In the world of industrial flow control, the actuator valve stands out as a crucial component, pivotal in regulating the flow of various types of liquids and gases. These valves operating through the automation provided by actuators, ensure precision, efficiency, and safety in number of industrial applications, from simple water pipes to complex petrochemical systems.

what is an actuator valve
An actuator valve is a mechanism that controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially opening various passageways. This process is achieved through an actuator, a type of driving power that is responsible for moving or controlling the valve.
What are 4 examples of actuators | different types of valve actuators
There are several types of actuators, such as:
1. Manual actuators
Manual actuators are require human intervention to control the valve, usually through a handwheel or lever.
2. Electric actuators
Electric actautors often use electric or servo motors to operate valves. They are commonly used for remote control of valve operations, especially in vast or potentially hazardous installations.
3. Pneumatic actuators
Pneumatic actuators are use compressed air to apply force and initiate valve movement, usually used for emergency application, or reliable and fast respond condition.
4. Hydraulic actuators
Hydraulic actuators are utilize pressurized liquid, such as oil to control valve opening. These are often employed in heavy-duty industrial settings due to their high force capabilities.
how does an actuator valve work
An actuator valve works by converting energy into mechanical motion to open, close, or control the position of a valve. The energy used can be pneumatic (air or gas), electric, or hydraulic (liquid fluid). Different actuators have different working principle, we will introduce it one by one.
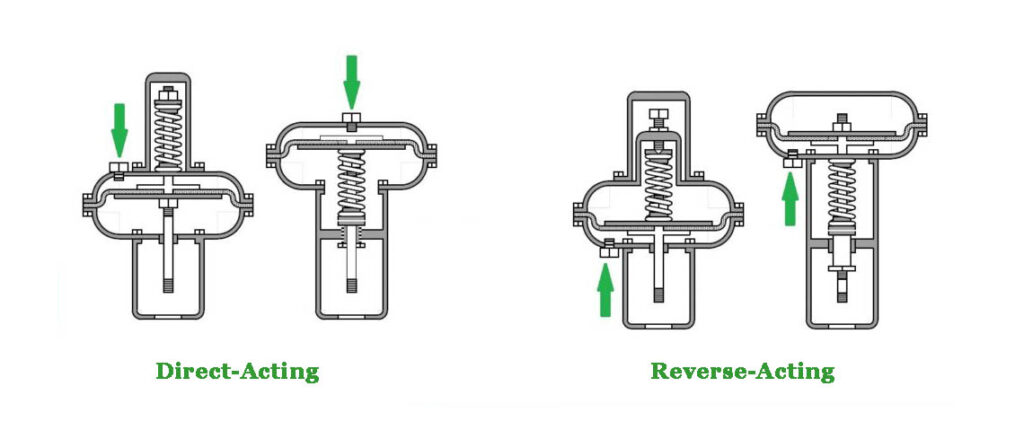
Pneumatic Actuator Valves
Pneumatic actuator valves use air or gas pressure to driving valve action. The pressure is applied to a piston within a cylinder or a diaphragm, which then moves the valve stem or rotates the valve control element. They are common in “fail-safe” applications where the valve needs to close or open if the power is lost, it means the actuator is single-acting/spring return type, using spring action to move the valve to its safe position.
Electric Actuator Valves
Electric actuator valves use electric motors or motorized actuator to move a valve. They respond to electrical signals sent from a control system to open, close, or throttle a valve. It has precise positioning and smooth motion, and electric actuator valves are often used when remote control is necessary.

Hydraulic Actuator Valves
These use liquid fluid like oil hydraulic under pressure to drive the valve opening. They are similar to pneumatic actuators but can used for higher forces, making them suitable for larger, high-pressure valves or when high force is required for operation.
how to install actuator valve
Installing an actuator valve involves several key steps to ensure proper setup and functionality. Here’s a general guide for your reference:
Step 1. Remove the Old Actuator
If you’re replacing an actuator, first disconnect power and remove the old one from the valve. Ensure all energy sources are safely isolated before proceeding.
