In the industrial process, the key stations have requirements for their emergency failure positions for control valves. It is necessary to ensure that the control valve is in a safe position under different failure issues. For example, in the case of loss of instrument air supply or loss of power, this post will tell you specifically about the different fail-safe modes.
control valve failure modes
The control valve has four options for fail-safe positions for emergency conditions.
a.) Valve Fully Closed
b.) Valve Fully Open
c.) Valve in The Last Position
d.) Valve Continues to Control
For instrument air supply pressure loss or power loss, it is the bench-set setting spring range of the pneumatic actuator that drives the plug of the control valve to its failure-safe valve open or closed position.
I. Instrument Air Supply (IAS) Pressure Loss
a.) Valve fully closed
For the reverse action of the control valve, the fail mode is air to open(ATO), which means the failure-safe position is the valve fully closed.
When the loaded instrument air pressure approaches 0 psig, the actuator’s bench-set range spring “drives” the valve plug to the valve closed position.
Due to instrument air supply piping systems providing air power for a wide range of equipments in the field, so the decay of instrument air supply may action slowly, which will cause operation issues for control valves.
In this case, it may be necessary to use a 3-way pilot switching valve to “predict” the eventual IAS loss and quickly drive the control valve to the failure position to eliminate the transient operational effects of slow decay.
b.) Valve fully open
For the direct action of the control valve, the fail mode is air to open(ATC), which means the failure-safe position is the valve fully open.
When the loaded instrument air pressure approaches 0 psig, the actuator’s bench-set range spring “drives” the valve plug to the valve fully open position.
To remove transitory effects, a technique similar to a. preceding may be used for ATC FO configurations for failure valve open control valves.
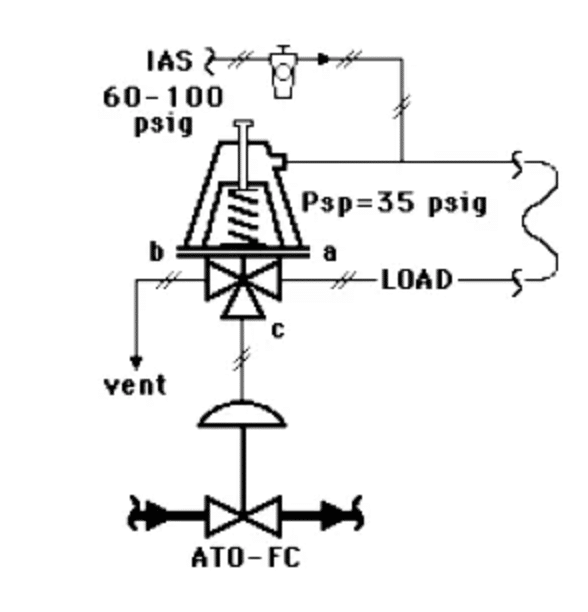
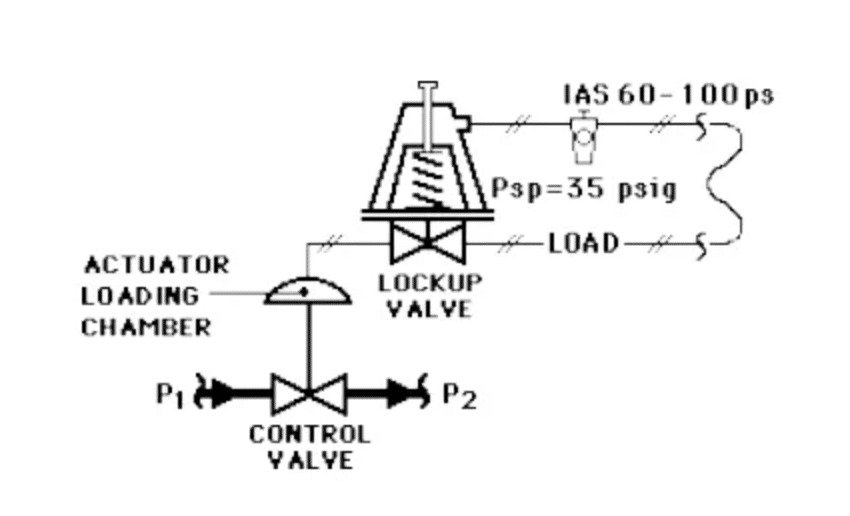
c.) Valve in the last position
This is accomplished by an air lockup valve, which is a two-way pilot switching valve. If the air set of the control circuit loses pressure, the air lockup valve will close and lock the air in the air chamber of the pneumatic actuator.
