What is Set Pressure of Safety Valve?
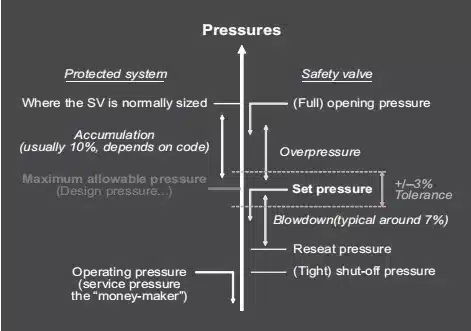
Set pressure is the predetermined pressure at which the safety valve starts to open under operational conditions, measured as gauge pressure at the valve inlet. At this pressure, under specified operational conditions, the force generated by the medium pressure to open the valve is balanced with the force keeping the valve disc on the valve.
At this pressure, there begins to be a measurable opening height, and the medium exhibits a continuous discharge state that can be perceived visually or audibly.
a.) Safety Valves for Steam Boilers
A steam boiler safety valve is a critical component in boiler systems, designed to ensure safety and prevent catastrophic failures. Here’s an overview of its function, importance, and operational principles:
Function of Steam Boiler Safety Valve
Pressure Regulation
The primary function of a safety valve is to release excess steam when the pressure inside the steam boiler exceeds a predefined limit, known as the set pressure. This helps to prevent potentially dangerous overpressure conditions.
Automatic Operation
Safety valves are designed to open automatically at a set pressure and close when the pressure drops to a safe level. This automatic response is crucial for immediate pressure relief.
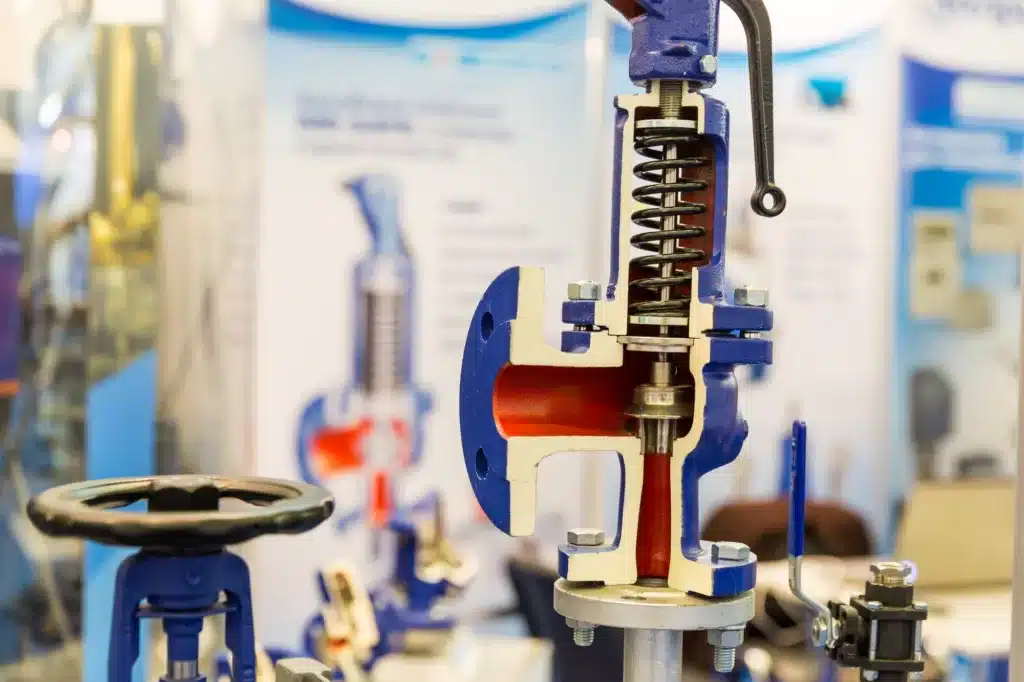

Importance in Steam Boiler Operations
- Preventing Explosions: Overpressure can lead to boiler explosions, which can be devastating. The safety valve is a fail-safe device that prevents such scenarios by releasing excess pressure.
- Compliance with Regulations: Safety valves are mandated by various safety standards and regulations. They are essential for legal compliance and for passing safety inspections.
