Brief
The main difference between a flow control valve and a throttle valve is the type of control they offer. A flow control valve provides automatic, precise regulation of the flow rate by means of an adjustable valve stem or disc that moves up and down to vary the opening size. A throttle valve, on the other hand, offers manual, coarse regulation of the flow rate by means of a hand lever or handwheel that moves left and right to adjust the valve position. Both types of valves can be used for controlling fluid flow, but each is better suited for different applications.
Flow control valves are most often employed in applications where precise regulation of the flow rate is essential, such as in pipelines, chemical processing, and medical device manufacturing.
Throttle valves offer a more limited range of control and are usually used in applications where coarse regulation is required, such as in water supply systems or HVAC systems.
What is a flow control valve?
Flow control valves prevent excessive flow or rate control by limiting flow to a pre-selected maximum rate regardless of line pressure changes. The pilot control responds to the differential pressure generated across the orifice plate mounted downstream of the valve.
How a flow control valve work
A flow control valve is any device made to change the flow rate or pressure of a fluid. They are designed to fit into complex pneumatic and hydraulic systems. Flow control valves respond to signals generated by devices such as thermometers or flow meters. These valves have simple tool orifices and a complex set of electro-hydraulic valves to accommodate different variations in pressure and system temperature.
Flow control valve Solution
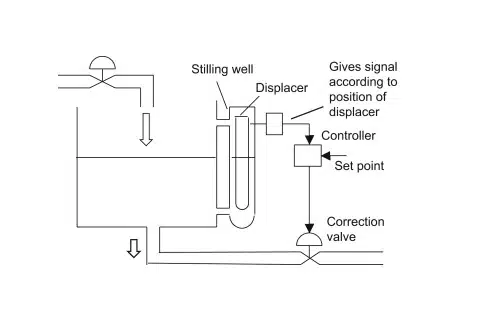
One method is shown below of how to use a flow control valve to control the level in a vessel. Surface turbulence may occur as liquid enters the vessel or as the liquid agitates or possibly boils, and this high frequency “noise” in the system is usually filtered out by using a stilling well, as shown in Figure 6. However, it must be recognized that the stilling well constitutes a U-tube in which low frequency oscillations of the liquid surface may occur. The vertical motion of the displacer causes a signal to be transmitted to the controller. This can be achieved by the motion causing the slider of the potentiometer to move on its track.
In the semiconductor industry, we generally think of flow control valves as being adjusted to control flow rates independent of pressure and throttle valves as being adjusted to control pressure independent of flow.
This is just convention, and there is no technical definition to drive this distinction. In semiconductor processing, flow control is used upstream of the process zone, while the pressure in the process zone is controlled by a throttle downstream of the process zone. This makes the control of the processing zone relatively independent of upstream and downstream conditions.
Terminology: Throttle Valve
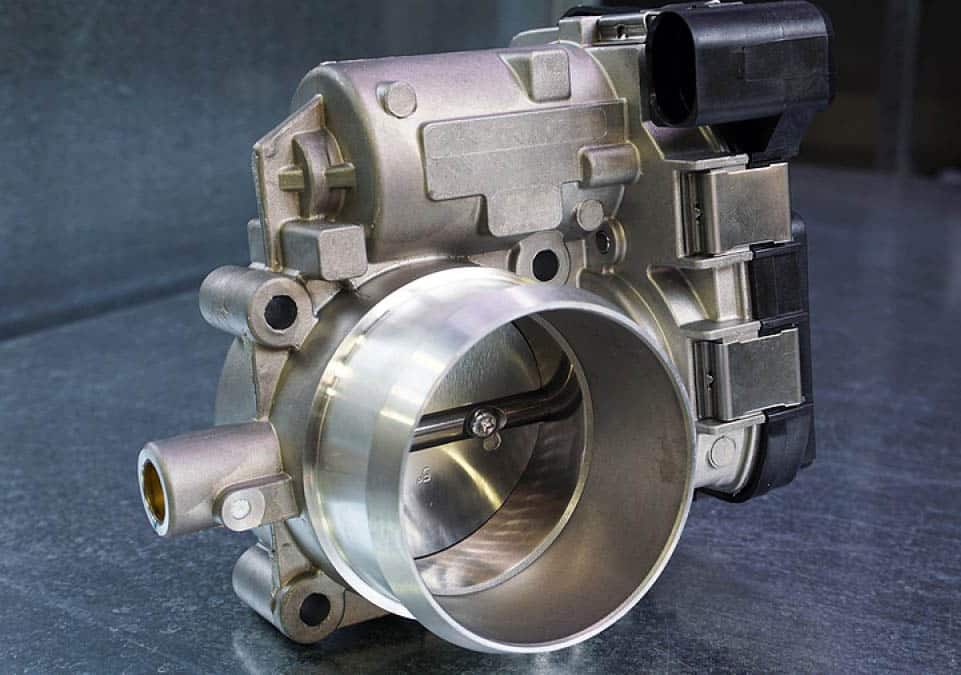

In other terminology, flow control valves are mostly used in industry, while throttle valves are mostly used in automotive engines. So don’t get wrong about the throttle valve if it’s a part of the engine, not an industrial valve used for industries.
