Introduction
Pneumatic control systems have become increasingly popular in various industries due to their reliability, cost-effectiveness, and simplicity. They offer a multitude of advantages, such as precise control, energy efficiency, and low maintenance requirements. This comprehensive guide will provide an in-depth understanding of pneumatic control systems, their components, and their applications across various industries. By the end of this article, you’ll be well-equipped with the knowledge to optimize your industrial processes using pneumatic control systems. So let’s dive in!

What is Pneumatic Control
Pneumatic control is an automated system that uses compressed air or other gases to drive a wide variety of mechanical devices. It is widely used in industrial and commercial applications, particularly in the areas of manufacturing, construction, and transportation. At its most basic level, pneumatic control utilizes pressure changes within a sealed chamber to move pistons and activate switches which then control motors and other machines.

Understanding Pneumatic Control Systems
Pneumatic control systems utilize compressed air as the medium for transferring energy to perform mechanical work. The air is compressed and channeled through valves, cylinders, and other components to control and regulate various processes. These systems are commonly used in industries such as manufacturing, packaging, material handling, and more. The main components of a pneumatic control system include:
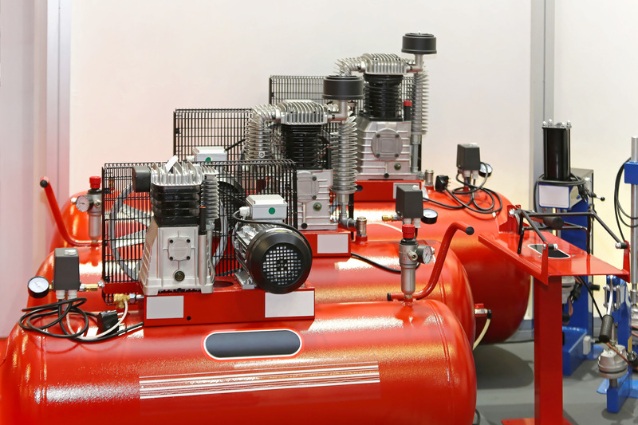
1. Air Compressor
The air compressor is responsible for supplying compressed air to the system, typically through pipes that connect to the other components. It is also used to regulate the pressure within the system and ensure it meets the specifications of a given application.

2. Control Valves
Control valves are responsible for regulating the flow of air and controlling how much pressure is applied to an actuator or device at any given time. They can be manually operated or actuated using electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic signals.
3. Sensors/Actuators
Sensors detect changes in pressure, temperature, or other variables within a system and then activate devices such as pumps or motors in response. Actuators convert input signals into movement (such as rotating a shaft) which can be used to open and close valves or drive machines such as conveyor belts.
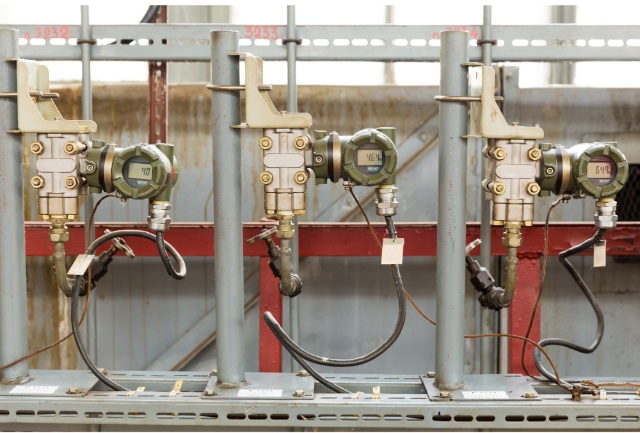