- Operational Safety: They ensure the safety of the equipment and, more importantly, the safety of personnel operating or working near the steam boiler.
Operational Principles
Set Pressure
This is the specific pressure at which the valve is designed to open. It is carefully calibrated based on the boiler’s maximum allowable working pressure.
a. The set pressure for safety valves on the drum (shell) and superheater should adhere to the values specified in Table 1.
b. For economizers, reheaters, and once-through boiler start-up separators, the safety valve set pressure is 1.1 times the working pressure of the installation site.
c. Set Pressure Deviation: For set pressures ≤0.5MPa, the deviation is ±0.015MPa. For set pressures between 0.5~2.3MPa, it’s ±3% of the set pressure. For 2.3~7.0MPa, it’s ±0.07MPa, and for pressures >7.0MPa, the deviation is ±1% of the set pressure.
Table 1: Set Pressure of Safety Valves on Drum (Shell) and Superheater
| Rated Working Pressure (MPa) | Set Pressure of Safety Valve (MPa) |
|---|---|
| ≤0.8 | Working Pressure +0.03 |
| 0.8<P≤5.9 | 1.04 times the working pressure |
| >5.6 | 1.05 times the working pressure |
Note: Boilers must have a safety valve adjusted to the lower set pressure specified in the table. For boilers with superheaters, the safety valve set for lower pressure must be the one on the superheater, ensuring it opens first. The working pressure in the table refers to the location where the impulse is connected for pulse-type safety valves, and the installation location of the safety valve for other types.
Balance of Forces
The valve is designed so that under normal conditions, the force exerted by the boiler pressure keeps it closed. When the internal pressure exceeds the set pressure, the increased force pushes the valve open, allowing steam to escape.
Re-seating Pressure
After opening, the valve will close again once the pressure drops to a safe level, known as the re-seating pressure. This is typically lower than the set pressure to provide a safety margin.
Testing and Maintenance
Regular testing and maintenance are essential to ensure that safety valves function correctly. They must be kept in good working order and free from obstructions.
Types of Safety Valves for Steam Boilers
- Conventional Safety Valves: These have a spring holding the valve closed and open when pressure forces against this spring exceed its force.
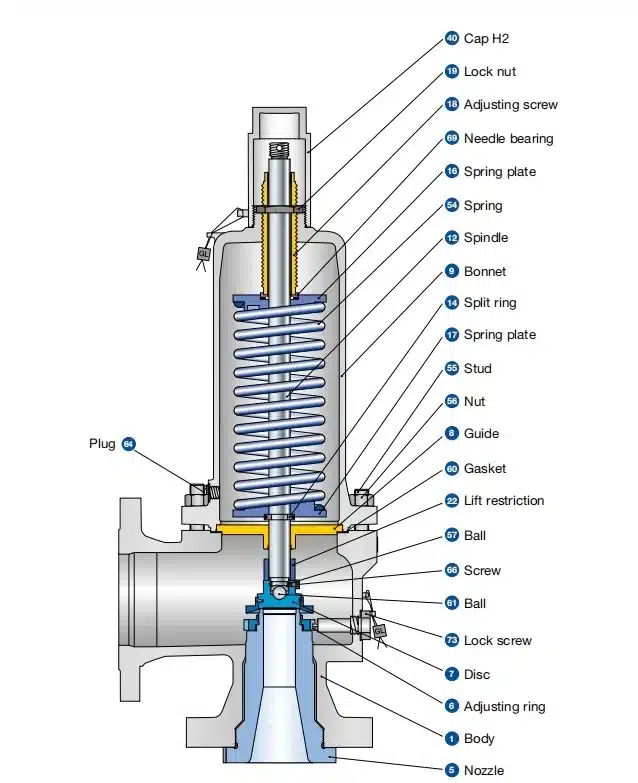
- Pilot-operated Safety Valves: These use system pressure to assist in opening the valve and can be more responsive and precise in operation.
- Full Lift Safety Valves: Designed to open rapidly for a full discharge of steam when the set pressure is reached.
b.) Safety Valves for Hot Water Boilers
Safety valves for hot water boilers are essential components designed to ensure the safe operation of hot water heating systems. They serve a similar purpose to those in steam boilers but are tailored to the specific requirements of hot water systems.
