In the world of air compressors, ensuring safe and efficient operation is critical. At the heart of this safety framework lies a simple yet crucial component – the air compressor safety valve also known as pressure relief valve. This key safety device plays a crucial role in preventing overpressure incidents that could compromise both equipment and safety. Picture this: when the system pressure surpasses set pressure limits, the safety valve rapidly swings into action, automatically opening to release excess air until the pressure reduces to normal level. In this exploration, we dive into the workings of the air compressor safety valve, explaining its mechanisms and its vital role in diverse industrial settings. Join THINKTANK as we uncover the key aspects of how these valves operate, safeguarding not just machinery but also the integrity of operational environments.
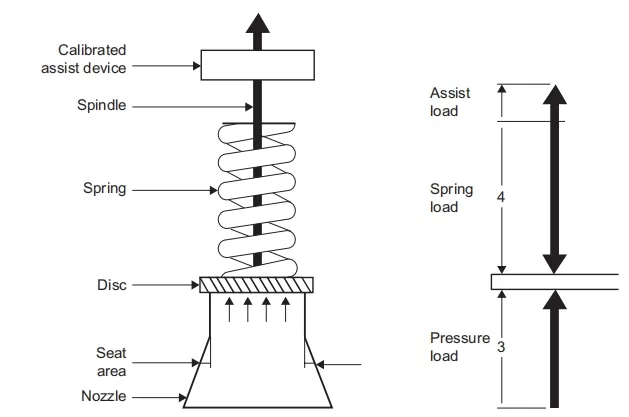
The Basics of Air Compressor Safety Valves
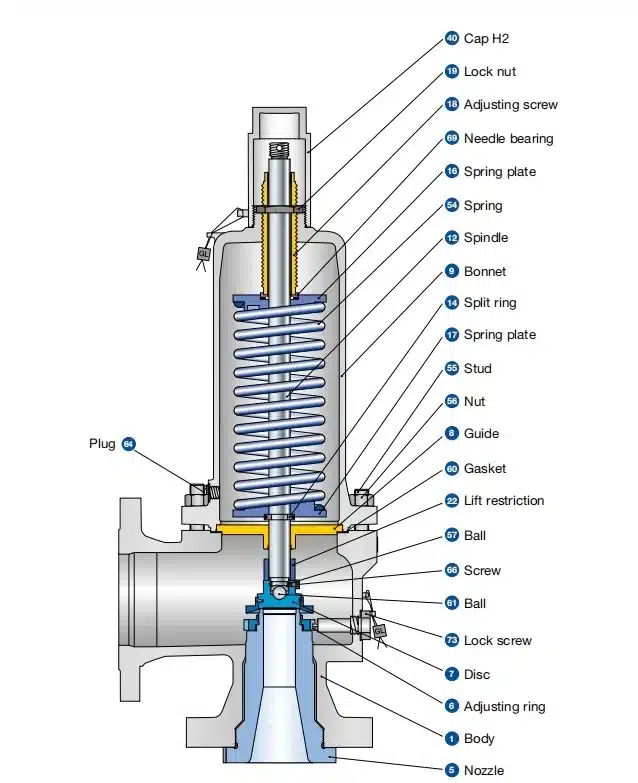
In the world of air compressor systems, air compressor safety valve embody simplicity in their design, functioning as spring-loaded mechanisms that automatically respond to heightened pressure conditions. As the system pressure escalates beyond the preset limit, the valve disc rapidly lifts from its seat, facilitating the controlled release of compressed air into the atmosphere. Complying to the ASME relief valve standard, these valves are adjusted to achieve their full discharge capacity when the system pressure hovers within a 10% margin above the predetermined set pressure. Crucially, they exhibit a full shutoff capability when the system pressure dips below 90% of the set pressure value, aligning with strict safety measures.
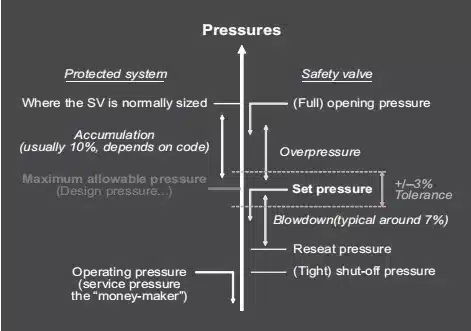
Precision Mechanism of Action
An air compressor safety valves or pressure relief valves prevent excessive pressure buildup to ensure the safety of an air compressor system. Here’s how it works:
1. Basic Functionality
The primary function of a safety valve in an air compressor is to automatically release air if the pressure within the compressor tank exceeds a predetermined safe level. This helps prevent potential risk such as tank rupture or compressor failure due to overpressure.
