To convert a valve’s CV (flow coefficient) to SCFM (Standard Cubic Feet per Minute), you need to consider the specific application conditions, including the type of fluid (gas), its pressure, and temperature. The CV value represents the flow rate of water in gallons per minute (GPM) through a valve with a pressure drop of 1 psi, while SCFM measures the flow rate of air or gas under standard conditions (1 atm pressure and 60°F).
To convert CV to SCFM for gases, you can use the following general formula, which accounts for different conditions and properties of the gas:
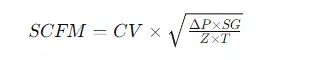
Where:
- SCFM is the flow rate in standard cubic feet per minute.
- CV is the flow coefficient of the valve.
- ΔP is the pressure drop across the valve in psi.
- SG is the specific gravity of the gas (air = 1).
- Z is the compressibility factor of the gas (for many applications, this can be approximated as 1 for air under standard conditions).
- T is the absolute temperature in Rankine (°R = °F + 459.67).
This formula is a simplification and assumes the gas behaves ideally, which is a reasonable approximation for many practical purposes but might not be accurate for all gases or under all conditions.
For more precise calculations, especially for gases with high compressibility, different temperatures, or high pressure, more complex equations of state or software simulations might be necessary.
If you have specific values for CV, ΔP, SG, Z, and T, we, THINKTANK’s valve experts can help you calculate the SCFM.