Step2. Prepare the Valve
Before installing the new actuator, the valve should be manually positioned to match the actuator’s starting position. Usually we should setting the valve to a closed position.
Step 3. Mount the Actuator
Align the actuator with the valve stem or linkage and secure it in place using the provided hardware. Please kindly make sure the actuator is properly seated and securely fastened to prevent any play or movement.
Step 4. Electrical Connections
For electric actuators, connect the actuator to the power source and control system as per the manufacturer’s guidelines. If you buy the actuator valves from THINKTANK, you can call our experts in anytime to support your installation. Please ensure compatibility between the actuator’s voltage requirements and the power source, and make sure you enter the correct voltage for the actuators.
Step 5. Configuration and Testing
After installation, configure any settings (like rotation limits, control signals, etc.) according to the manufacturer’s installation guide. Then, test the actuator by operating it through several open and close cycles to ensure correct function and proper installation.
What is the function of actuator
A pneumatic valve actuator works by converting air pressure into motion to facilitate the opening or closing of valves. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it functions:
1. Air Pressure Application
Pneumatic actuators operate using compressed air. The air pressure is applied to a piston or diaphragm within the actuator, creating force that generates motion, please note the right air power for the actuator, if over required air pressure, it will damage the actuator.
2. Movement Creation
The force exerted by the compressed air causes the piston or diaphragm to move. This movement is then transferred to the valve stem, which is connected to the internal components of the valve, leading to the opening or closing of the valve.
3. Valve Positioning
Depending on the design of the actuator and the valve system, the actuator can either open, close, or partially move the valve to a specific position to regulate flow. The valve’s position can be “normally closed” or “normally open” in its resting state, depending on the system’s requirements.
4. Air Pressure Release
Once the desired valve position is reached, the air pressure can be maintained or vented, depending on whether the valve needs to stay in position or return to its original state.
what is valve automation
Valve automation refers to the process of using mechanical, electronic, and instrumental means to adjust a valve’s position or operational status automatically, without the need for direct human intervention. This is typically achieved through the use of a valve actuator and a control system. The actuator can be powered in various ways, including electric, pneumatic(air), hydraulic(liquid), or manual means, and it’s responsible for moving or controlling the valve.
The primary benefits of valve automation include the ability to precisely control flow and pressure within a system, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced safety, particularly in hazardous environments. It allows for remote operation, which is crucial in locations that are inaccessible or dangerous for individuals, and it can significantly reduce operational costs over time. Automated valves are essential components in various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, manufacturing, and more, where they’re used to control the flow of liquids, gases, and slurries within a system or process.
How do I know if my valve actuator is bad
Identifying a malfunctioning valve actuator involves observing several key signs:
Improper Operation
If the valve doesn’t open or close correctly, this could indicate an issue. Electric actuators may have incorrect voltage supply, while pneumatic actuators require sufficient air power.
Unusual Noises
Strange sounds during operation can signal internal problems, such as broken components or issues with the motor.
Physical Damage
Visible damage to the actuator, broken springs, or issues with seals indicate physical problems that could affect functionality.
Unreliable Acting
Inconsistent operation or unexpected movements are signs of potential actuator failure.
Excessive Condensation
Too much moisture within the system can lead to actuator malfunctions.
Response to Diagnostic Tests
For more sophisticated systems, using diagnostic tools or actuator tests can help determine functionality, such as changes in the engine’s audible note when testing variable valve timing actuators.
Regular maintenance and timely response to these warning signs are crucial in preventing operational failures and expensive repairs. THINKTANK provide a professional maintenance manual for our customers, and also offer 24/7 service in case we can assistance the end-users in time.
What is the difference between an actuator and an actuator valve
Actuator: An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving or controlling a mechanism or system. It requires a source of energy, typically electric current, hydraulic fluid pressure, or pneumatic pressure, and converts that energy into motion. It’s a fundamental part of the mechanisms of machines, particularly those that require precise control. Actuators are often used in industrial applications or where there is a need for automated movement.
