As a valve expert from THINKTANK, I’ll answer each of your questions in the context of steam systems and valve technology:
1. Can Ball Valves Be Used for Steam
Yes, ball valves can be used for steam services if they are designed to withstand the temperature and pressure of the steam. They should be made of suitable material and have the proper seat material for steam service, especially for seat material, based on the working temperature, there are two options for material, soft-seat and metal-to-metal. For specific conditions, please feel free to contact us for professional selection and sizing.

2. Why Ball Valves Are Not Used in Steam Service
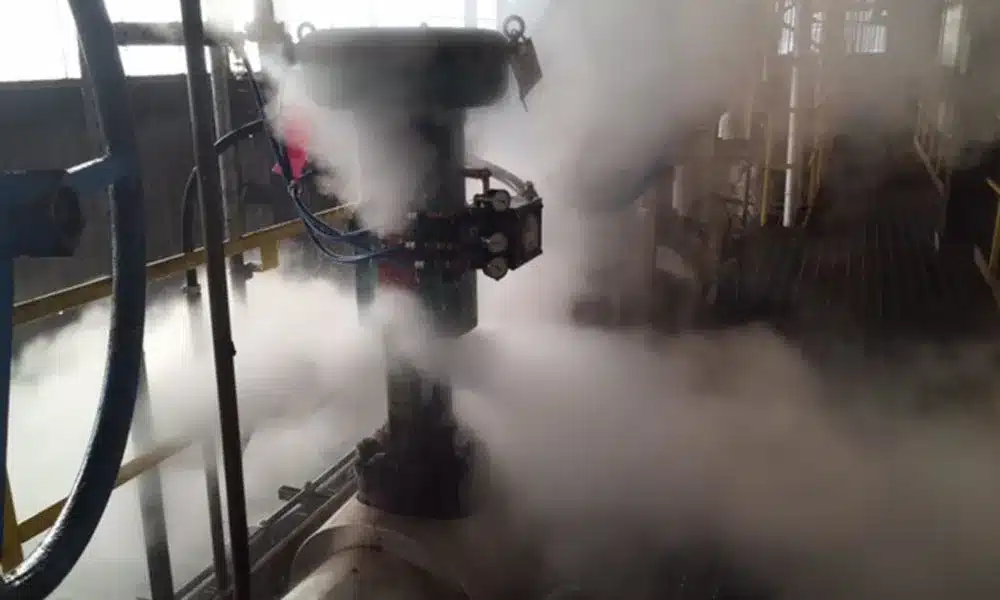
It can not be simple to say ball valve is suitable for steam service or not. If for on/off application, we think the right selection of ball valves is common to use in steam service. But they are not ideal for throttling applications and can suffer from steam damage to the ball and seats, leading to leaks.
3. Are There Replacement Steam Valves for Old Type Valves
For replacing old steam valves, modern equivalents are often available that match the size, pressure rating, and flow characteristics needed for the application. It’s important to select valves that are specifically rated for steam service and compatible with the existing piping and operating conditions.
4. Are Vacuum Relief Valves Needed for Model Steam Engines Boilers
Vacuum relief valves are important for model steam engines and boilers to prevent a vacuum from forming inside the boiler as it cools down. A vacuum can cause the boiler to collapse. Therefore, a vacuum relief valve helps maintain atmospheric pressure inside the boiler to prevent damage.
5. Can Clogged Steam Vent Valves Cause Short Cycling
Yes, clogged steam vent valves can cause short cycling in steam heating systems. If the vent valves are clogged, air trapped in the radiators cannot be expelled, leading to uneven heating and causing the boiler to cycle on and off more frequently than necessary. This not only reduces efficiency but can also lead to wear and tear on the boiler.
6. Can Condensation in Steam Valves Cause High Pressure Problems
Condensation in steam valves can potentially cause high pressure problems if it leads to water hammer, which occurs when condensate is trapped in portions of the steam system. This can result in sudden pressure surges that may damage the system.
7. Can WOG Ball Valves Be Used with Steam
WOG stands for Water, Oil, Gas, indicating the types of fluids a valve is designed to control. Whether a WOG ball valve can be used with steam depends on its material, temperature, and pressure ratings. It’s important to ensure the valve is rated for the steam’s temperature and pressure.
8. Can You Control Steam Pressure with Globe Valves
Globe valves are well-suited for throttling applications and can be used to control steam pressure effectively. They offer fine control over flow, making them ideal for adjusting the steam pressure in a system.

9. Do Different Floors Need Different Air Valves (Steam)
In a multi-story building’s steam heating system, different floors may require different types of air valves or air vent settings to ensure even heating. This is due to differences in pressure and the time it takes for steam to reach radiators on different floors.
10. Do You Use Globe Valves on a Steam System
Globe valves are commonly used in steam systems for their throttling capabilities and ability to provide precise flow control, which is beneficial for regulating steam distribution and pressure.
11. How are brass steam valves manufactured
Brass steam valves are typically manufactured through a process called hot forging, followed by machining. In forging, brass is heated and then molded to the desired shape under high pressure. The forged parts are then machined to precise dimensions, drilled to create passageways, and threaded if necessary. Components like the ball, stem, and handle are often produced separately and assembled later.
12. How are steam valves manufactured
Steam valves are manufactured through various processes, depending on the material. For metal valves, the process generally includes casting or forging the valve body and other components, followed by machining to achieve precise dimensions, and assembly of the parts. They are then tested to ensure they meet the required pressure and temperature specifications.