If there is no air leakage, the control valve will remain in the last position. Such a loop is usually localized. Usually, a safety failure that holds the final position will have time-limited because the air chamber, tubing, or accessories instrument of control valves will cause an air leakage, which makes the lockup air in the pneumatic actuator volume gradually decreases, so the last position will tend to fully open or fully closed.
d.) Valve continues to control
This is a specially designed engineered instrumentation system that can be accomplished in two different ways.
1.) Adding a Backup Volume tank
A capacity tank stores a limited supply of instrument air supply to maintain the regular operation of the control valve for a limited period of time, i.e., approximately one hour or more, designing the tank volume/capacity shall be according to the customer’s requirements.
2.) Alternate Gas Supply
A high-pressure cylinder with a backup gas, usually GN2, is stored on standby. If the instrument air supply pressure drops below 50 psig, the backup gas will take over the supply pneumatic control. The high pressure will allow several hours of continuous operation with enough time to recover from an emergency loss of IAS.
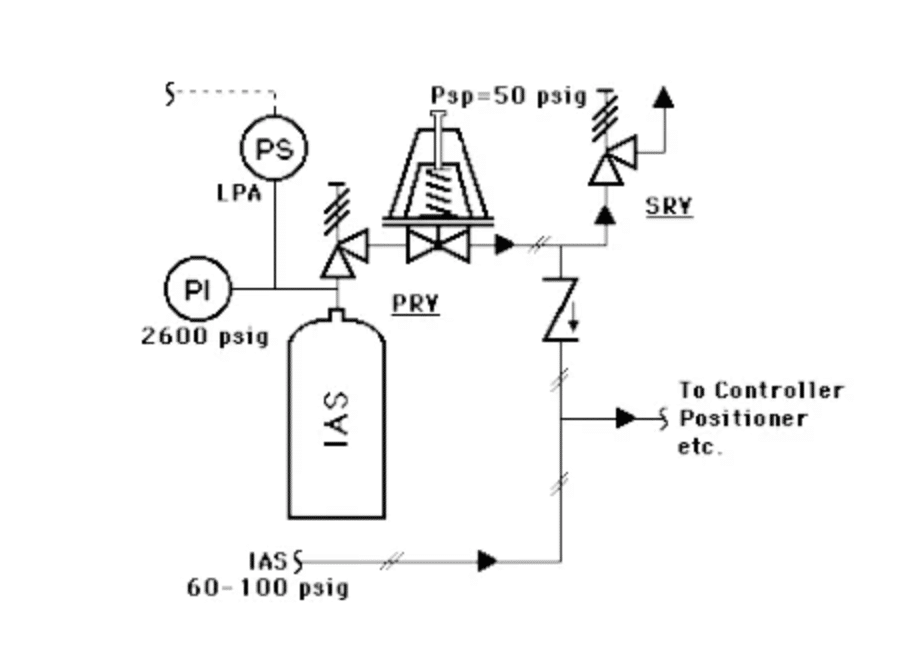
This application is typically used for very critical operating conditions. Such loops are usually local and pneumatically controlled only; i.e., no electrical power is involved except for a low-pressure alarm switch.
II. Loss of Electrical Power
Protection against power loss is achieved indirectly through the use of a solenoid valve. In regular operation, the solenoid valve is energized; in the event of an emergency power failure, the solenoid valve is de-energized and jumps to the “on hold position.” The solenoid valve voltage can be selected as 24 VDC, 120 VAC, 220 VAC, etc.
a.) Valve fully closed
By blocking the load air to the actuator and venting the air in the actuator load chamber to the atmosphere (P = 0 psig), the actuator’s bench-set range spring drives the plug to close the valve. The solenoid valve is a 3-way type.
