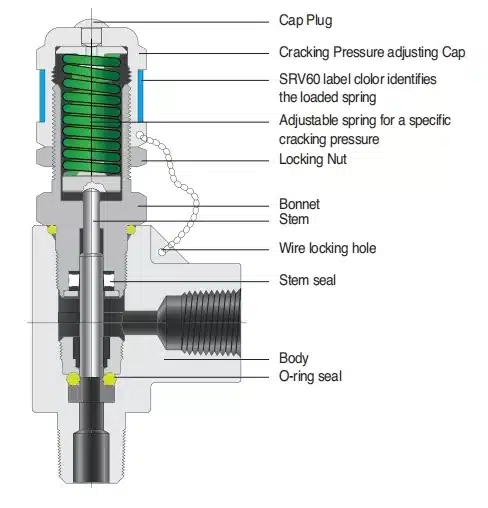
The air compressor safety relief valve automatically opening to release excess pressure when the compressor pressure switch fails, because the pressure hits the predetermined system pressure limit and seamlessly closing once normal levels are restored.
Their role in maintaining safety and optimizing equipment performance is irreplaceable. Regular checks are crucial, ensuring these valves remain in good condition, undamaged, and in optimal working condition. Periodic inspections not only safeguard against potential equipment failures but also contribute to a secure environment, shielding both property and personnel from potential hazards.
Today, THINKTANK will share with you what is a compressor safety valve, how to inspect your compressor safety valve, and also note the importance of maintaining a compressor safety valve regularly.
Understanding Compressor Safety Valves
Understanding the mechanics of compressor safety valves is essential for maintaining a secure operational environment. These valves main role is preventing overpressure scenarios in air compressor systems. Understanding their functionality involves recognizing the set pressure limits, compressor’s pressure vessel, where the valves automatically open to release excess pressure. Key components include the valve disc, seat, and spring, working together to create a balanced and safe system. In essence, these safety valves are precisely adjusted to respond with precision, ensuring seamless operations and safeguarding against potential hazards. Regular understanding of their mechanisms contribute to a proactive approach in preserving equipment integrity and preventing costly malfunctions.
Parts and Materials
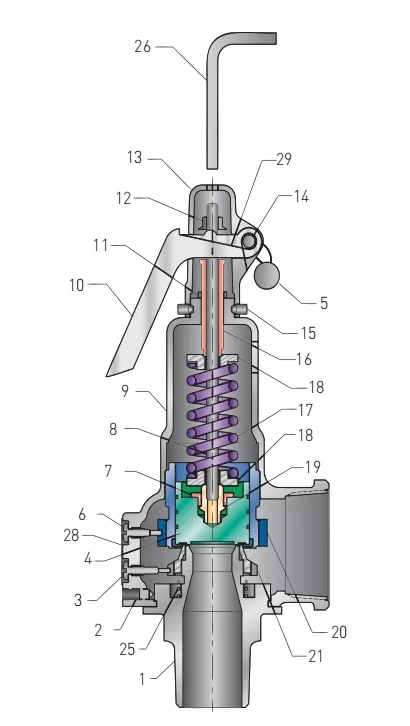
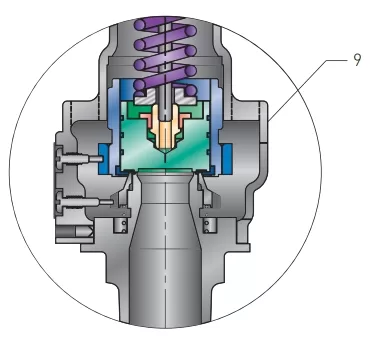
| 1 | Nozzle | BRS B283-C48500 or BRZ SB623 |
| 2 | Body set screw | STL A108 Black oxide |
| 3 | Warn ring set screw | SS 18-8 |
| 4 | Disc | BRS B21 C485004 |
| 5 | Wire and seal | SS wire and lead seal |
| 6 | Guide set screw | SS 18-8 |
| 7 | Retainer nut2 | BRS B16 |
| 8 | Stem | SS A582-303 for D orifice SS A582-416 for E thru J orifice |
| 9 | Body | BRZ B584-C84400 |
| 10 | Lever | STL A109 or JIS SPCC equivalent/ZN plated yellow |
| 11 | Compression screw locknut | BRS B16 |
| 12 | Lift nut | STL A108-1018/ZN plated |
| 13 | Cap | Aluminum, anodized |
| 14 | Lever pin | STL A108-12L14 |
| 15 | Cap set screw10 | STL A108 Black oxide |
| 16 | Compression screw | BRS B16 |
| 17 | Spring | ASTM A-313 TY 631 |
| 18 | Spring step | BRS B16 |
| 19 | Stem end12 | BRS B16 |
| 20 | Guide | BRS B283-C37700 |
| 21 | Warn ring7 | BRS B283-C37700 |
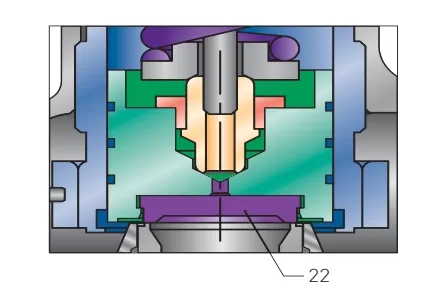
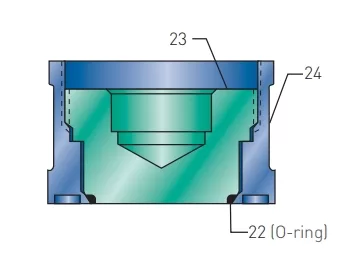
| 22 | Seat | Teflon, Stainless Steel, Alloy Steel |
| 23 | Seat retainer8 | BRS B165 |
| 24 | Soft seat disc8 | BRS B21 C485005 |
| 25 | Warn ring spring6 | SS A313-302/316 |
| 26 | Gag screw9 | STL A108-1018/ZN plated |
| 27 | Pop rivet | Aluminum |
| 28 | Nameplate | Aluminum |
| 29 | Vibration dampener spring | PH BRZ B159-C51000 |
Frequency of Inspection
Ensuring the smooth operation of air compressor safety valves involves understanding how often to inspect them. In this section, we explore general guidelines and factors influencing the frequency of these crucial inspections.