13. How do steam air valves work
Steam air valves, or air vents, work by automatically venting air out of a steam system while retaining the steam within. As steam enters the system, it heats the air inside, causing it to expand and exit through the air valve. Once the air is purged and steam reaches the valve, the temperature rise causes the valve to close, preventing steam from escaping.
14. How steam engine valves work
Steam engine valves regulate the entry and exit of steam into the cylinders. In a typical reciprocating steam engine, the valve slides back and forth to alternately expose and cover steam ports, allowing steam to enter for the power stroke and then to exhaust after the stroke.
15. How to clean steam air valves
Cleaning steam air valves typically involves removing them from the system and disassembling them if possible. Internal components can be soaked in a descaling solution or vinegar to remove mineral deposits, then rinsed, dried, and reassembled.
16. How to fix heating steam valves
Fixing heating steam valves may involve disassembling the valve to replace worn seals or gaskets, cleaning any deposits from the valve seat, and ensuring that the valve stem moves freely. In some cases, it might be more cost-effective to replace the entire valve.
17. How to mount steam valves
Mounting steam valves involves positioning the valve in the desired location on the piping, ensuring proper alignment with the flow direction, and securing it using bolts or screws. Threaded valves are screwed onto pipe fittings, while flanged valves are bolted to matching flanges on the pipe.
18. How to size steam pressure relief valves
Sizing steam pressure relief valves requires calculating the required capacity to relieve pressure at a rate that prevents the system pressure from exceeding a predetermined limit. This involves knowing the maximum steam flow rate and the set pressure of the system.
19. How to size steam vent valves in residential systems
To size steam vent valves in residential systems, consider the volume of air to be vented, the pressure in the system, and the speed at which you want to vent the air. The valve’s air venting capacity should be appropriate for the size of the radiator and the heating requirements of the space.
20. How valves steam works
Steam valves work by controlling the flow of steam through a system. They open to allow steam to pass through and close to stop the flow. The operation can be manual or automated, and the design of the valve provides the necessary sealing to prevent leaks when closed.
21. should steam valves fail open or closed
Whether steam valves should fail open or closed depends on the application and the safety requirements of the system. For example, a fail-open position might be used for a vent valve to ensure that excess pressure can be relieved, while a fail-closed might be used for isolation valves to contain steam within the system in case of power failure.
22. What freight class is steam valves
The freight class for shipping steam valves depends on their weight, size, and density. Valves are typically classified under a machinery freight class, but the specific class can vary. Freight classes are used to standardize shipping rates.
23. What is supercritical pressure and temperature for steam valves
Supercritical pressure and temperature refer to the conditions above which water exists neither as a separate liquid nor as a separate gas. For water, this is above a pressure of 22.1 MPa (3200 psi) and a temperature of 374°C (705°F). Steam valves designed for supercritical applications must be able to withstand these extreme conditions.
24. What is valves steam turbine
A steam turbine valve is used to control the flow of steam into a turbine. These valves can precisely regulate the steam to optimize the turbine’s performance and efficiency. They play a critical role in the operation of power plants, including those in nuclear, coal, and gas-fired stations.
25. Why open steam valves slowly
Steam valves should be opened slowly to prevent water hammer and thermal shock. A water hammer can occur when steam rapidly condenses into water in a cooler pipe, creating a shock wave. Gradual warming of the pipes helps to ensure a smooth transition to operating temperature and pressure, minimizing stress on the piping system and reducing the risk of accidents.
Steam Valves Applications
For applications requiring more precise control, durability under high temperatures, and reliable operation under steam conditions, the following types of valves may be more suitable:
- Globe Valves: Offer better throttling capabilities and are designed to handle the pressure drops associated with modulating flow.
- Ball Valves: Provide a tight seal and quick operation for on/off control.
- Butterfly Valves: Offer a compact solution for flow regulation with faster operation than gate valves.
- Steam Traps: Specifically designed for steam systems to remove condensate while preventing steam escape.
Why Gate Valve not be the best choice for certain steam applications
Gate valves are advantageous for their ability to provide a straight-through pathway for fluid flow with minimal resistance when fully open, making them suitable for on/off control of liquids, their design and operational characteristics can present challenges in steam systems. Here are some reasons why gate valves may not be ideal for steam applications:
Lack of Throttling Capability
Gate valves are designed primarily for fully open or fully closed positions. Using them in a partially open position to throttle steam can lead to seat and gate damage due to the high velocity of steam and the particulate matter it may carry. This erosion can affect the valve’s sealing capability and overall lifespan.
Wear and Tear
The sliding motion of the gate across the valve seats can cause wear, particularly in applications involving abrasive media or high temperatures, like steam. Over time, this wear can lead to leaks and reduced performance.
Slow Operation
Gate valves require multiple turns of the handwheel to open or close fully, which can be a drawback in situations where quick action is needed. In steam systems, especially emergency shut-off scenarios, faster-acting valves (e.g., ball or butterfly valves) might be preferred.
Potential for Galling
In steam applications, the high temperatures and pressures can increase the risk of galling—where the gate and the seats stick together due to metal-to-metal contact. This can make it difficult to operate the valve and may require more frequent maintenance or replacement.
Sealing Issues
While modern gate valves are designed to be more reliable with improved sealing materials, they can still be prone to leaks over time, especially under fluctuating temperatures and pressures typical in steam applications. Ensuring a tight seal is crucial in steam systems to maintain efficiency and safety.
Conclusion
In steam systems, selecting the right type of valve is crucial for operational efficiency, safety, and longevity. It’s important to consider the specific requirements of the application, including the need for flow control, response time, and resistance to high temperatures and pressures, when choosing the most appropriate valve type. If you have steam application need to select the right industrial valves, please do not hesitate to contact us.







