In the world of machines and industrial systems, ensuring they operate smoothly in a high pressure environment is crucial. Among the key players in this field is pressure safety valve or safety relief valve, that keep system pressure in control. Today, let’s take a look at a vital aspect: adjusting the pressure on the safety valve to ensure that our systems operate in their safest and smoothest ways. Join us as we explore the details of this process, uncovering the adjustments that maintain the safety and optimal performance of our industrial systems.

Understanding Safety Valve Mechanics and Adjusting Them
Adjusting the pressure setting on a safety valve, also known as a pressure relief valve, is a critical process that must be carried out with precision and understanding of the valve’s mechanics and the pressurized system it protects. The steps for adjusting the safety valve’s set pressure typically involve:
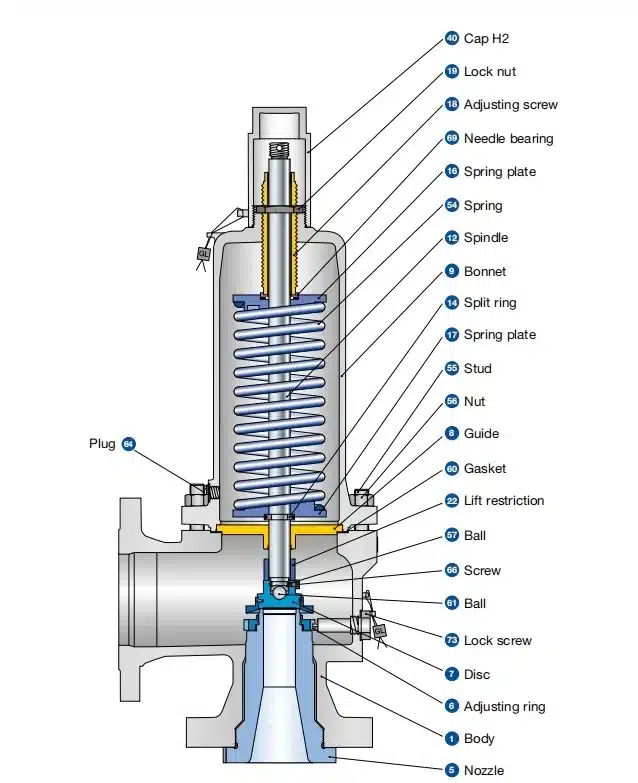
1. Understanding the Valve Type: Different safety valves have different mechanisms for setting the pressure. The most common types are spring-loaded valves.
2. Ensuring Safety and Compliance: Before making any adjustments, ensure that it is safe and compliant with relevant regulations and standards. Unauthorized or incorrect adjustments can lead to system failure or hazardous situations.
3. Isolating the Valve: If possible, isolate the valve from the system. This might involve shutting down the system or isolating the section where the valve is installed. check the pressure gauge to ensure that there is no pressure in the system before proceeding.
4. Accessing the Adjustment Mechanism: For spring-loaded valves, the adjustment is typically made by turning a screw or bolt that compresses or decompresses the spring. This screw is usually covered by a cap or a seal. In some cases, breaking the seal can void the warranty or violate inspection regulations.
5. Making the Adjustment:
- Increasing Pressure: To increase the set pressure, turn the adjusting screw in a direction that compresses the spring (usually clockwise). This means the spring will require more force (and hence more pressure) to open the valve.
- Decreasing Pressure: To decrease the set pressure, turn the adjustment screw in a direction that decompresses the spring (usually counterclockwise). This means the spring will require less force to open the valve.
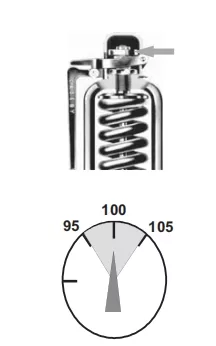
The field spring adjustment needs to be within +/-5% of the set pressure. This means that the SRV must be capable of being reset differently from the factory nameplate set pressure by +/- 5% with no change of any parts or impaired performance (instability, not full lift at 10% overpressure, blowdown, etc.)
Note that the valve must be set within the spring’s set pressure range. However, it is important to note that once the valve is shipped, it becomes a ‘used valve’ and it may be reset +/- 5% outside the published spring range.
6. Proceeding with Caution: Make small adjustments and proceed cautiously. Over-tightening or forceful adjustments can damage the valve.
7. Testing and Calibration: After adjustment, the valve should be tested to ensure it opens at the correct set pressure. This is typically done using a test bench or in-situ testing equipment. The valve’s performance must be verified to ensure it operates safely at the desired set pressure.