Actuator Valve (or Actuated Valve): The term “actuator valve” generally refers to the combination of a valve and its actuator. The valve itself is a device that regulates, directs, or controls the flow of a fluid by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. When an actuator is connected to the valve, it controls these mechanisms automatically or remotely, depending on the setup. Essentially, the actuator operates the valve without the need for manual effort.
The main difference between them is their function. The actuator is responsible for providing motion or force, while the “actuator valve” refers to the combination of the valve and the actuator working together to control the flow in a system.

What happens when an actuator fails
As an engineer at THINKTANK, I understand the critical role actuators play in our industrial processes. If an actuator fails during operation, several consequences can occur, depending on the specific application of the actuator:
1. Process Trouble
Actuators are integral to maintaining flow, pressure, and temperature within process systems. A malfunction can cause disruptions, leading to downtime, inefficiency, and in some cases, the halting of entire production lines.
2. Safety Hazards
In systems where actuators control the flow of potentially hazardous materials or operate under high pressures, failure could result in leaks, spills, or explosions, presenting significant safety risks to personnel and the environment.
3. Equipment Damage
Unexpected actuator failure can lead to uncontrolled pressure or flow, potentially damaging other equipment in the process line, and leading to costly repairs or replacements.
4. Non-Compliance
For industries regulated under strict compliance standards, actuator failure can result in conditions that violate these standards, leading to legal consequences or the imposition of fines.
We help our customers mitigate these risks by using our high-quality, reliable actuator valves, assisting our customers in implementing rigorous maintenance schedules, and employing real-time monitoring systems. Moreover, we encourage the end-users proactive replacement and servicing of actuators and associated components to anticipate failures before they lead to more significant issues. This approach helps ensure safety, compliance, and uninterrupted productivity in our industrial processes.
What is the difference between solenoid valve and actuator
The main difference between a solenoid valve and an actuator lies in their function and operation mechanisms:
Solenoid Valve
This is an electromechanically operated valve controlled by an electric current through a solenoid coil. When energized or de-energized, the solenoid creates a magnetic field that either opens or closes the valve, regulating the flow of liquids or gases in a system. Solenoid valves are known for their quick opening and closing response and are often used in fluid control systems.
Actuator
An actuator, on the other hand, is a device that converts energy (typically electric current, hydraulic fluid pressure, or pneumatic pressure) into motion. This motion can be linear or rotary, depending on the type of actuator. Actuators are used to operate a valve that controls the flow of the medium but can also be used in various other applications that require movement, like adjusting machinery components or operating doors. Actuators offer more control options, such as positioning feedback and varying degrees of opening, and they can be used to drive various types of valves, not just on/off types like solenoid valves.
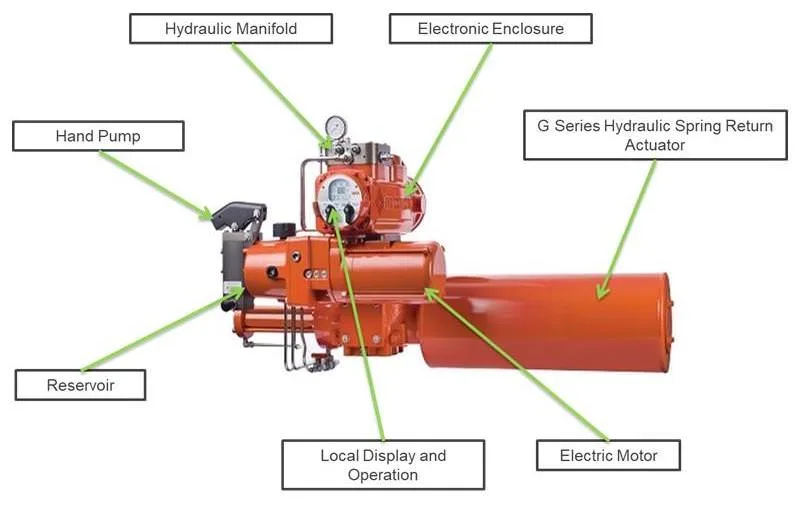
How is an actuator connected to a valve
An actuator is connected to a valve through a series of components and steps that ensure proper alignment, operation, and control. Here’s how the connection is typically made:
Mounting Interface
Actuators and valves have standardized mounting interfaces. For instance, many actuators and valves follow the ISO 5211 standard for flange mounting, which ensures compatibility and proper alignment between the actuator and the valve.
