¿Por qué se utilizan las válvulas de control?
Las plantas de proceso constan de cientos, o incluso miles, de circuitos de control, todos están conectados en red para producir un producto que se pondrá en venta. Cada uno de estos lazos de control están diseñados para mantener alguna variable importante del proceso, como presión, flujo, nivel, temperatura, etc., dentro de un rango operativo requerido para garantizar la calidad del producto final. Cada uno de estos bucles recibe y crea internamente perturbaciones que afectan negativamente a la variable del proceso, y la interacción de otros bucles en la red genera perturbaciones que influyen en la variable del proceso.
Dicho lo anterior, y para que sean reducidos los efectos de estas perturbaciones de carga, los sensores y transmisores lo que van haciendo es ir recolectando información sobre las variables del proceso y su relación con ciertos puntos de ajuste requeridos. Posteriormente, el controlador almacena y revisa esta información y decide qué se debe hacer para restaurar la variable de proceso a su posición adecuada después producirse la perturbación de la carga. Una vez acabadas todas las mediciones, comparaciones y cálculos, un determinado elemento de control final se encargará de ejecutar la estrategia seleccionada por el controlador.
Principios de Operación
El elemento de control final más común en las industrias de control de procesos es la válvula de control. La válvula de control manipula un fluido que fluye, como gas, vapor, agua o compuestos químicos, para compensar la perturbación de la carga y mantener la variable de proceso regulada lo más cerca posible del punto de ajuste deseado.
Las válvulas de control pueden ser la parte más importante, pero a veces la más descuidada, de un circuito de control. La razón suele ser la falta de familiaridad del ingeniero de instrumentos con las múltiples facetas, terminologías y áreas de las disciplinas de la ingeniería, como la mecánica de fluidos, la metalurgia, el control de ruido y el diseño de tuberías y recipientes que pueden estar involucrados según la severidad de las condiciones de servicio.
Cualquier lazo de control generalmente consta de un sensor de la condición del proceso, un transmisor y un controlador que compara la “variable de proceso” recibida del transmisor con el “punto de ajuste”, es decir, la condición de proceso deseada. El controlador, a su vez, envía una señal correctiva al “elemento de control final”, la última parte del bucle y el “músculo” del sistema de control del proceso. Mientras que los sensores de las variables del proceso son los ojos, el controlador el cerebro, el elemento de control final son las manos del bucle de control. Esto lo convierte en la parte más importante, a veces la menos comprendida, de un sistema de control automático. Esto se debe, en parte, a nuestro fuerte apego a los sistemas electrónicos y las computadoras, lo que provoca cierta negligencia en la comprensión y el uso adecuados de todo el hardware importante.
¿Qué es una válvula de control?
Las válvulas de control regulan automáticamente la presión y / o el caudal y están disponibles para cualquier presión. Si diferentes sistemas de planta operan hasta y a combinaciones de presión / temperatura que requieren válvulas Clase 300, a veces (cuando el diseño lo permita), todas las válvulas de control elegidas serán Clase 300 para intercambiabilidad. Sin embargo, si ninguno de los sistemas excede los valores nominales de las válvulas Clase 150, esto no es necesario.

Las válvulas de globo se utilizan normalmente para el control y sus extremos suelen tener bridas para facilitar el mantenimiento. Dependiendo de su tipo de alimentación, el disco es movido por un actuador hidráulico, neumático, eléctrico o mecánico. La válvula modula el flujo a través del movimiento de un obturador de válvula en relación con el puerto o puertos ubicados dentro del cuerpo de la válvula. El obturador de la válvula está unido a un vástago de la válvula que, a su vez, está conectado al actuador.
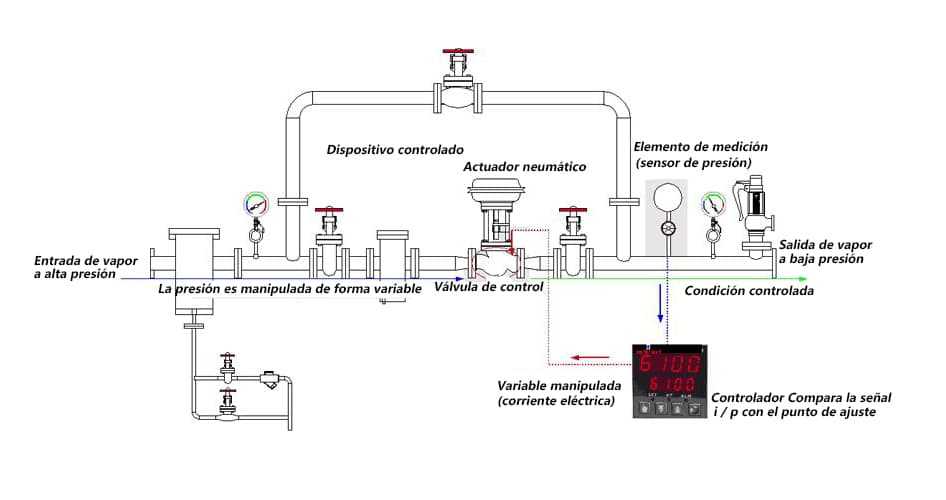
Disposición de la válvula de control
La siguiente imagen muestra cómo se puede usar una válvula de control para controlar la tasa de flujo en una línea. El “controlador” recibe las señales de presión, las compara con la caída de presión para el flujo deseado y si el flujo real es diferente, ajusta la válvula de control para aumentar o disminuir el flujo.
Pueden idearse disposiciones comparables para controlar cualquiera de las numerosas variables del proceso. La temperatura, la presión, el nivel y el caudal son las variables controladas más comunes.
Válvula de control
TIPOS DE VÁLVULAS Y APLICACIONES TÍPICAS
| Tipo de válvula | Servicio y función | |||
| IoS | TH | PR | DC | |
| Puerta | SI | NO | NO | NO |
| Globo | SI | SI | NO | SI (nota 1) |
| Cheque | (nota 2) | NO | NO | NO |
| Detener la comprobación | SI | NO | NO | NO |
| Mariposa | SI | SI | NO | NO |
| Bola | SI | (nota 3) | NO | SI (nota 4) |
| Bola | SI | (nota 3) | NO | SI (nota 4) |
| Diafragma | SI | NO | NO | NO |
| Dispositivo de seguridad | NO | NO | SI | NO |
Leyenda:
• DC = cambio de dirección
• IOS = aislamiento o parada
• PR = alivio de presión
• TH = estrangulamiento
Notas:
1. Solo se pueden usar válvulas de globo en ángulo para un cambio de 90 grados en la dirección del flujo.
2. Las válvulas de retención (distintas de las válvulas de retención) detienen el flujo solo en una dirección (inversa). Las válvulas de retención se pueden utilizar y se utilizan como válvulas de cierre, bloqueo o aislamiento, además de utilizarse como válvula de retención.
3. Algunos diseños de válvulas de bola y tapón (comuníquese con el fabricante de la válvula) son adecuados para el servicio de estrangulamiento.
4. Las válvulas multipuerto de bola y tapón se utilizan para cambiar la dirección del flujo y los flujos de mezcla.