8. Documentation and Sealing: Document any changes made to the settings for future reference and compliance. If the valve has a seal or a lock, ensure it is securely replaced.
9. Seeking Professional Assistance: If you are unsure about any aspect of the adjustment process, consult a professional or the manufacturer. Safety valves are critical safety devices, and incorrect adjustments can have serious consequences.
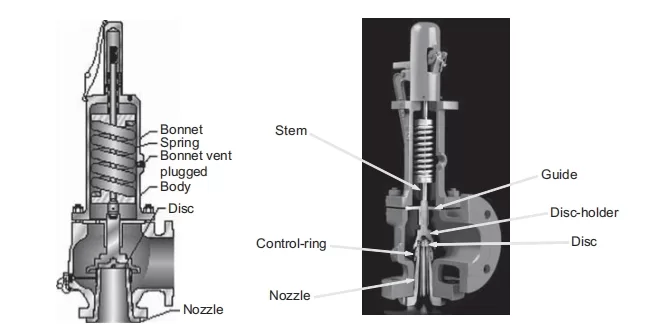
Factors Influencing Pressure Adjustment
1. System Requirements: The specifics of pressure adjustment in safety valves are designed to meet the specific demands of the industrial system. Adapting the valve settings to system complexities ensures optimal performance and reliability.
2. Environmental Considerations: Pressure adjustments aren’t just about the system itself; they also account for external factors. Environmental considerations, such as temperature fluctuations and potential exposure to corrosive elements, play a vital role in the calibration process.
3. Operational Variables: The successful adjustment of pressure involves a detailed understanding of operational variables. Factors like flow rates, operational loads, and the dynamic nature of industrial processes contribute to the detailed adjustment of safety valves.
4. Regulatory Compliance: Pressure adjustments must align with industry standards and regulatory requirements. Ensuring compliance with safety regulations is paramount for maintaining a secure and legally sound operational environment.
Testing The Correctness Of The Adjustments:
Precision in pressure adjustments for safety valve is not just a matter of meeting specific numerical values; it’s about aligning the safety valve with the unique demands of the system it protects. Ensuring optimal performance requires a complete understanding of the system’s details, from normal operating conditions to potential stress factors. By adjusting the pressure settings with careful attention, operators can guarantee that the safety valve responds precisely when needed, preventing both false activations and missed opportunities to relieve excess pressure. With that being said, incorrectly adjusting the pressure on a safety valve can lead to serious issues within an industrial system. If the pressure setting is closer to the maximum set pressure, the valve may not open when necessary, causing unnecessary disruptions and potentially leading to equipment damage. The consequences of such inaccuracies can range from inefficient operations to severe safety risks.
Common Mistakes To Avoid:
- Neglecting Regular Inspections: One common mistake is overlooking the need for regular inspections of safety valve. Without routine checks, operators may miss signs of wear, corrosion, or other issues that could impact the valve’s performance during pressure adjustments.
- Ignoring Environmental Factors: Failing to consider environmental conditions can lead to inaccurate pressure adjustments. Factors like temperature fluctuations, corrosive atmospheres, or exposure to external elements can affect the valve’s response and compromise its effectiveness.
- Overlooking System Changes: Systems evolve over time, and failing to account for these changes can result in improper pressure adjustments. Whether it’s alterations in operating conditions or modifications to the overall system, overlooking these aspects can lead to safety risks.
Troubleshooting Tips:
- Conducting Regular Testing: To troubleshoot pressure adjustment issues, regular testing of safety valve is crucial. Implementing a robust testing protocol ensures that the valves respond appropriately to pressure changes and helps identify any malfunctions.
- Monitoring Valve Operation: Continuous monitoring of safety valve operation provides insights into its performance. Unusual sounds, vibrations, or inconsistent responses during testing could signal potential issues that require troubleshooting.
- Collaboration with Experts: When faced with persistent problems in pressure adjustment, seeking collaboration with valve experts like THINKTANK can be invaluable. These professionals can offer insights into system-specific challenges and recommend designed solutions to optimize safety valve performance.
Summary
Remember, safety valves are designed to protect against overpressure situations. Any adjustments should prioritize system safety and comply with engineering standards and local regulations. For a deeper understanding of safety valves or pressure relief valves, we encourage you to explore more insights in THINKTANK blogs. Our comprehensive resources provide valuable information on maintaining a safe and efficient industrial environment.