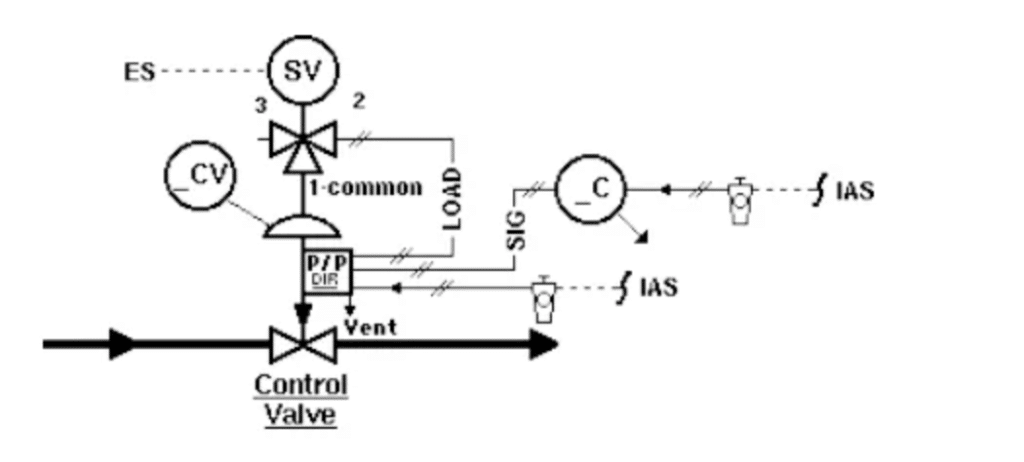
b.) Valve fully open
By blocking the load air to the actuator and venting the air in the actuator load chamber to the atmosphere (P = 0 psig), the actuator’s bench-set range spring drives the plug to open the valve. The solenoid valve accessories and tubing design are the same as case a.)
c.) Valve in the last position
A two-way solenoid valve accomplishes this failure-safe design. In the energized state, the solenoid valve port is open, and loading air passes through. In the powered-off state, the solenoid valve is closed, trapping air in the actuator’s loading chamber.
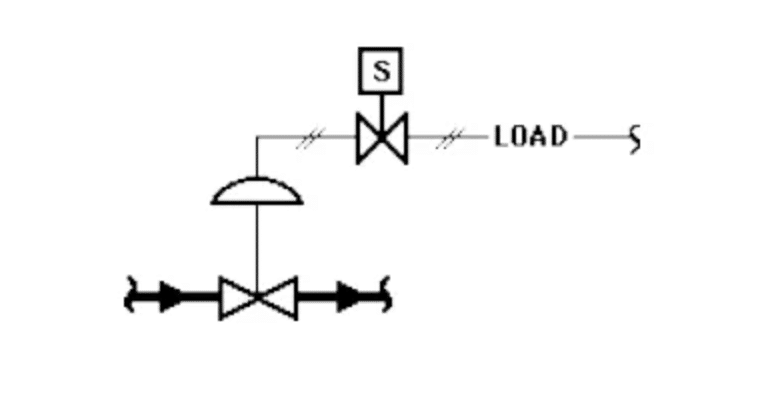
Abbreviations of valve terms
IAS: Instrument Air Supply
FTC: Fail/failure to Close
FTO: Fail/failure to Open
FO: Fail/failure Open
FC: Fail/failure Close
S/SV: Solenoid Valve
Solutions of pneumatic control valve Fail Position – Keep Valve at Last Position
In industrial automation control, sometimes need pneumatic control valves should fail to keep at the last position, the following three solutions are to keep the valve failure at the last position for double-acting pneumatic control valve failure.
Solution 1: the program is mainly composed of a pneumatic control valve, solenoid valve, valve positioner, air lockup valve, check valve, diaphragm pump pressure reducing valve, storage tank, etc.

working principle
When the control system air source fails (loss of instrument air supply), the air lockup valve (which acts in the opposite way to the air lockup valve ) automatically opens, the control of the solenoid valve air source is withdrawn, the solenoid valve slide valve reset under the action of the spring, one of the two solenoid valves exhaust, the other into the air, the one-way valve closed, the air source stored in the gas storage tank to the valve supply, so as to achieve the fully close or open valve. The conversion of fully closed or fully open can be achieved by adjusting the connection of the air controller.