Function of Safety Valves in Hot Water Boilers
Pressure Relief
The primary role of a safety valve in a hot water boiler is to prevent excessive pressure build-up. If the pressure within the boiler exceeds a certain threshold, the valve opens to release water and lower the pressure, thus averting potential hazards.
Automatic Response
Like steam boiler safety valves, these valves are designed to open automatically at a predetermined set pressure. They close again once the pressure decreases to a safe level.
Importance in Hot Water Boiler Operations
- Preventing Overpressure Conditions: Excessive pressure in a hot water system can lead to boiler damage, system failure, and in extreme cases, explosions. Safety valves are critical in preventing such scenarios.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to safety standards and regulations is essential. Safety valves in hot water boilers are required for legal compliance and ensuring the system passes safety inspections.
- Operational Safety and Reliability: Safety valves contribute to the overall safety of the heating system, ensuring it operates within the designed pressure range and preventing damage to the system.
Operational Principles
Set Pressure Calibration
Safety valves in hot water boilers are calibrated to open at a specific pressure, which is determined based on the boiler’s design and operating parameters.
a. The set pressure for safety valves should follow the standards detailed in Table 2.
b. Set Pressure Deviation: ±0.015MPa for set pressures ≤0.5MPa, and ±3% of the set pressure for pressures >0.5MPa.
Table 2: Set Pressure of Safety Valves for Hot Water Boilers (MPa)
| 1.12 times the working pressure but not less than the working pressure +0.07MPa |
| 1.14 times the working pressure but not less than the working pressure +0.10MPa |
Note: Each boiler must have a safety valve adjusted to the lower set pressure in the table. The working pressure here refers to the pressure of the components directly connected to the safety valve.
Temperature Considerations
In hot water systems, both pressure and temperature are closely interrelated. Safety valves must be capable of handling the thermal expansion that occurs in these systems.
Maintenance and Testing
Regular testing and maintenance are crucial to ensure the valve operates as intended. This includes checking for any blockages or mechanical failures that could impede the valve’s function.
Types of Safety Valves for Hot Water Boilers
- Pressure-Only Relief Valves: These valves respond solely to excessive pressure irrespective of the temperature.
- Temperature and Pressure Relief Valves (TPR Valves): Common in residential hot water systems, these valves are designed to open in response to excessive temperature as well as pressure, providing a dual safety mechanism.
- Vacuum Relief Valves: While not directly related to overpressure, these valves prevent a vacuum from forming in the system, which can be equally hazardous.
c.) Safety Valves for Fixed Pressure Vessels
Safety valves for fixed pressure vessels are critical components designed to ensure the safe operation of these vessels, which are commonly used in various industries for storing liquids and gases under pressure. These valves serve as a safeguard against the potential dangers of overpressure, which can arise due to process upsets, equipment failures, or other operational issues.
a. If only one safety valve is installed on a fixed pressure vessel, its set pressure should not exceed the design pressure of the vessel. When multiple safety valves are installed, the set pressure of one valve should not exceed the vessel’s design pressure, while the others may be slightly higher but not more than 1.05 times the design pressure.
b. Set Pressure Deviation: ±0.015MPa for pressures ≤0.5MPa, and ±3% for pressures >0.5MPa.
d.) Safety Valves for Mobile Pressure Vessels
a. The set pressure for these valves ranges from 1.05 to 1.10 times the design pressure of the tank, with a return pressure not less than 0.8 times the opening pressure. For low-temperature cryogenic tank trucks, the set pressure must not exceed the tank’s design pressure.
b. Set Pressure Deviation: ±0.015MPa for pressures ≤0.5MPa, and ±3% for pressures >0.5MPa.
