The CV value in the context of a valve refers to the valve’s flow coefficient. It is a measure of the capacity of the valve to flow a fluid under specific conditions. The CV value is used to quantify the flow rate of fluids (liquids and gases) through a valve at a given pressure drop across the valve. The higher the CV value, the higher the flow rate that can pass through the valve with a given pressure drop.
The formal definition of the CV value is the number of US gallons of water at 60°F that can flow through the valve per minute with a pressure drop of 1 psi across the valve. It is a crucial parameter for selecting the appropriate valve for a particular application, ensuring that the valve can handle the required flow rate without causing excessive pressure drop or flow restrictions.
what is valve cv
The valve Cv means valve flow coefficient, is a crucial parameter in fluid dynamics that quantifies the flow capacity of a valve. It represents the volume of water in U.S. gallons that can pass through a valve per minute at a temperature of 60°F with a pressure drop of 1 psi across the valve. Essentially, the Cv value provides an indication of how much fluid can flow through a valve, thereby helping in selecting the right valve for specific flow requirements in various applications, such as in piping systems, HVAC, water treatment, and more.
The higher the Cv value, the greater the flow rate that can pass through the valve with a given pressure drop, indicating a larger flow capacity. Conversely, a lower Cv value indicates a smaller flow capacity, suitable for applications requiring finer control of the flow rate at lower volumes.
Here’s a breakdown of what the CV value indicates in valve selection and operation:
High CV Value
A high CV value indicates a larger flow capacity. This means the valve can allow more fluid to pass through at a lower pressure drop. Valves with high CV values are suitable for applications requiring high flow rates.
Low CV Value
A low CV value indicates a smaller flow capacity. This means the valve restricts flow more significantly, resulting in a higher pressure drop for a given flow rate. Valves with low CV values are used in applications where flow control or restriction is needed.
Understanding the CV value is essential for engineers and technicians to ensure that the selected valve meets the operational requirements of the system, providing adequate flow control without causing excessive pressure losses or other hydraulic issues. If you have any questions about CV Value, you are welcome to contact THINKTANK’s specilists to help you sizing your valves.
what is flow coefficient
The flow coefficient, often denoted as Cv(in the United States) or Kv(in metric system countries), is a standardized value used to describe the flow capacity of a valve, nozzle, or other types of flow passages. It quantifies how much fluid can flow through a device, providing a measure of the device’s efficiency in allowing fluid passage under specific conditions.
Valve CV Value Calculator: An Essential Tool for Precision Flow Management
In the complex world of fluid dynamics and system design, precision is not just a goal; it’s a necessity. At THINKTANK, we understand the critical importance of selecting the perfect valve for each unique application. It’s not just about managing flow; it’s about optimizing efficiency, ensuring safety, and maximizing performance. That’s why we’re excited to introduce our free tool: The THINKTANK Valve CV Value Calculator.
Developed by our team of seasoned engineers, this calculator represents a leap forward in fluid system design. It encapsulates our commitment to precision engineering, offering an intuitive, user-friendly interface that simplifies the calculation of a valve’s flow coefficient (CV). This tool is designed to empower system designers, engineers, and maintenance professionals with the ability to make informed decisions quickly and accurately.
Key Features of the THINKTANK Valve CV Value Calculator
Precision Engineering
Use our well-developed tool, created from years of fluid dynamics research, to calculate the exact CV value needed for your specific application.
User-Friendly Interface
Designed with the user in mind, our calculator allows for easy input of critical parameters, including fluid type, temperature, pressure drop, and flow rate.
Versatility
Whether you’re working with liquids or gases, at high temperatures or under extreme pressure, our calculator adapts to a wide range of conditions.
Instant Results
Receive immediate calculations, enabling swift decision-making and optimization of your fluid system design.
Educational Insights
Not only does our calculator provide you with the necessary numbers, but it also offers insights into how different variables impact your system’s performance.
How It Works:
At the heart of our calculator is the CV formula, which quantifies the flow rate of fluids through a valve based on a given pressure drop. By inputting your system’s specifics, our tool calculates the CV value required for optimal performance. This process demystifies valve selection, ensuring that your system operates within its intended parameters, thus avoiding common pitfalls such as excessive wear, noise, or system failure.
To create an calculator for CV value, we need to consider the basic formula for CV calculation. The CV value is used to determine the flow rate through a valve and is calculated based on the flow rate (Q), specific gravity of the fluid (SG), and the pressure drop across the valve (ΔP). A simplified formula to calculate CV is:
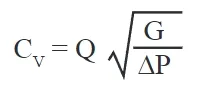
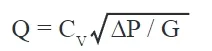
where:
- Q is the flow rate in gallons per minute (GPM),
- ΔP is the pressure drop across the valve in pounds per square inch (PSI),
- ΔP=Upstream P1(inlet pressure) – Downstream P2(outlet pressure)
- SG is the specific gravity of the fluid (water = 1).