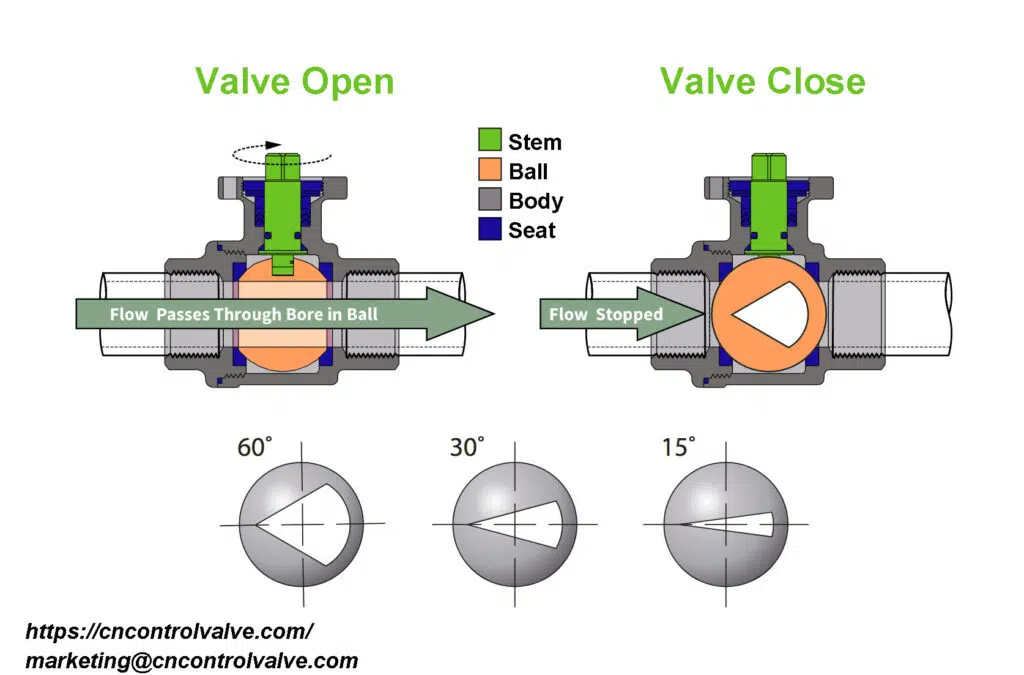
Coupling
A mechanical component known as a coupling connects the actuator stem or output shaft to the valve stem. This coupling transfers the rotational or linear motion from the actuator to the valve, enabling it to open, close, or modulate. The coupling must be properly sized and aligned to ensure efficient transfer of motion.
Position Indicators and Limit Switches
After physical installation, position indicators are often set up to provide visual indication of the valve’s position (open or closed). Additionally, limit switches may be installed and adjusted to provide electrical confirmation of the valve’s position and to prevent over-rotation or over-travel of the valve.
Configuration and Calibration
Once installed, the actuator may require configuration and calibration, particularly for modulating service, to ensure it responds correctly to control signals and accurately positions the valve.
The specific process can vary based on the type of actuator (electric, pneumatic, hydraulic) and the type of valve (ball, butterfly, gate, globe, etc.)