4. Piplines
Connecting pipelines are used to transfer fluids between different parts of a system, allowing them to communicate with each other so that valves can be opened or closed when necessary and sensors can detect changes in pressure throughout the system.
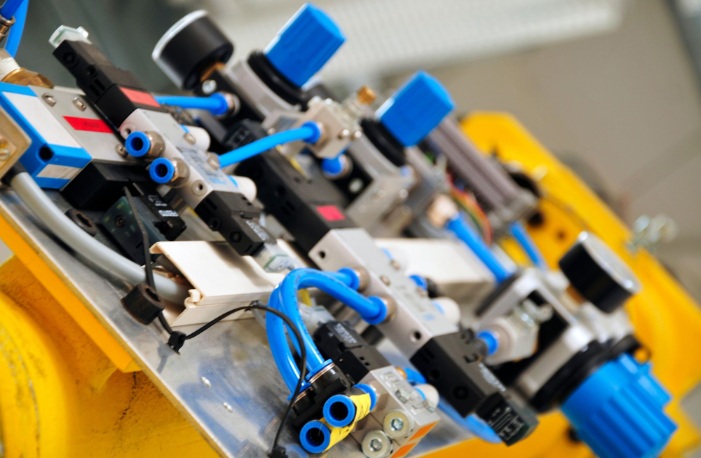
5. Fittings and Tubing
Connect various components of the system and transport the compressed air.
6. Pressure Regulation Equipment
A variety of equipment such as pressure gauges, regulators, solenoid valves, and safety relief valves are used to monitor and adjust pressures within a pneumatic system in order to ensure the safe operation of all components.
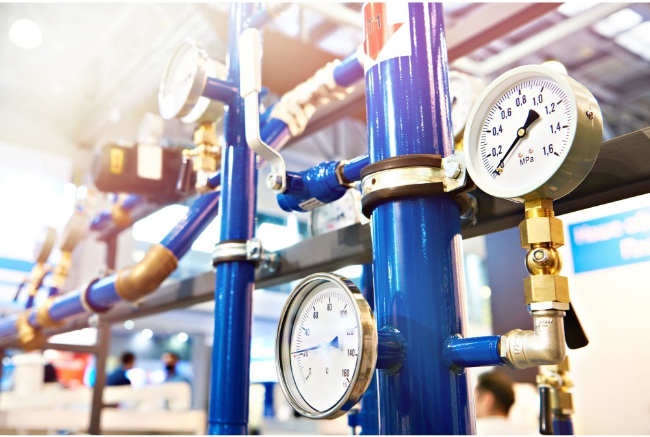

Types of pneumatic control systems
There are several solutions or design types for pneumatic control systems, depending on the specific application.
1. Single Pressure System
This is the simplest option and uses a single valve to control pressure in the system. It is best suited for applications that require a consistent pressure level.
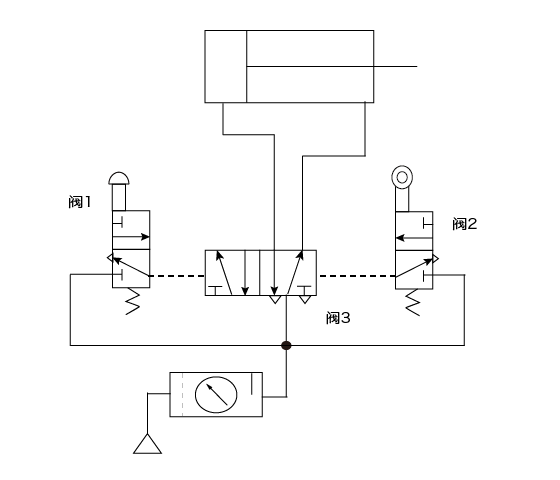
2. Dual Pressure System
This system uses two valves to control pressure levels and is often used in applications that require accurate speed control, or where there is a need for two separate pressure zones in the system.
3. Modulated Pressure System
This type of system uses multiple valves to create a stepped pressure increase which can be used for precise flow control over a wide range of pressures, making it ideal for applications such as fuel injection systems and spray painting.
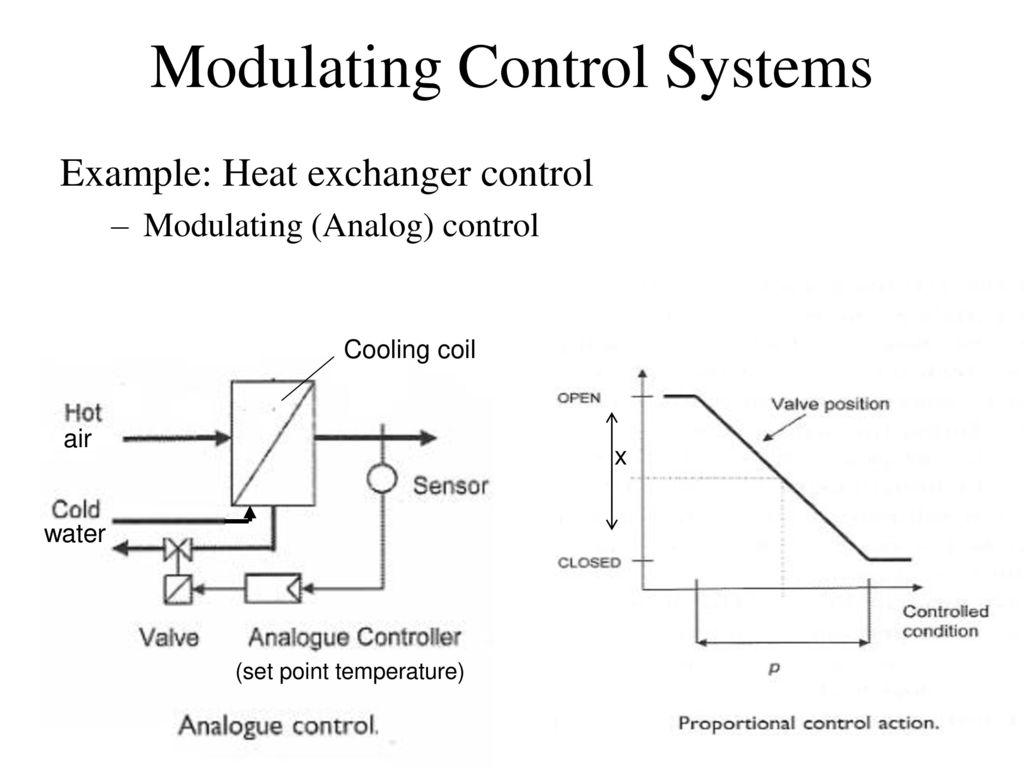
4. Pulse Controlled System
This system utilizes quick pulses of compressed air to actuate various devices, making it useful in applications such as robotic assembly lines where accuracy and fast response times are required.