Valve CV Value Calculator with Convertible Units
Example Cv calculation for water
To calculate the Cv value of a valve for a water flow of 25 GPM (gallons per minute) with a differential pressure of 12 psi,
- Q = 25 GPM
- SG = 1
- dp = 12 psi
To calculate the Cv value of a valve for a water flow of 25 GPM (gallons per minute) with a differential pressure of 12 psi, the Cv value is calculated to be approximately 7.22. This means that under these conditions, a valve with a Cv of 7.22 will allow 25 GPM of water to flow through it with a 12 psi pressure drop across the valve.
Cv-value calculator liquids & gasses
Difference Between Cv and Kv Flow Coefficients
The Cv and Kv flow coefficients are essential metrics used in the valve and fluid dynamics industries to quantify the flow capacity of control valves, nozzles, and other types of fluid conduits. Despite serving similar purposes, Cv and Kv are based on different measurement systems—imperial (U.S.) units for Cv
and metric units for Kv. Understanding the distinction between these two coefficients, their calculation, and conversion is crucial for accurately specifying equipment in fluid systems to ensure compatibility and efficiency across global operations.
Cv Flow Coefficient Definition
The Cv value represents the number of U.S. gallons of water at 60°F that can flow through a valve per minute with a pressure drop of 1 psi across it.
- Units: U.S. gallons per minute (GPM) of water, temperature at 60°F, and pressure in psi.
- Usage: Predominantly used in the United States and countries that utilize the imperial measurement system.
- Purpose: Cv is used to rate the flow capacity of valves, enabling engineers to select the correct valve size for their requirements, ensuring the system operates efficiently without unnecessary pressure loss.
Kv Flow Coefficient Definition
The Kv value indicates the flow rate of water in cubic meters per hour (m³/h) that passes through a valve with a pressure drop of 1 bar.
- Units: Cubic meters per hour (m³/h) of water, with the pressure drop measured in bar.
- Usage: Widely adopted in countries using the metric system, making it common in international specifications and documentation.
- Purpose: Similar to Cv, Kv is used to determine the appropriate valve size for a given application, ensuring optimal performance.
Conversion Between Cv and Kv
The difference in base units between Cv and Kv necessitates conversion formulas for engineers and professionals working on international projects or with equipment from different measurement system regions. The conversion is straightforward, using the following relationship:
1Cv =1.156K
Conversely:
1Kv = 0.865Cv
This conversion is critical when selecting valves for a system designed in different units than the valve specifications. Using the correct coefficient ensures the valve will meet the system’s flow requirements without causing excessive pressure drop or flow restrictions.
Practical Implications
- System Design and Valve Selection: Understanding the flow capacity and correctly converting between Cv and Kv ensures that valves and other components are appropriately sized for the intended application, whether it’s for HVAC, water treatment, gas handling, or other fluid systems.
- International Projects: For engineers and professionals working across countries with different measurement preferences, mastering both coefficients and their conversion is essential for specifying the right components, avoiding errors, and ensuring project success.
- Efficiency and Safety: Correct valve sizing not only impacts the efficiency of a fluid system by optimizing flow and reducing energy consumption but also plays a crucial role in ensuring operational safety.
In summary, while Cv and Kv serve the same purpose in valve and fluid flow specifications, their differences reflect the measurement systems they are based on. Accurate conversion and application of these coefficients are fundamental to the design, operation, and international collaboration on fluid handling projects.
Instructions for Use
- Flow Rate (GPM): Input the flow rate through the valve in gallons per minute.
- Specific Gravity of Fluid: Input the specific gravity of the fluid (use 1 for water).
- Pressure Drop (PSI): Input the pressure drop across the valve in pounds per square inch.
- Calculate CV Button: Click this button to calculate the valve’s CV value. The result will be displayed below the button.
This calculator provides a quick and easy way to estimate the CV value for valves based on the specified conditions. It’s a useful tool for engineers, technicians, and students working in fields related to fluid mechanics and valve selection.
What is the flow coefficient
The flow coefficient, often denoted as Cv, is a measure used to describe the flow capacity of a valve, nozzle, or other types of flow passage. It quantifies the rate at which a fluid can flow through a device. Specifically, the Cv value represents the volume of water (in US gallons) that can pass through the valve per minute at a temperature of 60°F, with a pressure drop of 1 psi across the valve.
The flow coefficient is crucial in the design and selection of flow devices in piping systems, as it helps engineers and technicians determine whether a particular valve or nozzle meets the flow requirements of their application. By knowing the Cv, one can predict the flow rate through the device for a given pressure drop, or conversely, estimate the pressure drop for a known flow rate.
The Cv value is determined under standardized conditions to ensure consistency and comparability between different devices. It’s particularly important in applications involving liquids, where the flow dynamics can significantly impact system performance and efficiency.
In practical terms, a higher Cv value indicates a larger flow capacity, meaning the device can allow more fluid to pass through it at a lower pressure drop. Conversely, a lower Cv value suggests a smaller flow capacity, which might be suitable for applications requiring precise control of the flow rate at lower volumes.