If you want to realize the valve to keep at the last position, assemble a pneumatic valve and change the pipeline connection, use the air lockup valve to directly control the valve, solenoid valve, check valve, and gas storage tank.
Solution 2: if you want to achieve if loss of air source to ensure that the valve has a number of times the action, the control valve can be used in the following program.
This program consists of a gas storage tank, check valve, blocking valve, shut-off valve, etc. Its working principle is as follows.

When the gas source fails (loss of gas), the check valve closes, the blocking valve loses of gas, the slide valve in the blocking valve resets under the action of the spring, the gas circuit reversal, disconnect the system’s gas source pipeline, connected to the gas storage tank pipeline, the gas supply from the storage tank to the valve, to ensure that the valve has a number of actions to achieve the purpose of continuous control. Due to the limited capacity of the storage tank and the pressure of the gas source in the storage tank with the valve action decreases, can not use the storage tank for a long time to supply air to the valve. The capacity of the gas storage tank used in this program should be larger than the capacity of the general protection gas storage tank. This program in the case of a broken gas source, the number of valve actions, and the capacity of the storage tank.
Solution 3: Pneumatic control valve between the positioner and the actuator in series with an air lockup valve and a two-way three-port solenoid valve.
In the case of a gas break with air lockup valve to keep at the last position. in the case of a signal break, use the solenoid valve to keep at the last position. However, the solenoid valve must be interlocked with the positioner (set in the control program), which means if the positioner has a signal, the solenoid valve must have power, once the positioner loses signal, the solenoid valve must immediately power off.
Electric Control Valve Failure Modes
For the electric control valve, when there is a loss of the signal, it can stay in any of the positions of fully open, fully closed, or held based on the setting of the control module, while when there is a loss of the power, it naturally stays in the failure position, or the electric actuator with reset device can also operate the valve position to fully open or fully closed.
What are three common valve failures for diaphragm pneumatic globe control valves?
There are three common failures for diaphragm pneumatic globe control valves, loss of air supply, loss of electric power, and loss of signal. Generally, when we select the right pneumatic control valves for application, we need to know whether the air to open or close the valve, which means selecting the failure-safe position.
If the process requires the diaphragm pneumatic control valve (spring-turn) to open when loss of air supply, then choose the normally open type control valve.
If requires the diaphragm pneumatic control valve (spring-turn) to close when loss of air supply, then choose the normally closed type control valve.
But if the control system requires three common failures, namely, loss of air supply, loss of electric power, and loss of control signal at the same time, then the control valve needs to be configured with some accessories to form a protection system to achieve the control requirements, these accessories are mainly the air lockup valve, solenoid valve, gas tank, etc. The following are two modes of solutions for a single-acting pneumatic diaphragm control valve and a double-acting pneumatic control valve.
I. Solution for Diaphragm pneumatic globe type control valve (Single acting, spring-return)
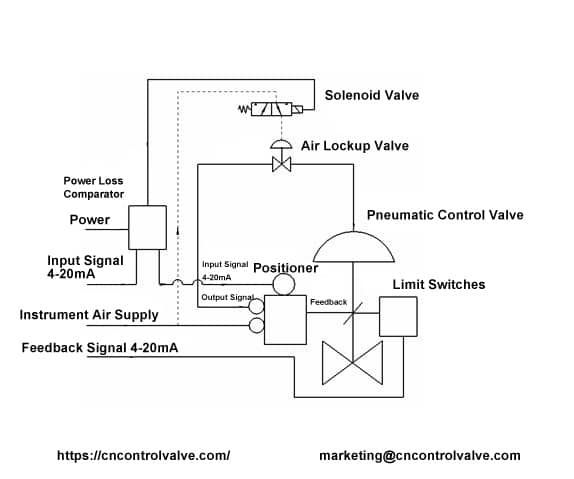
This program mainly consists of a diaphragm pneumatic control valve, an electric-pneumatic valve positioner, a loss of power comparator, a single electronically controlled solenoid reversing valve, an air lockup valve, limit switches, etc. Its working principle is as follows:
1. Loss of air source
When the control system air source failure, the air lockup valve automatically closes to lock the output signal pressure of the positioner in the diaphragm chamber of the pneumatic control valve, and the output signal pressure is balanced with the counter force generated by the actuator spring of control valve, and the valve position of the pneumatic control valve is maintained in the fault position. The air lockup valve should be set to start when it is slightly below the minimum value of the air source.