2. Set Pressure
Each safety valve is designed to open at a specific pressure known as the “set pressure.” This is the maximum pressure that the air compressor is designed to handle safely. The set pressure of the valve is typically a little higher than the maximum operating pressure of the compressor.
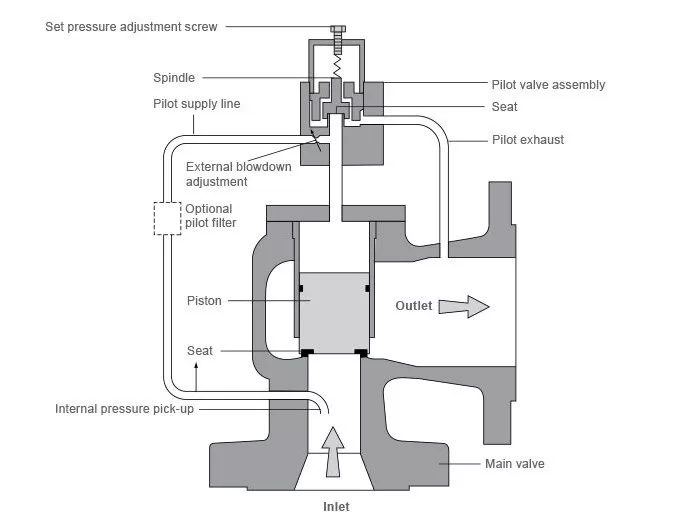
3. Spring-Loaded Design
Most air compressor safety valves are spring-loaded. A spring inside the valve is calibrated to provide a force that keeps the valve closed under normal operating pressures. The force exerted by the spring is balanced against the pressure of the air inside the compressor tank.
4. Pressure Exceeds Set Point
When the air pressure in the tank exceeds the set pressure of the valve, the force exerted by the pressurized air overcomes the force of the spring. This causes the valve to open, allowing excess air to escape. The released air decreases the pressure inside the tank.
5. Automatic Reclosing
Once the pressure in the tank drops back below the set pressure, the spring force pushes the valve back into its seat, sealing it closed. This automatic reclosing ensures that the air compressor can continue normal operation without manual intervention, provided the overpressure condition has been resolved.
6. Venting Air
When the valve opens, it releases air in a rapid, often audible burst. This venting of air not only reduces the pressure but also serves as an audible warning that the system has reached or exceeded its maximum safe pressure.
7. Regular Testing and Maintenance
Safety valves should be tested regularly to ensure they open at the correct set pressure and reseal properly. Over time, valves can become stuck or corroded, which may hinder their operation.