How Pneumatic Control Works
Pneumatic control systems use pneumatics, which is the process of using pressurized air in order to power machines and equipment. It works by using air compressors to create a high pressure of air that is then directed through pipes into different components such as actuators, valves, cylinders, and motors. This creates a set of controlled movements that can be used to automate certain processes or operations. Pneumatic control systems are often used in both industrial and automotive applications, providing precise control over an array of mechanical parts.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Pneumatic Control Systems
In order to keep a pneumatic control system functioning properly, it is important to perform regular maintenance on the components. This includes inspecting and cleaning the air compressor, valves and fittings for any signs of damage or wear. Additionally, the pressure levels should be monitored regularly to ensure that they are within their optimal range.

Troubleshooting a pneumatic control system typically involves locating and isolating the problem before performing repairs or replacing parts as necessary. It is important to check all components of the system to ensure that they are functioning correctly before re-activating the system. If a part needs to be replaced, it is important to use parts that are compatible with the rest of the system in order to maintain its functionality. The following is the simple procedure table for your routine maintenance and troubleshooting of the pneumatic control system.
| Maintenance Procedures |
| Regular lubrication of pneumatic components |
| Periodic inspection of pneumatic hoses and fittings |
| Cleaning and replacement of air filters |
| Testing and calibration of pressure regulators and control valves |
| Inspection and replacement of worn or damaged components |
| Troubleshooting Procedures |
| Check for air leaks |
| Check for incorrect pressure settings |
| Check for clogged or damaged pneumatic components |
| Check for malfunctioning control valves or actuators |
| Check for incorrect wiring or electrical issues |
Advantages of Pneumatic Control Systems
Pneumatic control systems offer several advantages over other control mechanisms, such as hydraulic and electric systems. Some of these benefits include:
- Cost-effectiveness: Pneumatic systems generally have lower initial costs and maintenance requirements compared to other systems.
- Safety: Compressed air is non-flammable, reducing the risk of fire hazards.
- Reliability: Pneumatic systems are less prone to contamination and can withstand harsh operating conditions.
- Simplicity: Pneumatic components are relatively simple to design, install, and maintain.
Applications of pneumatic controls
Pneumatic control systems have a wide range of possible applications, including:
🟢 Automotive
Pneumatic control systems are used in a variety of automotive applications, including braking and steering systems, suspension systems, engine and transmission controls, fuel injection systems, and various other vehicle components.
🟢 Industrial
These systems can be used for machine tooling operations, material handling automation, conveyor speed control, welding process, control device, and safety device activation.

🟢 Mining
Pneumatic control systems enable more efficient mining operations by controlling ventilation doors, providing ventilation pressure monitoring, and remote control of underground diesel pumps.
🟢 Manufacturing
In manufacturing environments, these systems are used for controlling process variables such as temperature or pressure as well as manipulating valves to direct the flow of material.
🟢 Aerospace
The aerospace industry relies on these types of components to provide precise movement for aircraft instruments like trim tabs and elevator tabs or for flap and slat actuators.