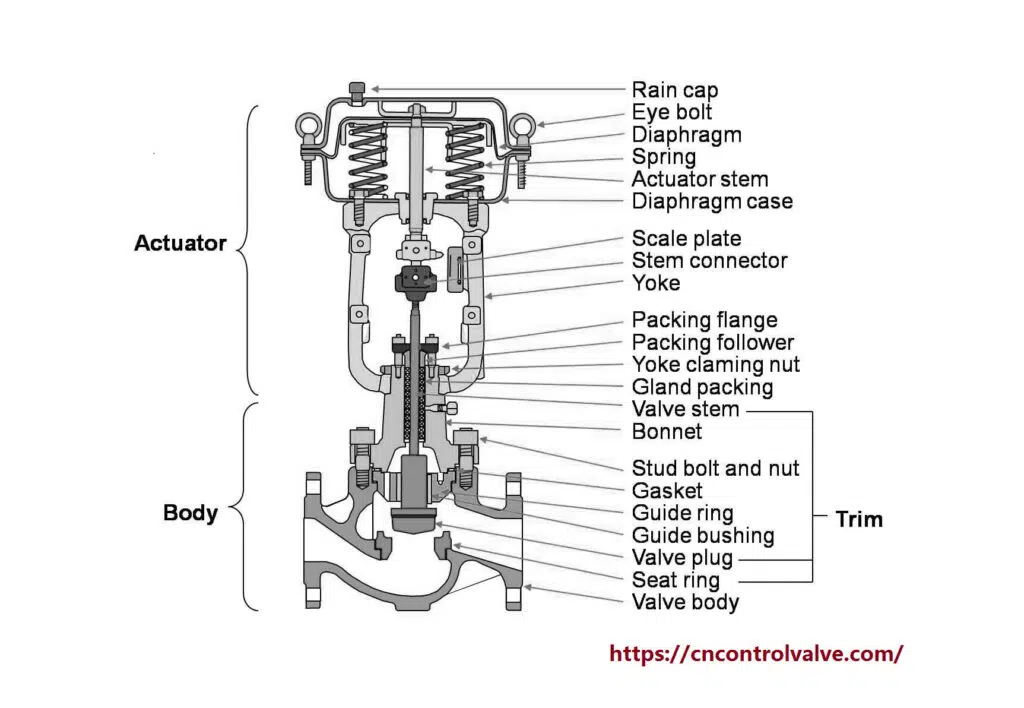
What are electric actuators
Electric actuators convert electrical energy into mechanical motion. They produce linear movements and are commonly connected to valves. These devices are powered by single-phase or three-phase AC or DC motors, often used in combination with different gears.
The Advantages of Electric Actuators
Electric actuators have user-friendly interfaces and meet diverse programming needs. They work well in fast production scenarios and are adaptable. Compared to hydraulic actuators, electric actuators have the advantage of lower long-term costs, particularly in terms of cleaning up hydraulic fluid spills.
Electric actuators excel in medical applications. They are precise, reliable, and have compact designs that easily fit into existing systems without compromising performance. As the medical field prioritizes efficiency, these actuators ensure optimal functionality.
Understanding the Design
An electric actuator consists of an electric motor, a screw, a nut, and gears (for smaller motors). It creates movement when the nut moves along the screw. Rotary electric actuators use the motor’s electromagnetic power to rotate and operate like butterfly valves, ball valves, and plug valves. They allow for multiple stops in each stroke. On the other hand, linear electric actuators are used with valves like pinch, globe, diaphragm, and others. They are ideal for precise requirements. Linear motion is achieved using an ACME screw assembly or a motor-driven ball screw.
Type of Electric Actuators
Electric actuators come in two types: rotary and linear. When selecting a rotary actuator, check the torque and motion range. For linear actuators, consider factors such as the number of turns, actuating force, and valve stem stroke length.
TOP 10 famous valve actuator manufacturer in the world
According to industry leaders until 2022, the following companies are globally known for their high-quality valve actuators:
1. Emerson Electric Co.
Emerson Electric Co offers a variety of actuators, known for its Fisher, Bettis, and El-O-Matic brands, Emerson has a strong reputation for producing reliable electric, pneumatic, and hydraulic actuators. Here are the types and models of actuators available from Emerson:
- Electric Actuators
Emerson provides a range of electric actuators under their Bettis™ and EIM™ lines. These actuators are known for their smart functionality and have been utilized globally in sectors such as oil and gas, water and wastewater, marine, and power generation.
- Pneumatic Actuators
The company also offers pneumatic actuators, which are market leaders known for their high performance. These actuators use air pressure to control or move mechanisms and are widely used in various automation challenges.