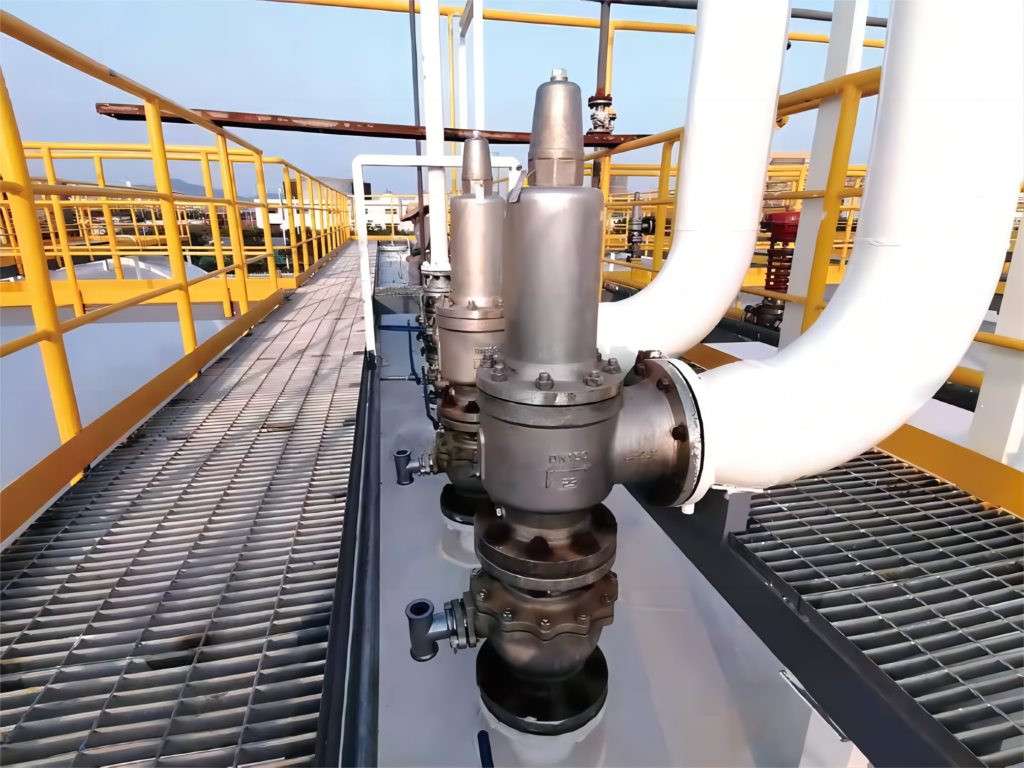

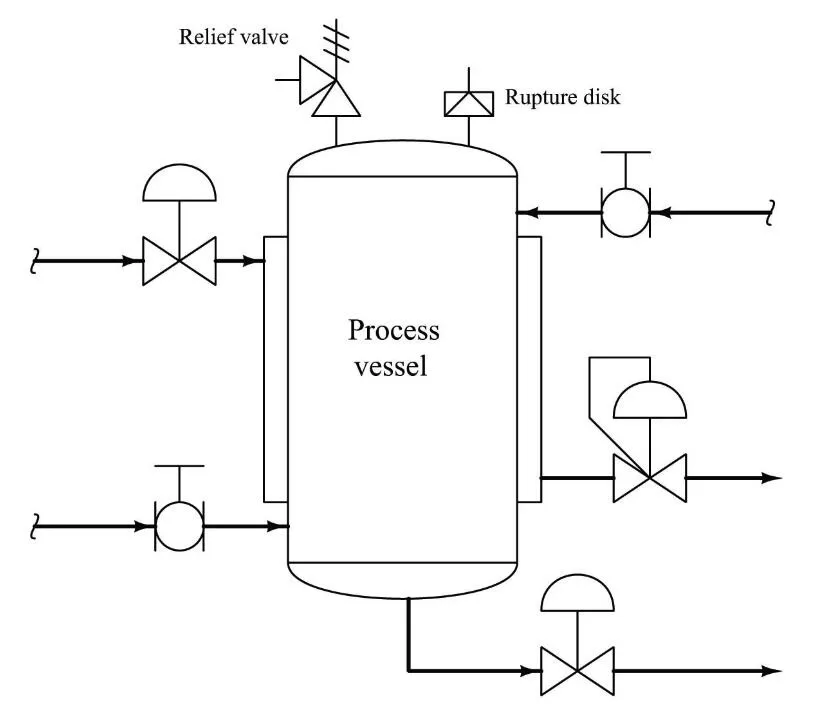
Common Causes of Overpressure in Air Compressor Systems
A. Factors Leading to Overpressure
- Inadequate system maintenance, including irregular checks on drain valve and air tank
- Fluctuations in demand and usage, influenced by the efficiency of pressure switch
- Malfunctioning pressure regulators causing unintended spikes
- Accidental valve closures impacting pressure levels
- Improper installation of components, including air tanks and pressure switches
B. Role of Safety Valves in Mitigating Overpressure
- Automatic pressure relief mechanism, safeguarding against drain valve failures
- Quick response to sudden pressure spikes detected by pressure switches
- Prevents damage to compressor components, including air tanks
- Safeguards against potential system failures, especially in the absence of functioning pressure switches
- Ensures optimal performance and longevity, with regular checks on drain valves, air tanks, and pressure switches
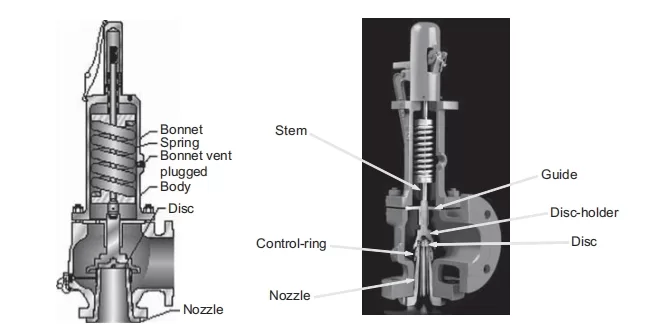
Summary
In summary, the air compressor safety relief valve stands as a crucial safety measure, automatically releasing excess pressure to safeguard against potential equipment damage or accidents caused by overpressure. This crucial component plays a pivotal role in maintaining optimal system functionality and ensuring a secure operational environment. Regular maintenance checks on associated elements like drain valves, air tanks, and pressure switches contribute to the longevity and reliability of the safety relief valve, promoting an efficient and safe air compressor system.