Benefits of using pneumatic control in these applications
🟢 Automotive
Using pneumatic control systems in automotive applications allows for greater precision and accuracy when controlling vehicle parts. This improves the overall performance of the vehicle and increases safety.
🟢 Industrial
These systems provide efficient, reliable operation which saves time and money while also reducing errors. Additionally, they can be easily programmed to follow specific instructions and integrate with other industrial processes.
🟢 Mining
Pneumatic control systems allow for remote access and monitoring of operations which increases safety by limiting the physical presence of workers underground.
🟢 Manufacturing
These systems enable precise control of process variables like temperature or pressure, resulting in improved product quality. They also reduce variability in production runs by maintaining consistent operating conditions.
🟢 Aerospace
By using pneumatic control systems for aircraft instruments, engineers are able to make pressure controls achieve more precise movement functionality which is essential for safe operation.
Types of Pneumatic Valves
Pneumatic valves play a critical role in controlling the flow of compressed air within the system. The three primary types of pneumatic valves are:
1. Directional control valves
These valves direct the flow of compressed air to different parts of the system and are commonly classified by their port and position configurations.
2. Flow control valves
These valves regulate the flow rate of compressed air in the system, allowing for precise control over the speed of actuators.
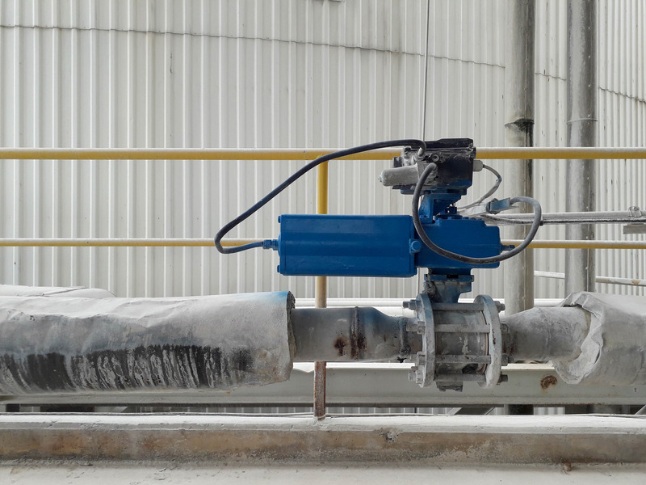

3. Pressure control valves
These valves maintain the desired pressure levels within the system by regulating the pressure of the compressed air.

Pneumatic Actuators
Pneumatic actuators convert the energy from the static pressure of the compressed air into mechanical motion, which drives various processes in industrial applications. The two main types of pneumatic actuators are:
- Linear actuators: These actuators produce linear motion and are often used in applications such as pushing, pulling, or lifting loads.
- Rotary actuators: These actuators generate rotational motion and are commonly used for tasks such as turning, mixing, or tightening.
Optimizing Pneumatic Control Systems
To get the most out of your pneumatic control system, consider the following tips:
✅ Proper system design
Ensure that the system is designed to meet your specific application requirements, taking into account factors such as pressure, flow rate, and actuator speed.
✅ Regular maintenance
Perform routine maintenance checks, such as inspecting for leaks, monitoring pressure levels, and lubricating components, to ensure the system operates efficiently and reliably.
✅ Energy efficiency
Utilize energy-saving components, such as variable speed compressors and pressure regulators, to reduce energy consumption and operating costs.
✅ Training
Provide training for personnel to ensure they are knowledgeable about the operation and maintenance of pneumatic control systems.

Conclusion
Pneumatic control systems offer numerous advantages for various industrial applications, from manufacturing and packaging to material handling and robotics. By understanding the fundamentals of pneumatic control systems, their components, and their applications, you can optimize your industrial processes for increased efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Regular maintenance, proper system design, energy efficiency measures, and training of personnel are essential for maximizing the benefits of these systems.
Embracing pneumatic control technology can greatly improve your operations and help your business stay competitive in today’s fast-paced industrial landscape. So, take the time to explore the potential of pneumatic control systems for your specific needs, and watch your productivity soar. THINKTANK is a reliable pneumatic valves manufacturer in China for over three decades, welcome to contact our representitive for a free consultation at anytime.