- Hydraulic Actuators
While specific models are not mentioned in the provided resources, Emerson is known for its high-quality hydraulic actuators, which use liquid pressure for operation and are commonly used in heavy-duty industrial applications.
2. Flowserve Corporation
Flowserve offers a variety of actuator types, including but not limited to:
- Electric Actuators: Flowserve manufactures electric actuators designed to control the flow of liquid, gas, or air in various applications. They offer both linear and rotary motion electric actuators.
- Pneumatic Actuators: These actuators use air pressure to facilitate motion and are used in various industrial applications. Flowserve’s pneumatic actuators are known for their reliability and efficiency.
- Hydraulic Actuators: Using fluid power to generate motion, Flowserve’s hydraulic actuators provide high force in applications requiring precise control of heavy loads.
- Electro-Hydraulic Actuators: These combine elements of hydraulic and electric actuators, offering precision control with robust power.
- Rotary Actuators: Specifically designed for rotating equipment, these actuators can be used in various applications where precise positioning is required.
- Linear Actuators: These are used in applications requiring linear motion, such as opening or closing a gate or moving a control rod.
3. Rotork Plc
Rotork is a major player in the actuator industry with innovative solutions. Here are some types of actuators that Rotork is known for:
Electric Actuators
Rotork offers a variety of electric actuators suitable for different industries. One of the well-known product lines is the IQ range, which is designed for multi-turn applications and known for its intelligence, reliability, and robustness.
Pneumatic Actuators
Rotork’s pneumatic actuators are designed for reliability and high performance. The product range includes the GP (pneumatic) and GH (hydraulic) range scotch-yoke actuators which are used for their high torque output.
Hydraulic Actuators
Similar to their pneumatic counterparts, Rotork’s hydraulic actuators deliver high force in a reliable format. The RH range is known for its hydraulic actuators.
Electro-Hydraulic Actuators
The Fluid Systems range provides a solution for both rotary and linear operation, utilizing a combination of electrical and hydraulic power, often used when high torque is required but there’s a preference for electrical control.
Process Control Actuators
These actuators are used in the control of process flows in various industrial applications. The CP range is commonly used for control and process applications.
Subsea Actuators
Designed for underwater applications, these actuators can withstand high pressure and harsh environmental conditions.
4. Schlumberger Limited
Particularly through its Cameron brand, Schlumberger, being a leading company in the oilfield services, is known for providing a variety of sophisticated technology solutions, including valve actuators, for the oil and gas industry.
Typically, the types of actuators that might be available from a company like Schlumberger would include:
① VA Series LEDEEN Actuators
For on-off or modulating control of any ball, plug, or butterfly valve utilizing compressed air, natural gas, or nitrogen actuator supply.
② SY Series LEDEEN Actuators
For on-off or modulating control of any quarter-turn operated valve.
③ Scotch-Yoke LEDEEN Actuators
For on-off control of any natural gas transmission ball or plug valve using the high-pressure natural gas from the pipeline with a gas-over-oil configuration.
④ CAMERON® LEDEEN Quarter Turn Actuator GS Series – IP67 Pneumatic
5. IMI plc
IMI plc offers linear actuators designed for demanding applications in industries like power, oil, and gas. These actuators are used to drive control valves, including those in turbine bypass applications.
Digitally Configurable Actuators
IMI plc also provides digitally configurable actuators with a wide range of setup options, offering flexibility in control and automation.
Industrial Linear Actuators
IMI Critical Engineering, a division of IMI plc, manufactures expertly crafted pneumatic linear piston actuators, contributing to industrial automation and control systems.
Customized Actuation Systems
IMI STI, a part of IMI plc, specializes in designing and manufacturing complete actuation systems that can be tailored to meet specific customer needs and applications,
6. SMC Corporation
SMC Corporation excels in offering an extensive range of actuators tailored to a myriad of applications, ensuring precision, efficiency, and reliability. Their product lineup includes:
Dual Rod Actuators
Engineered for high stability, these actuators come with two parallel rods, providing non-rotating, precise linear motion, ideal for handling asymmetrical loads with minimal deflection.
