Many customers have asked us how to select the actuator with our linear type control valves. For example, the calculation of the thrust of the pneumatic actuator, and the calculation of the thrust of the electric actuator. This article is about how to select the right actuator for the control valve. There are various types of actuators that can be assembled with control valves, pneumatic actuators, electric actuators, or hydraulic actuators, how to select the right actuator for the control valve is an important thing.
Step to Step Selection of Control Valve Actuator
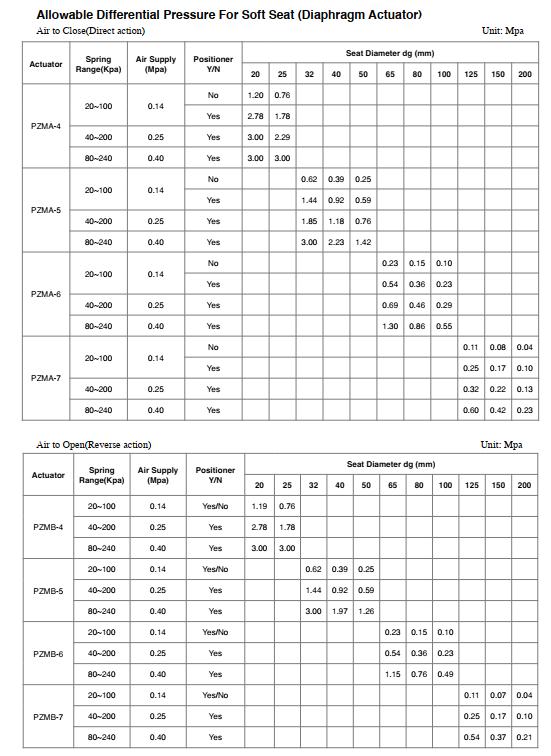
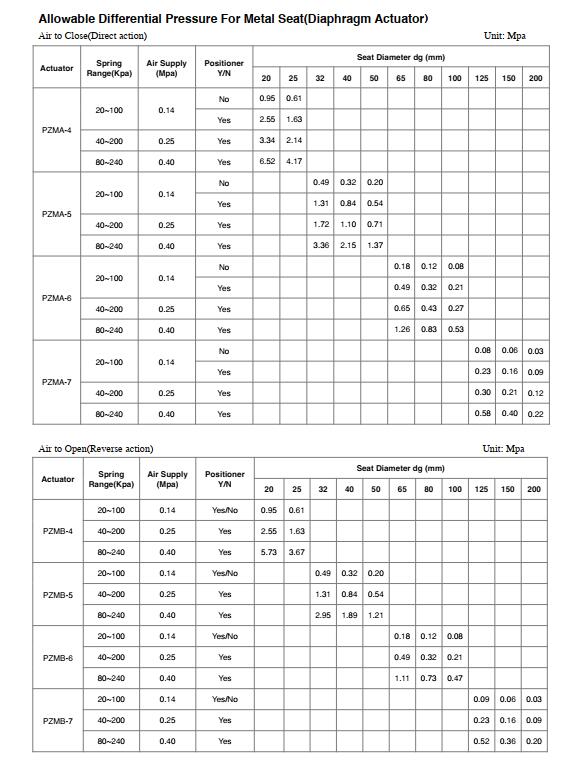
1. Maximum Differential Pressure & Allowable Differential Pressure
Refer to the manufacturer’s catalogs, which will be marked with differential pressure range sheets, according to normally open or normally closed, and the actuator model will be matched according to the standard valve seat diameter. So in the selection, we first need to confirm whether the maximum allowable differential pressure of the valve is within the allowable differential pressure range in the catalogs’ table, if it is less than the allowable differential pressure in the table, then assemble the standard actuator is ok. If the maximum allowable differential pressure of the valve is greater than the allowable differential pressure in the table, then the standard actuator thrust is small, and we need to change the trim design or increased the actuator thrust or torque. The following sheets are allowable differential pressure of single-seated globe type control valves, for soft-seat and metal-seat.
If you are interested in a complete catalog of THINKTANK control valves, you can refer to our download page to free download.
2. Electric Actuator – Control Valve Actuator
For the selection of an electric actuator, you can according to the thrust of the pneumatic actuator supplied, just equal to or a bit greater than it.
3. Outlet/Downstream Pressure for Control Valve Actuator Sizing
In the selection of a pneumatic actuator, or in the calculation of the valve diameter, we need to determine outlet/downstream pressure, there are two ways to estimate the value of outlet pressure.
a. If the inlet pressure of the valve is not very large, such as P1 = 70 bar (<100 bar), the outlet pressure can choose 0 bar. If the inlet pressure is greater than 100 bar, then outlet pressure according to the atmospheric, the pressure in the liquid level to take the value (not necessarily 0 bar).
b. The Actual Outlet Pressure = Inlet Pressure – Differential Pressure
If you do the above steps, there is generally won’t make mistakes in the process of selecting the actuator, and in the processing and assembly and pressure testing, we will verify again whether the selection is correct. Therefore, each control valve received by the customer needs to go through dozens of processes to complete. I believe that after understanding such a complex selection, you will be more willing to work with a professional control valve manufacturer to support your business, rather than just looking for a low-priced trader, and rashly give your project to them to produce.