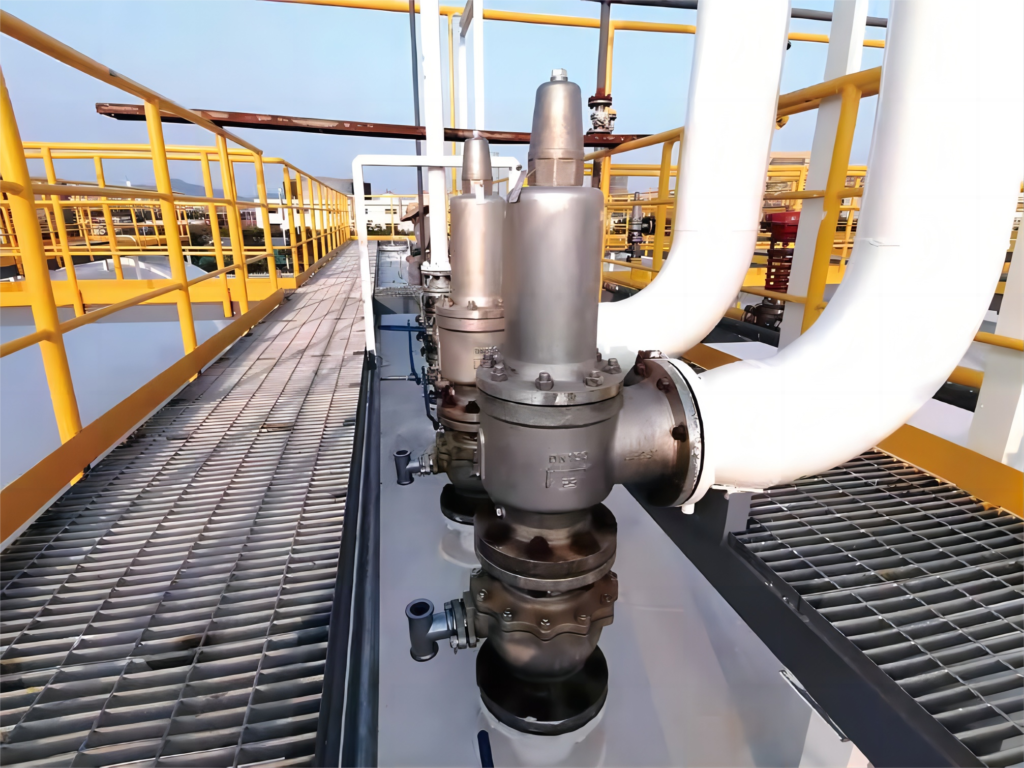

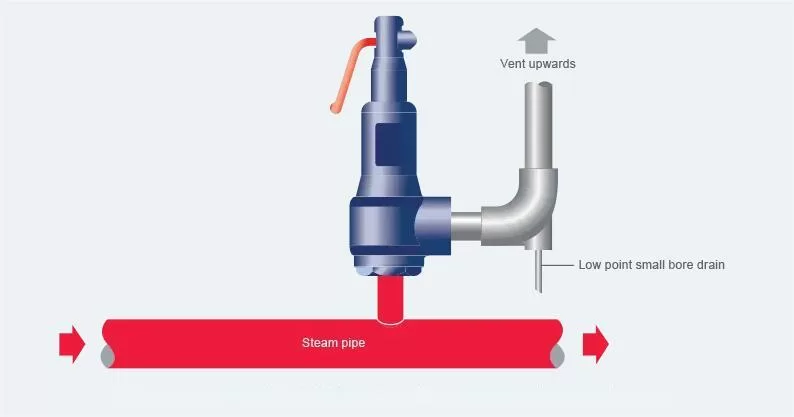
e.) Safety Valves for Pressure Pipelines
a. The set pressure for safety valves in industrial metal pipelines is 1.05 to 1.1 times the maximum working pressure. For pipelines in oil and gas stations, it’s 1.05 to 1.15 times the maximum working pressure.
b. Set Pressure Deviation: ±0.015MPa for pressures ≤0.5MPa, and ±3% for pressures >0.5MPa.
f.) Safety Valves for Medical Hyperbaric Oxygen Chambers
a. The set pressure for these safety valves is the maximum working pressure + 0.02 MPa.
b. The set pressure deviation is ±0.015MP
Conclusion
In conclusion, the set pressure of safety valves is a fundamental aspect of ensuring safety and operational efficiency in various industrial systems, including steam boilers, hot water boilers, fixed and mobile pressure vessels, and pressure pipelines. The set pressure is not merely a number, it represents a critical balance point where safety and functionality intersect. It must be precisely calculated and rigorously maintained to protect equipment and personnel from the dangers of overpressure. THINKTANK is a reliable safety relief valve supplier in China, we provide breather valves, flame arresters, safety valve, N2 blanketing valve for tank storage system. Should you have any questions, just feel free to contact us.