a. Establishing a Routine
Guidelines suggest regular checks for air compressor safety valves to ensure optimal functionality. This routine inspection is typically recommended at least once every six months, but industry-specific regulations or the equipment manufacturer’s guidelines may influence the frequency.
b. Influential Factors
Several factors impact inspection frequency, including the operating conditions, system criticality, and the environment where the compressor operates. Harsher conditions or high-demand environments might necessitate more frequent checks to maintain safety standards. It’s crucial to align inspection schedules with the unique demands of the air compressor system to guarantee reliability.
Signs of Wear and Common Issues
To maintain the reliability of air compressor safety valves, it’s essential to recognize signs of wear and address common issues promptly. This section explores indicators that valves may need attention, providing insights into potential problems and ensuring a proactive approach to system safety.
A. Identifying Signs of Wear
Wear and tear are inevitable aspects of any mechanical component, including air compressor safety valves. Look out for any signs such as leaks, corrosion, or unusual sounds, as these could indicate potential wear. By understanding these indicators, individuals can proactively address issues before they escalate, preserving the optimal functioning of the air compressor safety valves.
B. Common Issues Impacting Safety Valve Performance
Ensuring the reliability of air compressor safety valves involves addressing common issues like debris accumulation, corrosion, spring fatigue, calibration errors, and malfunctioning seals. Regular inspections and cleaning are crucial to prevent debris-related malfunctions, while protective measures and corrosion-resistant materials combat corrosion issues. Monitoring and replacing worn-out springs, ensuring proper calibration and addressing seal malfunctions through routine examinations are essential practices.
Step-by-Step Guide for Checking Safety Valves
Checking a compressor safety valve, also known as a pressure relief valve, is a crucial maintenance task to ensure the safety and proper functioning of an air compressor. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to check it:
Step 1. Read the Manufacturer’s Instructions
Before starting, it’s important to consult the manufacturer’s manual for specific instructions and safety precautions related to your particular compressor and safety valve.
Step 2. Ensure Compressor is Off and Depressurized
Turn off the air compressor and release any pressure in the tank. This can typically be done by opening the drain valve at the bottom of the tank until all air has escaped and the pressure gauge reads zero.
Step 3. Locate the Safety Valve
The safety valve is usually a small valve with a ring or a lever on top, located on the air tank. It’s designed to automatically open at a predetermined set pressure.
Step 4. Manual Testing
– Pull the Ring or Lever
Gently pull the ring or lever on the safety valve. This should manually open the valve, and you should hear air hissing out if there’s residual pressure in the tank.
– Release the Ring or Lever
Upon releasing the ring or lever, the valve should snap back into its closed position. If it doesn’t, or if it continues to release air when the ring or lever is released, the valve might be faulty.
Step 5. Inspect for Damage or Corrosion
Visually inspect the valve for any signs of damage, corrosion, or debris that might prevent proper functioning.
Step 6. Check for Leaks
With the compressor running and the tank pressurized, listen for any air leaks from the safety valve. Any continuous hissing sound when the compressor is at normal operating pressure indicates a leak.
Step 7. Pressure Check
Observe the compressor’s pressure gauge as the tank is pressurizing. The safety valve should not open before the compressor reaches its maximum rated pressure. If the valve opens prematurely, it may be set at too low a pressure or may be malfunctioning.
Step 8. Professional Testing (if applicable)
For critical applications or if there’s any doubt about the valve’s performance, have the safety valve professionally tested. This testing may involve using specialized equipment to verify that the valve opens at the correct set pressure.
Step 9. Replacement if Necessary
If the safety valve is faulty, it should be replaced immediately with a new valve of the same rating and type. Do not attempt to adjust or repair a faulty safety valve yourself.
Step 10. Document the Inspection
Record the date of inspection and any actions taken. Regular inspections should be part of your routine maintenance schedule.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
A. Role of Maintenance in Prolonging Safety Valve Lifespan
Maintenance plays a pivotal role in extending the lifespan of air compressor safety valves. Regular inspections, cleaning and adjustments, ensures optimal valve performance. By following detailed maintenance procedures, you can prevent premature wear and tear of the safety valves. A proactive approach to maintenance safeguards against potential malfunctions, contributing to the overall integrity and efficiency of the compressed air system.
B. Risks Associated with Neglecting Maintenance
Both safety valves and pressure relief valves prevent issues in pressure vessels, including those within the compressor’s pressure vessel. Neglecting the maintenance of these critical components poses significant risks to both safety valves and the overall air compressor system. Indicators such as leaks, corrosion, or unusual sounds should be promptly addressed, allowing users to proactively manage potential issues. Additionally, understanding common issues impacting safety valve performance is essential. Challenges like debris accumulation or malfunctioning components can compromise the effectiveness of the safety valves which affects the whole system.
Summary
Safety Note: Always follow established safety protocols during the air compressor safety valve inspection process to prevent any excessive compressor pressure incidents. If uncertainties arise, consider seeking guidance from a certified professional to ensure comprehensive evaluation. We THINKTANK company underscores the paramount importance of maintaining the safety valve’s integrity, as it stands pivotal for the secure and efficient operation of an air compressor system.