Heavy Duty Actuators
Built for rugged performance, these robust actuators are designed to withstand challenging environments and high-force applications, ensuring durability and long operational life.
Precision Actuators
Specifically designed for high accuracy and repeatability, precision actuators cater to the need for exact movement in critical applications, such as intricate assembly operations or precise machining tasks.
Electric Actuators
Incorporating high-performance motors, the EQ series delivers speed and exactitude, suited for complex and automated systems. The range includes various configurations like sliders, rod and rodless types, and grippers, highlighting series such as LEHZ, LEHZJ, and LEHF, known for their adaptability in diverse operations.
Pneumatic Actuators
Embracing both single and double acting cylinders, rotary actuators (vane and rack & pinion), and slide units, these actuators stand out for their efficiency and are the go-to choice for applications requiring compressed air power.
Rodless Cylinders
Eliminating the need for an external rod, these are ideal for confined spaces, reducing bending issues and offering a compact solution for linear motion requirements.
7. Festo AG & Co. KG
Festo is renowned for its high-quality, innovative automation solutions, and its range of actuators and drives is no exception. They provide a diverse selection designed to meet the needs of various industrial applications. Here are some categories of actuators and drives you can find at Festo:
Electric Actuators
Festo’s electric actuators are designed for precise control and positioning. They are energy-efficient and suitable for a wide range of industrial applications.
Pneumatic Actuators
Known for their reliability, Festo’s pneumatic actuators offer quick response times and simplicity in their design and operation, making them suitable for a host of applications.
Linear Actuators
These actuators deliver linear motion and are known for their accuracy, efficiency, and ability to handle a wide range of loads.
Semi-rotary Drives
Festo offers semi-rotary drives for tasks requiring rotational movement. These are compact, efficient, and perfect for operations requiring precision.
Process Automation Actuators
These actuators are designed for process automation and are robust enough to handle challenging environments, often found in process industries.
Grippers
Festo provides a variety of grippers designed for different tasks, ensuring the secure handling and movement of workpieces in automated systems.
Stopper Cylinders
These specialized cylinders are used to stop workpiece carriers at defined positions along transfer systems.
Motors and Controllers
Festo offers a range of motors and controllers that can be integrated into various systems for smooth, efficient, and precise control.
Festo’s actuators and drives are synonymous with quality, innovation, and performance. Their range is comprehensive enough to suit a myriad of industrial automation needs, providing the reliability and efficiency that customers have come to expect from a leader in the field of automation.
8. Parker Hannifin Corp
Parker Hannifin Corporation offers a diverse array of cylinders and actuators designed to meet and exceed the needs of customers across a wide spectrum of industries. Their range of actuators is comprehensive and includes the following categories:
Linear Actuators and Cylinders
Parker offers a variety of linear actuators and cylinders both in standard and custom configurations. These include tie-rod cylinders, rodless actuators, guided actuators, and more. They are known for their durability, reliability, and high performance.
Rotary Actuators
These actuators provide rotational motion and are designed for high torque and pneumatic operation, available in various configurations. They are used in a wide range of automation applications.
Grippers
Used extensively for picking and placing objects in various industrial applications, Parker’s grippers are efficient and have a compact design, making them suitable for operations requiring precision.
Pneumatic Actuators
Parker’s pneumatic actuators include a range of cylinders, from compact, round, and tie-rod cylinders to rotary actuators and grippers. They are known for their speed, force, and precise motion.
Electric Actuators
Designed for a range of industrial applications, these actuators offer an efficient, clean, and low-noise solution for motion control. They are available in various configurations and can be highly customized.
Electro-Hydraulic Actuators
These are self-contained units that use an electric motor to provide operational power and are known for their high force capabilities, precision control, and reliability in harsh environments.
Rodless Actuators
Parker’s rodless actuators are designed for a wide range of applications where space is at a premium. They offer guided motion and are known for their durability and reliability.
Miniature Actuators
These actuators are designed for applications requiring compact size and high precision. They are utilized in various industries, including medical, diagnostics, and semiconductors.