2. power failure
When the power supply of the control system fails, the loss of power comparator controls the output voltage disappears, the single electronically controlled solenoid-operated reversing valve loses power, the spool of the solenoid valve slides under the action of the reset spring, the solenoid valve reverses, the pressure of the membrane chamber of the air lockup valve is emptied, the lockup valve is closed, the output signal pressure of the positioner is locked in the membrane chamber of the pneumatic control valve, the output signal pressure is balanced with the counter force generated by the control valve spring, and the valve position of the pneumatic control valve is maintained in the fault position.
3. Loss of control Signal
When the control system signal failure is detected by the power loss comparator, the voltage signal of the single electronically controlled solenoid reversing valve is broken, the single electronically controlled solenoid reversing valve loses power, the slide valve inside the single electronically controlled solenoid reversing valve slides under the action of the reset spring, the solenoid valve reverses direction, the pressure of the membrane chamber of the pneumatic position-keeping valve is emptied, the pneumatic position-keeping valve is closed, the output signal pressure of the positioner is locked in the membrane chamber of the pneumatic control valve. The output signal pressure is balanced with the counter force generated by the control valve spring, and the valve position of the pneumatic control valve is maintained in the failure safe position.
The position feedback signal is given by the limit switches or valve positioner.

Three modes break protection when starting, the advantage of this program is system response is fast. The overall cost is relatively cheap.
Disadvantages of this solution: the solenoid valve is charged for a long time, affecting the service life. With more accessories, installation and commissioning are more complicated, and valve position feedback needs to be equipped with separate limit switches, in the case of a hand wheel is more complicated.
II.Solution for double-acting pneumatic control valve

This program mainly consists of a control valve, pneumatic controller, valve positioner, air lockup valve, check valve, pressure reducing valve, gas storage tank, etc. Its working principle is as follows.
When the control system air source failure, the self-locking valve automatically opens, the control air source of the pneumatic controller is withdrawn, the slide valve of the pneumatic controller is reset under the action of the spring, one of the two air-controlled reversing valves exhausts, the other feeds, the check valve closes, and the air source is supplied to the valve by the air source stored in the gas storage tank, thus realizing the full close or open valve. The conversion of fully closed or fully open can be achieved by adjusting the connection of the pneumatic controller.
If you want to achieve the valve to keep at the last position, install an air lockup valve and change the tubing connection, use the air lockup valve to control the valve directly, there is no need pneumatic controller, check valve, and storage tank.
If you want to make sure the number of times the action of the control valve is when loss of air supply, the following program can be used.
This program consists of a gas storage tank, check valve, blocking valve, stop valve, etc. Its working principle is as follows.
When the air source failure, the check valve closes, the blocking valve loses air, the spool in the blocking valve is reset under the action of the spring, the gas circuit reverses, disconnects the system’s air tubing, connects the gas storage tank pipeline, the gas supply from the storage tank to the valve, to ensure that the valve has a number of times the action, to achieve the purpose of continuous control. Due to the limited capacity of the storage tank, and the pressure of the gas source in the storage tank with the valve action decreases, can not use the storage tank for a long time to supply air to the valve. The capacity of the gas storage tank used in this program should be larger than the capacity of the general protection gas storage tank. The number of valve actions in this program is related to the capacity of the storage tank when the gas source is disconnected.
How do you troubleshoot a control valve?
control valve troubleshooting pDF
Summary
This post provides an overview of the different failure modes associated with control valves and how to detect them. Common issues such as poor calibration or stuck valves can be easily identified, while more difficult-to-diagnose faults need to control valve experts to analyze and solve. THINKTANK is a well-known brand of control valves in China, you can completely trust us to help you sizing and select the right control valves for your applications and projects. Contact us today you will get a free consultation.