The concept of the flow coefficient is not limited to water or liquids; variations of the concept are used for gases and steam, such as the Cg and Cs coefficients, respectively. These take into account the different properties of gases and steam, such as compressibility and expansion, which affect how they flow through valves and other devices.
Valve flow coefficient variables
The valve flow coefficient, denoted as Cv, is determined by several variables that influence the flow rate of fluid through a valve. The Cv value itself is a measure of the capacity of a valve to pass fluid, specifically defined as the number of U.S. gallons of water at 60°F that can flow through a valve per minute with a pressure drop of 1 psi. Understanding the variables that affect the Cv value is crucial for selecting the right valve for specific flow conditions in hydraulic and pneumatic systems. Here are the key variables involved:
1. Pressure Drop (ΔP)
This is the difference in pressure between the inlet and outlet of the valve. The Cv
value is based on a standard pressure drop of 1 psi, but actual conditions may vary, affecting the flow rate through the valve.
2. Fluid Density and Specific Gravity (SG)
The Cv calculation is standardized for water at 60°F, which has a specific gravity of 1. For fluids with a specific gravity different from water, the flow rate can be adjusted accordingly, as the fluid’s density affects its resistance to flow.
3. Fluid Viscosity
The thickness or stickiness of a fluid affects its flow through a valve. High-viscosity fluids flow more slowly than low-viscosity fluids under the same pressure drop. The standard Cv value is for water (a low-viscosity fluid), and adjustments may be needed for fluids with significantly different viscosities.
4. Valve Type and Design
Different types of valves (e.g., ball, gate, globe, butterfly) have different flow characteristics. The internal geometry of the valve, such as the size and shape of the flow path, affects the Cv value.
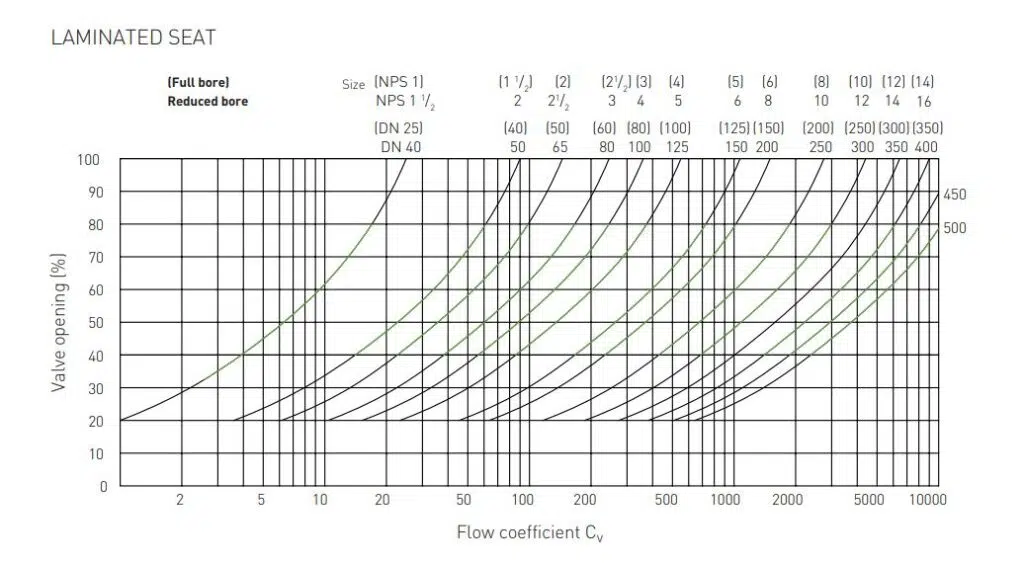
5. Valve Opening (Position)
The Cv value changes with the valve’s position. Many valves provide variable flow control, meaning the flow rate changes as the valve moves from fully closed to fully open. The relationship between valve position and flow capacity is often nonlinear.
6. Flow Condition
The condition of the flow (laminar vs. turbulent) can affect the valve’s flow coefficient. Turbulent flow typically results in a more significant pressure drop than laminar flow for the same flow rate.
7. Temperature
While the Cv value is standardized at 60°F for water, temperature changes can affect fluid properties like density and viscosity, thus impacting flow rates. For gases, temperature changes also affect volume and, by extension, flow rates measured in terms of mass flow or volumetric flow under standard conditions.
These variables are essential considerations when selecting a valve for a particular application, ensuring that it can handle the required flow rate under the expected operating conditions. Engineers often use detailed Cv charts provided by valve manufacturers, which account for these variables, to select the appropriate valve size and type for their specific application.
Why THINKTANK
At THINKTANK, we’re more than just engineers; we’re innovators committed to advancing the field of fluid dynamics. Our Valve CV Value Calculator is a testament to this commitment, offering a blend of precision, ease, and insight that reflects our broader mission: to engineer solutions that not only meet but exceed our clients’ expectations.
For more information, visit our website or contact our support team. Let THINKTANK be your partner in fluid system excellence, where precision engineering meets practical application.