9. Siemens AG
When it comes to advanced HVAC solutions, Siemens is a name you can trust. Siemens has range of valves and actuators are engineered with precision, integrating the latest technologies to meet the demanding needs of today’s HVAC systems. Here’s what sets our actuators apart:
Unparalleled Precision and Efficiency
Siemens actuators are designed for accuracy and energy efficiency, ensuring precise control in your HVAC systems. They work seamlessly with Siemens valves to guarantee consistent performance and comfort.
Comprehensive Range for Various Applications
Whether for commercial, industrial, or residential settings, there’s a Siemens actuator for every scenario. From non-spring return actuators to spring return models, Siemens offers solutions tailored for reliability, flexibility, and compatibility.
Innovative Features for Enhanced Performance
Siemens actuators come equipped with a host of innovative features such as manual override, position indicators, and adjustable span for modulating models, providing optimal control and ease of use.
Compatibility and Integration
Designed for seamless integration with Siemens valves, the actuators support a wide range of control signals and have multiple force options, making installation and commissioning hassle-free.
Trusted Quality and Durability
Backed by Siemens’ reputation for quality, our actuators are built to last. They undergo rigorous testing to ensure they meet global standards and deliver uninterrupted performance for years to come.
Sustainability and Energy Savings
Energy efficiency is at the heart of Siemens HVAC solutions. Their actuators contribute to significant energy savings, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
10. ABB Ltd
ABB pneumatic actuators are ideal for various applications involving the movement of air dampers, fan inlet vanes, louvers, diverters, lever-operated ball or butterfly valves, turbine governors, fluid drives, and similar control elements, whether the motion required is rotary or linear.
Linear pneumatic actuators LP
LP linear pneumatic actuators are used to regulate various final control elements such as dampers, inlet vanes, louvers, lever-operated valves, turbine governors, and fluid drives. These actuators receive input signals that enable them to position the final control element either in a linear or rotary motion using a lever linkage.
Universal pneumatic rotary actuators UP
The UP Pneumatic Universal Rotary Actuators are used to control various components such as dampers, fan inlet vanes, lever-operated valves, turbine governors, fluid drives, and other final control elements.
Electric Rotary actuator PME
Electrical rotary actuators have torque ratings ranging from 100 Nm to 16,000 Nm. These actuators are designed to operate final control elements, such as flaps, cocks, dampers, and more, that require a rotary movement of approximately 90°. The torque is transferred to the control element either through a lever or linkage bar assembly, or by directly coupling the actuator to the cock flange.
Electrical linear actuators of the LME… / RSD … series
The LME… / RSD … series of electric linear actuators are the best choice for operating final control elements that require linear movement. These actuators convert rotary motion to linear motion with minimal wear and transfer the force directly to the control element.
Case Study
These above top 10 manufacturers are renowned for their extensive experience, broad product range, global service networks, and consistent emphasis on innovation and reliability in the field of valve actuation.
Conclusion
Now we know actuator valves are pivotal components in modern industrial processes, providing efficient, automated control of valves, thereby no more need for manual operation. They are powered by various means, including electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic sources.
So, whether you’re an industry veteran or a newcomer seeking reliable flow control solutions, THINKTANK’s actuator valves deserve your attention. Visit our website, explore our wide range of products, and rest assured knowing you’re in capable hands.
Source
- cncontrolvalve.com – 3 Steps To Installing Your New Actuator Of Valve
- indelac.com – How to Install, Operate & Troubleshoot an Electric Actuator
- belimo.com – Valve Retrofit Installation Instructions for use with …
- pentair.com – Install Guide | Valve Actuator
- redwhitevalvecorp.com – A Guide to Valve Actuators
- inyopools.com – INTELLIVALVE™ 2-WAY, 3-WAY VALVE ACTUATOR
- valin.com – How to Select Valve Actuators for Rotary Valves
- mpofcinci.com – How to Select a Valve Actuator: Types, Sizing, Safety, More
- globalspec.com – Valve Actuators Selection Guide
- chemengonline.com – Valve Actuator Selection Guide
- instrumentationtools.com – How to Select an Actuator for Valve