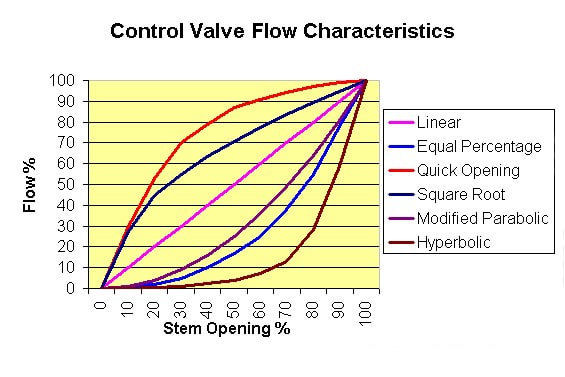
A flow control valve will provide some sort of linear/equal percentage-flow capacity relationship in response to an input signal applied to the process dynamics.
What is a throttle valve?
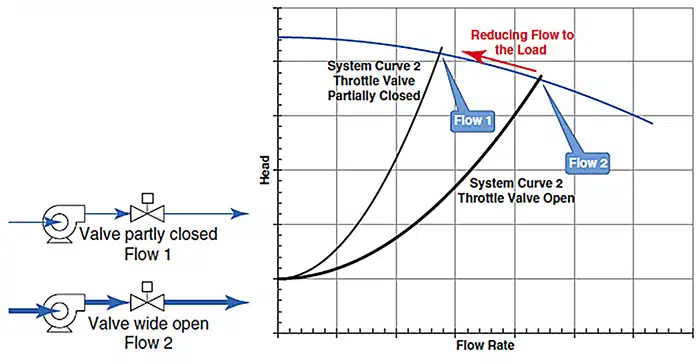
A throttle valve is a type of valve that controls the flow of fluid from one place to another by starting, stopping, and regulating it. Typically, there will be a significant pressure difference between the throttle valve’s upstream and downstream sides. With more flow restriction inside the throttling valve, the pressure drop grows. These kinds of valves may be controlled using a wide variety of control techniques. Under certain operating circumstances, many valves can function as throttling valves. We shall discover the fundamentals of throttling valves in this post.
Working principle of a throttle valve
In a throttle valve, a block is created inside the valve in order to obtain the desired parameters, such as flow rate, temperature, pressure, etc. The flow rate is influenced by the design limitations and the frictional forces generated during the flow. Generally, the stem is raised or lowered to adjust the size of the flow path through the valve. They can even close the valve completely to stop the flow.
If the throttling valve you encounter is used in an industrial application, then the throttling valve is actually a type of control valve and it can be used as a control valve.
Flow control valves are controlled by throttling the flow rate, which is adjusted between 0 and 100% of the valve opening, so any valve with throttling capabilities can be used as a control valve. However, conversely, we cannot say that control valves belong to throttling valves. The characteristics of flow and throttling will determine which type of control application the throttling valve in question can be used for.
In Conclusion
Through this post, we know that flow control valves and throttle valves are two distinct types of flow regulating devices. A flow control valve is adjusted to control flow rate independent of pressure, while a throttle valve adjusts to control pressure independently of flow. In the semiconductor industry, flow control is used upstream of the process zone while a throttle downstream controls the pressure in that zone.
The working principle behind each type of device varies depending on its application: for flow controlling applications, throttling must be done inside the valve; for industrial applications involving throttling valves as a form of control valve, stem movement determines size adjustments within it. Knowing which kind to use will help you create efficient systems with optimal performance levels.
THINKTANK is a professional control valve manufacturer, and we will provide free control valve sizing and selection for your condition. Please do not hesitate to contact our sales representative for a free consultation.





